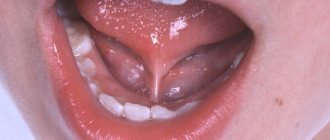
Symptoms of rhinolalia
With organic rhinolalia, the diagnosis is made in infancy. From the first days such children have problems with nutrition and breathing and are susceptible to respiratory diseases.
The formation of speech in children with rhinolalia is difficult and occurs after 2 years. A sick child pronounces sounds, syllables and words late. They are unclear and difficult to understand.
In the open form, the sounds have a nasal timbre and are indistinguishable from each other. Closed rhinolalia manifests itself in a violation of the pronunciation of nasal sounds and their replacement with others. The timbre of the voice also suffers.
The disease also causes other disorders - dysgraphia and dyslexia, as well as persistent psychological discomfort. That’s why diagnosing rhinolalia and treating it is so important.
Breathing exercises
Rhinolalics are characterized by breathing with exhalation both through the mouth and through the nose. Therefore, teaching a child to control inhalation and exhalation is very important. To control, you can use a piece of cotton wool or a napkin applied to your nose. The purpose of the exercises is to teach you to “blow” only through your mouth.
Inhale - exhale
This exercise will help you learn to control your breathing. The child inhales and exhales in a strictly defined manner. For example, inhale and exhale through your nose, the next time you inhale and exhale only through your mouth. We complicate the task - inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth, the next inhale-exhale through the nose, then only through the mouth. And so on.
Storm in a teacup
Playing with water will help to visually control your mouth breathing. Children enjoy blowing into the water through a straw, creating real storms and storms. To prevent the water from splashing, it is more convenient to take a bottle rather than a wide glass. Just be sure to be transparent so that the seething is clearly visible. When the child learns to blow into a tube, creating a gurgling sound, you need to try to lengthen the exhalation. For the storm to be “real,” the exhalation must be uniform and long.
Games for blowing out candles, kicking soccer balls made from cotton balls, various toy wind instruments and blowing up balloons are also very useful. However, what is important here is the gradual complication of the task and the absence of overload. Breathing exercises should not be long, so that the child does not feel dizzy.
Correction of rhinolalia at a speech therapy center in Moscow
Corrective work with children with rhinolalia should begin when a problem is detected in order to achieve positive results by adolescence. Depending on the form, speech therapy work can be the main or complementary work of other specialists.
The role of a speech therapist for rhinolalia is to consolidate sound pronunciation skills. Massage is used, the development of velopharyngeal closure, the development of exhalation and sound pronunciation, the elimination of nasality, the development of vocabulary and work on lexical literacy.
- Correction for functional rhinolalia. A positive effect can be achieved through sessions with a speech therapist. They include massage, breathing exercises, work on developing the correct pronunciation of sounds and auditory attention.
- Correction for organic form. The effectiveness depends on the surgical intervention, the timeliness of the operation and the completeness of the speech therapist’s work with the child.
Types of changes in sound pronunciation
Forms of rhinolalia are divided into three main types:
- Open.
- Closed.
- Mixed.
Open form of rhinolalia - air passes through the nasal cavity, as if the passage is open, as a result of this, sounds are pronounced with nasal impact.
The closed form of rhinolalia is characterized by the fact that the passage into the nasal cavity is constantly difficult, sounds are pronounced in the same way as with a severe runny nose, rather muffled.
The mixed form of rhinolalia combines and combines the previous types of rhinolalia.
Open and closed rhinolalia can be determined at home using a mirror. The mirror is brought to the nose and sounds are made.
When using words without nasal sounds, the glass will fog up when the rhinolalia is open, words with nasal sounds will cause the glass to fog up when the nasality is closed.
Closed rhinolalia
Also known as rhinophony. Sound comes out exclusively through the mouth, even with nasal sounds. The closed form of rhinolalia appears with defects of the nasopharynx and nasal cavity. Possible diseases: hypertrophy of the nasal mucosa or soft palate.
With the closed form of rhinolalia, there is a violation of phonemic sounds. [M] is heard as [b], and [n] as [d].
The classification of closed rhinolalia is divided into two types:
- Organic.
- Functional.
Closed organic rhinolalia is a sign of defects in the pharynx, nose and nasopharynx. It can be observed with polyps in the nose, as well as with a profuse runny nose. A deviated nasal septum can also be a cause.
Functional closed form of rhinolalia. This type affects children who are prone to colds and allergic reactions. The nasal passages are still quite narrow, and often a stuffy nose leads to “habitual” rhinophony.
A child gets used to using a nasal sound during illness and continues to imitate those sounds. The structure of the speech defect here lies solely in habit, but the timbre can be disrupted much more than with organic closed rhinolalia.
Open rhinolalia
The open form of rhinolalia can be congenital. With this disorder, the child’s tongue is in an unnatural position, as if it is being pulled back. The root of the tongue in such children is strong and protrudes upward, but the tip of the tongue is poorly developed and inactive. This structure also causes feeding problems.
The soft palate also does not work properly. It takes a sluggish part in important activities: chewing, swallowing, and also disrupts phonation.
Children with such disorders begin to speak very late and have difficulty, severely distorting their words.
Also, due to hearing impairment and defective articulation, the open form of rhinolalia leaves its mark on hearing. Children do not hear individual sounds, it is difficult for them to master all the lexical intricacies of speech, which results in GSD (general speech underdevelopment).
With open rhinolalia, there are disturbances in sound pronunciation [p], [t], [d], [v], [f], [l] and [r].
Open organic rhinolalia can be not only congenital, but also acquired.
Acquired rhinolalia can appear after injuries, bruises, burns of the throat, surgical removal of the tonsils, and other operations on the throat (tumors, polyps).
As a result, you may see:
- scars of the soft palate;
- paresis, paralysis;
- fistulas, clefts.
The mechanism of pronunciation of words changes, as the soft palate will lag behind the posterior pharyngeal wall, where a gap is formed. The soft palate can no longer act as a valve and block the air, so air enters the nasal cavity.
There is another type - functional open rhinolalia. This form occurs during hysteria. This is a temporary “nasality” that appears during hysterical attacks.
Also, functional rhinolalia sometimes occurs after healing of organic open rhinolalia. This happens due to the habit of the soft palate not to work, but to be in a lowered state. This form is less common and can be treated with a course of sessions with a speech therapist.
However, congenital rhinolalia is not so easy to eradicate; it will be necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
There are two types of correction for this disease:
- Cheiloplasty is an operation that restores the upper lip.
- Uranoplasty - restoration of the bottom of the nasal septum.
Surgeries are recommended even for newborn children, provided that they have no contraindications, which are discussed in detail with the attending physician.
The operation is contraindicated for children with anemia, intrauterine malnutrition, asphyxia, congenital heart disease and other serious diseases.
Uranoplasty is divided into two categories: gentle and radical. If gentle treatment can be carried out from one and a half years, then radical treatment, which is more successful for complete healing, will need to wait for at least three years.
Limberg invented a special method of uranoplasty, which is recognized as most effective for the “cleft palate” (congenital cleft of the hard and soft palate).
Mixed rhinolalia
Authors such as Zeeman and Mitronovich-Modrzejewska identify a separate type - a mixed type of rhinolalia.
It manifests itself as a combination of two components:
- decreased nasal resonance with nasal sounds;
- nasal timbre.
It turns out that the mixed form develops with insufficient activity of the palate (shortened soft palate) and nasal obstruction.
Diagnosis of the disorder
As you can see, the symptoms of rhinolalia strongly overlap with many known diseases. Making a diagnosis is not as difficult as determining the type of disorder. To accurately diagnose the species, you need to consult a specialist. Examination of patients is carried out by various specialists in the field of medicine:
- maxillofacial surgeon;
- otolaryngologist;
- neurologist;
- orthodontist;
- speech therapist;
- orthopedist;
- psychologist.
Research methods depend on the form of rhinolalia. When identifying different types of rhinolalia, special attention is paid to x-rays of the nasopharynx.
The sooner a child is diagnosed with rhinolalia, the sooner treatment can begin. Correcting a neglected form is much more difficult.
During an examination by a speech therapist, a specialist assesses the structure of the articulatory apparatus, the pronunciation of sounds, the understanding and use of words, and the presence of agrammatisms in speech.
Rhinolalia (its open form) is diagnosed based on Gutzman's research, when when pronouncing the vowel sounds [a] and [i], the child alternately begins to close or open the nasal passages. In school-age children, the specialist also examines the processes of writing and reading, which clearly indicate the presence and level of the problem.
Correction methods
Treatment of rhinolalia includes a whole range of measures aimed at maximizing the elimination of speech defects.
If a child is diagnosed with congenital rhinolalia, then correction of the disorder begins with the elimination of defects of anatomical origin. From birth, such children begin to be fed using a tube, which is selected taking into account the characteristics of the cleft.
A special prosthesis, an obturator, is also made to close the nonunion. This prosthesis facilitates the processes of eating, breathing and speaking.
Late use of an obturator is less effective, since the child begins to develop incorrect tongue position with age. The obturator changes as the child grows and is used until the moment of surgical intervention, which, unfortunately, cannot be done without.
Maxillofacial disorders are subject to surgical intervention. Nasality with open rhinolalia is treated both before and after surgery.
As a rule, cleft lip surgery is performed at 2–3 months of a child’s life. Operations on the palate are carried out after two years, if the child has lost all his teeth. In weakened children, surgery is postponed to a later date or carried out in several stages.
Surgeries allow you to restore the integrity of the speech apparatus and the proper functioning of the palate.
Articulation exercises
To correct articulation disorders caused by rhinolalia, special exercises are needed:
- “Snake or spade” - you need to learn to stick out your tongue with a pointed tip, and then widely flattened. The next stage is to alternate between “snake” and “shovel”.
- “Bend the back” - the tip of the tongue rests on the lower gums, and the back of the tongue curves up and down.
- “Inflate and deflate” - the cheeks need to be inflated and deflated, pulling them between the teeth. As an option, learn to inflate not both cheeks at once, but alternately. An adult can help deflate the puffy cheek by lightly touching it with a finger.
- “Rinse your teeth” - imitate rinsing your teeth without water (the air should press on your lips).
- “Elephant exercise” - the child must learn to hold his lips closed and extended forward with his “proboscis”, and then move it left and right and even rotate it.