Stage II: Automation of sound in words
Let's consider this stage of work using the example of the sound of L. The speech therapist draws a picture and asks the child questions. It is possible for the child to draw or color the picture himself.
Sample questions: “What do I draw?”, “What do I paint over?”, “What happened?”, “What word will I write under the picture?” etc.
Thus, the child pronounces one word several times, and the sound in the word is automated.
On a page in a child’s notebook there are 6 pictures in this way:
If a speech therapist or parent does not have artistic skills (and they are not the main ones here), then you can replace the drawings with ready-made pictures.
In this way, picture words are typed until the specialist is sure that the sound is introduced into speech at the word level. As a rule, words are first selected with a sound at the beginning of the word (lamp, magnifying glass, boat, skis...), then in the middle of the word with straight syllables (pigeons, baby, saw...) and in the middle of the word with a combination of consonants (shawl, ball, flag... ), only then with a practiced sound at the end of the word (table, woodpecker, football...).
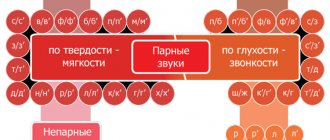
Stage I. Automation of sound in forward and backward syllables
The child is introduced to the sound symbols of M.F. Fomicheva.
The plane is humming L-L-L Anya is crying A-A-A Olya is groaning O-O-O The train is humming O-O-O The bear is growling Y-Y-Y
Next, they suggest placing pictures-symbols in the windows.
Moving the pictures along the path lines, the child simultaneously pronounces straight syllables.
For example:
“The plane is flying to Anya L-L-L-LA” “The plane is flying to Olya L-L-L-LO” “The plane is flying to the train L-L-L- LU” “The plane is flying to the little bear L-L-L- LY" Then they practice the reverse syllables: "Anya is going to the plane A-A-A-AL" "Olya is going to the plane O-O-O-OL" "The train is going to the plane U-U-U-UL" "The bear is going to airplane Y-Y-Y-YL"
Article:
The sounds [n], [n' - n] normally appear in a child between the ages of 1 and 2 years.
If a child at 2 years old does not have the sounds [n], [n'], be sure to consult a speech therapist.
If in the child’s speech the sounds [n], [n'] appear in the nasal version (maybe even before 2 years), contact a speech therapist as soon as you notice it. Distorted sounds are never restored on their own.
How to pronounce the sound [n].
- The sound is nasal;
- The soft palate is lowered, air passes through the nose;
- Lips and teeth are open;
- The tongue is wide, spread out, the front part of the tongue closes with the upper teeth or alveoli.
- Vocal cords are closed;
- Articulatory features of the sound [ n ] .
[n] – consonant sound. The air escaping from the oral cavity encounters a barrier;
[n] – nasal sound. The soft palate is lowered, part of the air passes through the nose;
[n] – ringing sound. When pronouncing the sound [n], the vocal cords are closed, vibrate, and a voice is formed;
[n] – stop-passive sound according to the method of formation. The front part of the back of the tongue forms a bridge with the upper teeth or alveoli, the air stream goes through the nose;
[n] – anterior lingual sound at the place of formation. The barrier is formed by the front part of the back of the tongue.
- Acoustic signs of sound [ n ] .
[n] – sonorant (sonorous) sound. Noise is involved to a minimal extent;
[n] - hard sound - the middle part of the back of the tongue does not take an active part.
- Sound disorders [ n ] .
The pronunciation of the sound [n] is extremely rarely violated:
- absence of sound [n];
- “closed nasality”, replacing [n] with [t], [n] with [d], with combinations [nta], [nda];
- sound mixing [n].
How to pronounce the sound [n'].
- The sound is nasal;
- The lips are in a neutral position, taking the position of the next vowel;
- The soft palate is lowered, air passes through the nose;
- When pronouncing the sound [n'], the tip of the tongue is lowered behind the lower incisors;
- Vocal cords are closed;
1). Articulatory features of the sound [n'].
[n'] – nasal sound. The soft palate is lowered, part of the air passes through the nose;
[n'] – consonant sound. The air escaping from the oral cavity encounters a barrier;
[n'] – voiced sound. When pronouncing the sound [n], the vocal cords are closed, vibrate, and a voice is formed;
[n'] – stop-passive sound according to the method of formation. The front part of the back of the tongue forms a bridge with the upper teeth or alveoli, the air stream goes through the nose;
[n'] – anterior lingual sound at the place of formation. The barrier is formed by the front part of the back of the tongue.
2). Acoustic signs of sound [n'].
[n'] – sonorant (sonorous) sound. Noise is involved to a minimal extent;
[n'] – soft sound. The middle part of the back of the tongue rises towards the hard palate.
3). Sound disorders [n'].
The pronunciation of the sound [n'] is extremely rarely violated:
- absence of sound [n'];
- “closed nasality”, replacing [n'] with [t'], [n'] with [d'], with combinations [n't'a], [n'd'a];
- mixing the sound [n'].