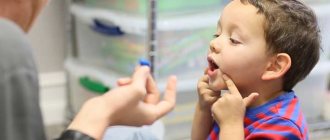
A clinical speech therapist is a doctor who studies various types of speech defects, determines the causes that provoke them, the symptoms and characteristics of the course that accompany these defects.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the speech pathologist and speech pathologist uses innovative correction techniques, which influence existing speech disorders. Individual classes with a speech therapist and the use of proprietary techniques make it possible to restore speech even to those patients who were abandoned by speech therapists at other medical centers.
A team of specialists (neurologist, psychologist, speech therapist, speech pathologist) is involved in restoring speech functions impaired after a stroke.
As a result of injuries and illnesses, the patient partially or completely loses the ability to speak coherently. In order to restore speech, thereby improving the patient’s communication abilities and quality of life, speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital develop and implement an individual rehabilitation program.
Who needs a specialist?
A speech therapist-aphasiologist is needed for people who have lost speech as a result of the following pathologies:
- traumatic brain injury;
- neuroinfection;
- brain tumor;
- brain surgery;
- other diseases.
Sometimes, as a result of these diseases and injuries, a person loses the ability to speak coherently, partially or completely. In order to restore speech, thereby improving the patient’s communication abilities and quality of life, a special individually developed rehabilitation program is necessary. This is exactly what a speech therapist-aphasiologist does.
Speech therapist aphasiologist - training and work features
Aphasia is a word of Greek origin. It consists of two parts: “a” is a negative particle, “phasis” is translated as “utterance” and, in general, means the impossibility of speaking. Thus, aphasia refers to all conditions when a person cannot speak fully or does not understand speech addressed to him. Such speech disorders can occur in both children and adults.
Why does aphasia occur?
Aphasia is a consequence of damage to the structures of speech centers located in the brain. They are affected by: traumatic brain injuries, including birth injuries; inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis, meningitis; vascular pathologies - ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes; brain tumors; "age-related" diseases - Alzheimer's disease; unsuccessful brain surgery. The severity of the manifestations depends on the size of the lesion and the localization of the process. It is reliably known that recovery is faster in younger individuals, whose body has maximum compensatory capabilities.
How does aphasia manifest?
The following speech disorders are characteristic: complete absence of speech; rearrangement of sounds and syllables; long pauses in speech; very weak voice; “telegraphic” style of speech; forgetting the names of objects; misunderstanding of individual words or phrases heard; inability to repeat a few words after the interlocutor; pathological verbosity with a complete lack of understanding of the speech of others; inability to read or read quickly, or understand what is read; handwriting disorder - clumsy handwriting or inability to reproduce elements of letters.
The work of a speech therapist-aphasiologist
In the case of aphasia, a whole team of specialists works with the patient, since it is necessary to determine the exact location of the lesion and its volume. Surgical and conservative therapy is carried out. During the recovery process, as early as possible, a speech therapist specializing in speech restoration - an aphasiologist - is involved in the work. His work is slow and consistent. Results appear earlier in children and adolescents. In older people it is much slower. But this does not mean that working with older people is not worth it. On the contrary, communication skills are so important for them that even small improvements have a tremendous positive impact. Therefore, classes with a speech therapist must be carried out diligently, regularly and for a long time, until a satisfactory result is achieved.
A speech therapist helps restore: 1. understanding of speech; 2. spontaneous speech; 3. writing, reading and counting skills; 4. synchronization of all speech processes. In his work, an aphasiologist uses special techniques, speech exercises and activities aimed at developing fine motor skills. An integrated approach helps to see the fruits of a speech therapist’s work after just a few full sessions.
How to become a speech therapist-aphasiologist?
If you are interested in issues of neurorehabilitation and aphasiology, and want to professionally help children and adults restore the skills of free oral and written speech, you can get a suitable specialty - become a speech therapist and aphasiologist.
To do this, you can enroll in a suitable department of a specialized university and receive a diploma.
If you already have a specialized higher education: medical, pedagogical, psychological or defectological, you can take advanced training courses and receive the appropriate certificate.
If you have a non-core higher education, then first you must undergo professional retraining in speech therapy for at least 500 hours.
What do they teach in advanced training courses?
By taking a refresher course in aphasiology, you will gain a lot of new and very interesting knowledge. So, at LogopedMaster, one of these courses is conducted by highly qualified speech therapist E. E. Shevtsova. She is a neuropsychologist, associate professor of the Department of Speech Therapy at Moscow State University for the Humanities. Sholokhov. The course is proprietary, classes are conducted individually. You will study all the topics necessary for quality work. What is aphasia and where are the speech areas of the cerebral cortex located. How this problem was studied in different historical periods, what methods were used. What causes aphasia. Study the classification of A. R. Luria and you will clearly distinguish between individual types of aphasia: motor afferent and efferent types; dynamic; acoustic-gnostic (sensory); semantic. Learn about disorders of non-speech functions. Master the basic skills of correctional work for different types of aphasia.
Speech therapist-aphasiologist - where to work?
Today, the profession of aphasiologist is in great demand. Specialists of this profile work in clinics, hospitals, psycho-neurological dispensaries, commercial medical institutions and diagnostic centers. Speech therapists-aphasiologists work with children and adults, helping them quickly restore speech, that is, the ability to communicate well with society and communicate with people around them. This is a noble cause, it brings a lot of positive emotions due to the opportunity to really help people and the joy of returning them to their usual level of comfort in life.
To become a speech and language therapist, contact us and enroll in a suitable course.
Recommended reading:
Wiesel T. G., How to regain speech: Stroke and speech disorders, aphasia, dysarthria
Shcherbakova M.M., Collection of tasks for speech restoration for patients with acoustic-gnostic aphasia. Part I.
Shcherbakova M.M., Larina O.D. Collection of tasks for speech restoration in patients with acoustic-mnestic aphasia
What disorders does the specialist treat?
The concept of “speech impairment” is too broadly defined. To fully appreciate the work of an aphasiologist, it is important to find out what types of violations there are.
The classification of speech lesions consists of three subtypes:
- dysarthria;
- apraxia;
- mnestic and semantic disorders.
And each of these subtypes is worth considering in detail in order to understand how different the manifestations of aphasia can be. And, therefore, the approach to each patient must be strictly individual.
Purpose of the program:
A speech therapist-aphasiologist is able to identify and correct dysarthria, stuttering, dyslexia and dysgraphia, and various types of aphasia;
knows methods of neurorehabilitation of patients with speech disorders. The purpose of the advanced training program for speech therapist-aphasiologists is to give the student an understanding of the profession of a speech therapist-aphasiologist, to teach methods for diagnosing speech disorders, and methods of correctional work.
Students choose this course to:
- fulfill your dream of starting to work in the field of clinical speech therapy;
- bring knowledge in your specialty into line with modern requirements for the profession of speech therapist-aphasiologist;
- get an interesting job with a high salary, beat out your fellow competitors.
Dysarthria
Speech is a complex process in which not only the vocal cords are involved, but also the facial muscles, breathing, and the area of the brain - the speech motor analyzer. If the brain is damaged, speech may disappear completely - in this case there is reason to talk about such a serious phenomenon as anarthria. With dysarthria, a person retains the ability to speak, but his speech becomes unclear, slurred, and slurred.
In order to eliminate the disease, it is not enough to simply develop speech with special training. Treatment includes observation of the patient by neurologists, psychiatrists, functional studies for diagnosis and for the purpose of monitoring treatment (EEG, MRI of the brain, EMG, ENR). It is important to find out the type of dysarthria depending on the specific area of brain damage that led to a change in speech quality:
- bulbar – due to atony of the oral muscles, speech is slurred and simplified;
- pseudobulbar - muscle hypertonicity or even paralysis makes it impossible to raise the tip of the tongue;
- subcortical - unconscious muscle contractions lead to involuntary cries and spasms of articulation.;
- cerebellar - impaired coordination of the speech process leads to the fact that speech becomes either sharp and loud, or slow and slurred;
- cortical - a violation of articulatory motor skills makes speech incomprehensible or completely deprives a person of the ability to speak.
Also, a speech therapist-aphasiologist should classify dysarthria depending on the severity of symptoms.
| I degree | Speech defects are practically invisible to others, and only with a special examination can deviations in the patient’s speech be revealed. |
| II degree | The patient’s speech is clear and intelligible, but some defects that distort speech are present and noticeable to others. |
| III degree | The patient’s speech is confused, incomprehensible, and the words he speaks can only be understood by very close people or specialists who work with him. |
| IV degree | Speech is incomprehensible or even completely absent. |
Apraxia
With apraxia, a person is deprived of the ability to reproduce certain movements and speak as a result of pathologies such as stroke, tumor, brain injury, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and others.
There are many classifications of apraxia that make up the diagnosis:
- by type of affected side: unilateral or bilateral;
- by localization of brain damage: frontal, cortical, motor, bilateral and premotor;
- by type of disorder: amnestic, oral, kinesthetic, articulatory, akinesthetic, afferent, constructive, ideokinetic, ideational and spatial.
Considering the variety of manifestations of apraxia and the fact of the presence of an organic lesion, a nephrologist, physiotherapist, social worker, and speech therapist-aphasiologist should work on the patient. Restoring speech is a long process, and even small progress can safely be considered a good result.
Mnestic and semantic speech disorders
Semantic speech disorders are observed with damage to the parietal and occipital parts of the brain. This pathology differs from others in that the patient ceases to understand the meaning of certain words: adverbs, proverbs, sayings, catchphrases, designations of relatedness or duration of time periods.
Thus, the patient’s speech becomes scant, dry, a significant decrease in vocabulary leads to the fact that speech, even clearly pronounced, is difficult to understand in the general context.
The mnestic type of speech disorder occurs when the temporal lobes of the brain are damaged. A feature of this type of aphasia is damage to auditory-verbal memory. That is, each new word heard erases the previous words heard from memory. Sometimes the patient repeats only the first and last word of each sentence he hears.
These types of aphasia are closely associated with impaired thinking. That is, in other cases, a person can retain all cognitive functions - the ability to remember, perceive and process information, but has difficulty speaking directly. In this case, the patient’s cognitive abilities are as impaired as their speech abilities.
Documentation
Certificates and licenses
Learn now - pay later!
The first six months are free.
No money to pay for tuition now? Start the program with payment in six months when you find a job!
Interesting? Your personal manager will tell you detailed conditions. Leave a request.
The offer is valid for retraining programs in all areas costing from 15,000 rubles
.
Your request has been accepted! We will contact you shortly!
Form processing error! Please write us an email!
*By clicking the button, you consent to the processing of personal data.
How does an aphasiologist work?
The services of a speech therapist-aphasiologist are required immediately after a thorough diagnosis has been carried out to determine the causes of the speech disorder. Doctors draw up a treatment plan for the patient, which necessarily includes observation by an aphasiologist. Once the neurological examination is completed and the acute phase of the disease has resolved, the speech rehabilitation specialist is the primary physician with whom the patient collaborates.
The interaction between the aphasiologist and the patient should be long and close. The specialist must provide the patient with the necessary psychological assistance in order to maintain his motivation to continue treatment and fight to restore the quality of his life.
The doctor selects a set of exercises for each person individually. In order not to tire the patient and maintain his interest in exercises, you need to start with light and simple exercises. Lessons should not last longer than 10 minutes.
As the patient gets used to the exercises, they can be increased to 40 minutes per day. In addition, it is important that the patient’s loved ones continue to practice at home, or that he repeats the exercises on his own at a convenient time.
Example exercises
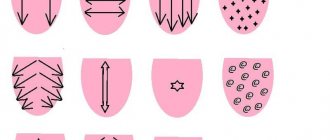
An aphasiologist has in his arsenal a huge number of exercises, from which he creates a complex for a specific patient. But to understand approximately what exercises the patient will have to perform under the supervision of a speech therapist-aphasiologist, it is necessary to cite several of them.
- Lick your lips, slowly moving your tongue to the right, then to the left. Continue the exercise by rotating your tongue in a circular motion across your lips.
- Try to roll your tongue into a tube.
- Unclench your teeth, but close your lips tightly. Slowly push the tongue between the teeth, then between the lips.
- Alternately stretch the tip of your tongue to your nose, then to your chin.
- Smacking loudly, pretend to blow a kiss with your lips.
At first glance, these exercises are very simple, even for a person with serious brain damage as a result of injury, stroke or disease. But in fact, behind these exercises there is a colossal work - the creation of new neural connections in the brain. The brain has reserves in the form of unused neurons. When performing a set of special exercises, new neural connections are created, and as they are created, the person again masters the skill of speech.
Teaching methods
1. We have developed an educational program for advanced training for speech therapists and aphasiologists so that training is easy without loss of quality. And the students underwent professional retraining to the end, and did not give up halfway due to the huge amount of information and difficult tasks. They could combine training with work or parallel education.
- The course is concise, but high quality. Teachers selected the most important information for lectures and webinars, based on the requirements of professional standards, Federal State Educational Standards, and personal work experience. Theoretical materials are presented in clear language, in a concentrated form, without “water” and lyrical digressions off topic.
- You can complete practical assignments, take tests and assessments at a convenient time within the study schedule.
- We help students not to be afraid of tests, tests, exams. For example, we give 3 attempts to pass the final interdisciplinary exam. Tests in intermediate modules and disciplines can be taken an unlimited number of times.
2. Students receive access to the distance learning system (DLS). During the course, they get acquainted with educational materials and complete tasks loaded into the LMS. Pass intermediate testing and final certification.
3. We use several types of content for theoretical training in professional retraining programs.
- Course materials – manuals, lectures on the program. The texts of educational materials are loaded into the LMS in the form of word files. It is convenient to work with them: copy or highlight the necessary information, download, print.
- Webinar library. Each webinar is dedicated to one topic.
4. Practical training of students is based on the study of typical working moments. We give creative tasks and teach how to draw up lesson plans that will be useful in the field.
Call a specialist to your home
Calling a speech therapist-aphasiologist to your home is often necessary. For example, if a person is immobilized or has difficulty moving.
When choosing a speech therapist-aphasiologist for your home, reviews are of enormous importance. After all, you need to be confident not only in the competence of the specialist, but also in his integrity.
But by finding a good doctor who can conduct classes at the patient’s home, you can make progress in treatment faster. The patient will be in a comfortable environment and will not be tired on the way to the medical center.
The only drawback of the method is that not in every city you can find a specialist who will work on his patient’s speech on his territory. That is, finding a speech therapist-aphasiologist in St. Petersburg or Moscow is unlikely to be difficult, but residents of small towns will have to work hard to find a doctor.
Article:
Aphasia is a word of Greek origin.
It consists of two parts: “a” is a negative particle, “phasis” is translated as “utterance” and, in general, means the impossibility of speaking. Thus, aphasia refers to all conditions when a person cannot speak fully or does not understand speech addressed to him. Such speech disorders can occur in both children and adults. Why does aphasia occur?
Aphasia is a consequence of damage to the structures of speech centers located in the brain. They are affected by: traumatic brain injuries, including birth injuries; inflammatory diseases, for example, encephalitis, meningitis; vascular pathologies - ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes; brain tumors; "age-related" diseases - Alzheimer's disease; unsuccessful brain surgery. The severity of the manifestations depends on the size of the lesion and the localization of the process. It is reliably known that recovery is faster in younger individuals, whose body has maximum compensatory capabilities.
How does aphasia manifest?
The following speech disorders are characteristic: complete absence of speech; rearrangement of sounds and syllables; long pauses in speech; very weak voice; “telegraphic” style of speech; forgetting the names of objects; misunderstanding of individual words or phrases heard; inability to repeat a few words after the interlocutor; pathological verbosity with a complete lack of understanding of the speech of others; inability to read or read quickly, or understand what is read; handwriting disorder - clumsy handwriting or inability to reproduce elements of letters.
The work of a speech therapist-aphasiologist
In the case of aphasia, a whole team of specialists works with the patient, since it is necessary to determine the exact location of the lesion and its volume. Surgical and conservative therapy is carried out. During the recovery process, as early as possible, a speech therapist specializing in speech restoration - an aphasiologist - is involved in the work. His work is slow and consistent. Results appear earlier in children and adolescents. In older people it is much slower. But this does not mean that working with older people is not worth it. On the contrary, communication skills are so important for them that even small improvements have a tremendous positive impact. Therefore, classes with a speech therapist must be carried out diligently, regularly and for a long time, until a satisfactory result is achieved.
A speech therapist helps restore: 1. understanding of speech; 2. spontaneous speech; 3. writing, reading and counting skills; 4. synchronization of all speech processes. In his work, an aphasiologist uses special techniques, speech exercises and activities aimed at developing fine motor skills. An integrated approach helps to see the fruits of a speech therapist’s work after just a few full sessions.
How to become a speech therapist-aphasiologist?
If you are interested in issues of neurorehabilitation and aphasiology, and want to professionally help children and adults restore the skills of free oral and written speech, you can get a suitable specialty - become a speech therapist and aphasiologist.
To do this, you can enroll in a suitable department of a specialized university and receive a diploma.
If you already have a specialized higher education: medical, pedagogical, psychological or defectological, you can take advanced training courses and receive the appropriate certificate.
If you have a non-core higher education, then first you must undergo professional retraining in speech therapy for at least 500 hours.
What do they teach in advanced training courses?
By taking a refresher course in aphasiology, you will gain a lot of new and very interesting knowledge. So, at LogopedMaster, one of these courses is conducted by highly qualified speech therapist E. E. Shevtsova. She is a neuropsychologist, associate professor of the Department of Speech Therapy at Moscow State University for the Humanities. Sholokhov. The course is proprietary, classes are conducted individually. You will study all the topics necessary for quality work. What is aphasia and where are the speech areas of the cerebral cortex located. How this problem was studied in different historical periods, what methods were used. What causes aphasia. Study the classification of A. R. Luria and you will clearly distinguish between individual types of aphasia: motor afferent and efferent types; dynamic; acoustic-gnostic (sensory); semantic. Learn about disorders of non-speech functions. Master the basic skills of correctional work for different types of aphasia.
Speech therapist-aphasiologist - where to work?
Today, the profession of aphasiologist is in great demand. Specialists of this profile work in clinics, hospitals, psycho-neurological dispensaries, commercial medical institutions and diagnostic centers. Speech therapists-aphasiologists work with children and adults, helping them quickly restore speech, that is, the ability to communicate well with society and communicate with people around them. This is a noble cause, it brings a lot of positive emotions due to the opportunity to really help people and the joy of returning them to their usual level of comfort in life.
Education
Aphasiologist is a promising and important profession. Restoring a person’s quality of life after a stroke or injury is an important part of professional activity and social relationships. Therefore, mastering this profession will give people who have experienced brain damage a chance to return to normal life.
Speech therapist-aphasiologist courses are designed specifically for speech therapists who can improve their qualifications. During the classes, future aphasiologists will learn how to correctly select a program for speech restoration depending on the type of aphasia, master all the necessary exercises, and gain psychological preparation skills for working with patients.
After completing the educational process, students will be examined, and, in case of a positive result, will receive certificates of advanced training, and can study vacancies for speech therapist-aphasiologist on the labor market.
Speech therapist's office
The speech therapist's office at the Yusupov Hospital is divided into several workers. They differ from each other in internal equipment. The speech correction area has 3 wall mirrors and posters. They depict bright pictures that help correct speech, and working tablets.
In the area intended for general speech underdevelopment, the following items are located:
- bright pictures for composing different stories;
- all kinds of crosswords, riddles, puzzles, word games;
- tablets with stories and fairy tales.
The speech therapy room has an educational area. It is necessary to restore writing skills. The common space in this area is equipped with a magnetic board, a pointer, and multi-colored magnets. In the speech therapist-aphasiologist's office there is a corner for speech correction. In this area there is a mirror with a large poster above it. It shows the main articulation exercises. The office is equipped with modern equipment that allows patients to control correct pronunciation.
Distance learning
For residents of those cities where there are no in-person courses for training aphasiologists, there is an opportunity to acquire the necessary skills remotely. Those who wish can obtain all the necessary knowledge by studying theoretical information and videos. Most courses that can be found on the Internet have a more reasonable price compared to face-to-face courses.
In addition, distance learning for speech therapists and aphasiologists often does not require any training. That is, every person can take the course as part of general development or to help a loved one who has lost speech as a result of brain damage.
Thus, an aphasiologist participates in the process of treating people who have lost their speech skills as a result of the disease, along with neurologists. The speed of rehabilitation of the patient and the quality of his entire future life depend on the professionalism, patience and talent of the doctor.
Main objectives of the program:
1. Fundamentals of legislation regulating the activities of speech therapist-aphasiologist.
2. Fundamentals of neurophysiology and higher nervous activity.
3. Anatomy, physiology and pathology of the organs of hearing, speech, vision.
4. Normal speech development and speech underdevelopment.
5. Special psychology.
6. Speech pathology in childhood.
7. Contents and forms of speech therapy work.
8. Dysarthria.
9. Stuttering. Corrective work to normalize the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech.
10. Methods of correctional work to eliminate reading and writing disorders.
- Practical: exercise, copying, dictation, writing from memory, game, modeling.
- Visual: observations, examination of drawings and layouts, showing a sample task and method of action.
- Verbal: story, conversation, reading.
11. Organization of neurorehabilitation of patients with speech pathology and other higher mental functions.
12. Aphasia. Types of aphasia.
- Total – lack of understanding and reproduction of speech.
- Motor – a violation of the intelligibility of speech while maintaining its understanding and the ability to reproduce sounds.
- Sensory – loss of understanding of speech while maintaining the ability to reproduce it.
- Amnestic - understanding speech with forgetting the meaning of some words.
13. Examination of persons with aphasia. Differential diagnosis of disorders. Correctional pedagogical work, parent counseling.
| №pp | Name of disciplines | Total labor intensity, in acad. hours | Work of a student in SDO | Forms of intermediate and final certification (DZ, Z) | ||
| Lectures | Testing | Practical lessons | ||||
| Regulatory section | ||||||
| 1 | Regulatory and legal basis for the activities of a speech therapist-aphasiologist | 36 | 24 | 2 | 10 | Z |
| Psychological and pedagogical section | ||||||
| 2 | Fundamentals of neurophysiology and higher nervous activity | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | Z |
| 3 | Anatomy, physiology and pathology of hearing, speech, vision | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | DZ |
| 4 | Normal speech development and speech underdevelopment (ontogenesis and dysontogenesis of speech development) | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | DZ |
| 5 | Special psychology | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | Z |
| Section of special disciplines | ||||||
| 6 | Speech pathology in childhood | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | Z |
| 7 | Contents and forms of speech therapy work | 46 | 22 | 4 | 20 | DZ |
| 8 | Dysarthria | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | Z |
| 9 | Stuttering. Corrective work to normalize the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | DZ |
| 10 | Reading and writing disorders (dysgraphia and dyslexia). Methods of corrective work to eliminate violations | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | Z |
| 11 | Organization of neurorehabilitation of patients with speech pathology and other higher mental functions | 44 | 20 | 4 | 20 | DZ |
| 12 | Aphasia. Types of aphasia | 48 | 22 | 4 | 22 | DZ |
| 13 | Examination of persons with aphasia. Differential diagnosis of disorders | 48 | 22 | 4 | 22 | Z |
| 14 | Corrective pedagogical work to overcome aphasia. Interaction with parents | 54 | 28 | 4 | 22 | Z |
| final examination | 12 | Final interdisciplinary exam | ||||
| TOTAL | 640 | |||||