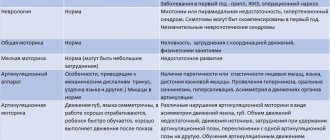
Dyslalia is a disorder of sound pronunciation in children with normal hearing and intact innervation of the articulatory apparatus. With dyslalia, there may be a violation and difficulty in pronouncing any phonemes of the child’s native language.
Dyslalia is characterized by replacement, confusion, distortion or absence of sounds in the child’s oral speech. Diagnosis of dyslalia involves a speech therapy examination of the structure and mobility of the speech apparatus, as well as diagnosis of the state of current sound pronunciation and phonemic hearing. In some cases, consultation with highly specialized specialists (dentist, neurologist, otolaryngologist) is necessary.
The causes of this speech disorder can be organic, hereditary, congenital or acquired factors.
Types of dyslalia
Dyslalia, as a form of speech pathology in children, has various types and forms. The classification depends on the reasons for which the sound pronunciation disorder occurs. Experts distinguish two forms of dyslalia: mechanical and functional.
Mechanical (organic) dyslalia is a form of speech pathology caused by the presence of defects in the structure of the articulatory apparatus.
The causes of functional dyslalia, in contrast to mechanical dyslalia, are associated either with social factors or with reversible neurodynamic disorders in the cerebral cortex.
Functional dyslalia has the following varieties:
- motor dyslalia: this pathology is characterized by imprecise and undifferentiated movements of the tongue and lips, which causes phonetic defects (distortion of sounds);
- sensory dyslalia: with this disorder, auditory differentiation of acoustically similar sounds (hard/soft, dull/voiced, etc.) is difficult, causing the child to mix and replace sounds in oral speech.
In addition, there are cases when experts identify the presence of sensory and motor speech insufficiency; this type of disorder is called “sensorimotor dyslalia.”
The lack of formation of certain signs of sounds and the nature of the speech defect allow us to distinguish the following types of dyslalia:
1. Phonemic dyslalia - the cause of this type of dyslalia is the immaturity of the operations of selecting sounds according to their articulatory characteristics. With this form of dyslalia, the articulatory base may or may not be fully formed. In the first case, the child simply selects the sounds incorrectly; the second option assumes that in the absence of the desired sound, the child replaces it with a simpler phoneme.
2. Phonetic dyslalia - the occurrence of this form of dyslalia is associated with the formation of incorrect articulatory positions. Such a speech disorder manifests itself in the fact that the child pronounces a sound that does not exist in the phonetic system of the language.
Taking into account the number of disrupted sounds, the following types of violations can be distinguished:
- simple dyslalia (monomorphic dyslalia) - characterized by incorrect pronunciation of one sound or several sounds from one group;
- complex dyslalia (or “erased” dyslalia, or polymorphic dyslalia) - characterized by incorrect pronunciation of several sounds from different groups.
Experts also distinguish physiological dyslalia (or age-related), which is characterized by disturbances in sound pronunciation up to 5 years of age, caused by insufficient development of the organs of articulation. This speech disorder goes away on its own after 5 years.
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a violation of sound pronunciation caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus (organic damage to the central part of the speech motor analyzer).
The speech of a dysarthric person is slurred, incomprehensible to others, like “porridge in the mouth.” The articulation of many groups of sounds is impaired: hissing, whistling, sonorants, and sometimes vowels. Speech breathing is shallow, arrhythmic. Hypersalivation (increased salivation) is observed. The mobility and sensitivity of the speech muscles suffers. Dysarthric has difficulty finding an articulatory posture (licking lips, placing tongue behind upper teeth, etc.). Impaired sound pronunciation with dysarthria is one of the symptoms of a more complex speech disorder. Speech hearing and auditory differentiation of sounds also suffer, a poor vocabulary, and unformed grammatical structure of speech are observed. Secondary mental layers (behavioral problems) are also observed. All these difficulties lead to persistent poor performance in school (dysgraphia, dyslexia, dysorthography).
Despite its similarities with dyslalia, dysarthria is a more complex and persistent disorder that requires help and psychological support.
In adults, correction of dysarthria is even slower than in children, but it is possible.
Case from practice
Kolya, 5 years old. The sound pronunciation of the sounds Ш, Ж, Х, Л, Л, Р, Рь is impaired . There is hypersalivation and difficulty in repeating the articulatory pattern. Phonemic processes are disrupted, lexico-grammatical structure is disrupted. As a result of 3 courses of correctional classes, dysarthria was compensated, sounds were automated, work continues on coherent speech, improving vocabulary and grammar.
Find out more about the Center's services and sign up for a consultation or lesson
You can call (812)
640-90-77
, or by filling out the form below.
Causes of dyslalia
The occurrence of speech impairment in a child can be due to a number of reasons. Somatic causes include physical and neurological weakness (due to long-term chronic diseases).
Mechanical dyslalia, as a rule, occurs due to organic or congenital defects of the articulatory apparatus (tongue, lips, teeth, jaws).
Social reasons (with functional dyslalia) for the occurrence of speech disorders are as follows:
- bilingualism (bilingualism in the family - in this case, the child inserts elements of one language into another);
- the child imitates the incorrect speech of adults (uses dialects, is in a hurry);
- adults, when communicating with a child, imitate baby babble (“lisp”);
- pedagogical neglect (parents do not correct deficiencies in their children’s speech and do not demonstrate examples of correct sound pronunciation).
In addition, factors such as:
- choice of incorrect articulation;
- underdevelopment of phonemic hearing (while physical hearing can be preserved).
Why does a defect occur?
The causes of dyslalia can begin in the womb during pregnancy or be acquired. The quality of speech is influenced by tempo, articulation, and intonation. Deterioration of its characteristics can be caused by insufficient mobility of the tongue, defects in the structure of the jaw and dentition.
This type of dyslalia, such as mechanical, is associated with the incorrect anatomical structure of the speech organs:
- short frenulum of the tongue - deformation of sounds occurs due to difficulty in moving the tongue (especially noticeable in the upper register);
- Too large or narrow and small tongue also impairs articulation;
- greater height to the upper palate;
- impaired tooth growth;
- malocclusion.
The occurrence of pathology is influenced by injuries and bruises during labor, rickets, and artificial feeding.
The causes of mechanical dyslalia are divided into anatomical and neurogenic. They can be irreversible, congenital or acquired. The second most common etiology of the defect is genetic predisposition and exposure to external factors.
A dentist is involved in eliminating deviations of a mechanical and anatomical nature. The best effect can be achieved with early treatment, when the permanent bite has not yet formed and the bone tissue is sufficiently plastic.
Often the etiopathogenesis of the disorder is associated with embryonic development and the neonatal period.
Dyslalia examination
Diagnosis of speech with dyslalia in children begins with collecting the following data:
- features of the course of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother;
- a list of diseases suffered by the child;
- whether there is early psychomotor and speech development;
- the condition of the child’s hearing, vision and musculoskeletal system.
After collecting the necessary information, the speech therapist proceeds to study the structure and mobility of the organs of the articulatory apparatus (visual inspection and assessment of the performance of a series of imitation exercises).
Diagnostics of oral speech at the First Children's Medical Center includes examination of the state of sound pronunciation and identification of incorrectly pronounced sounds. A speech therapy examination for this speech pathology makes it possible to identify the nature of the disorder in various positions, words, phrases, and texts.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for comprehensive, timely treatment of the disorder is positive in most cases. The sooner dyslalia of the mechanical type is eliminated, the greater the chance that the child will not lag behind his peers in academic performance and have problems with communication. The best age for correction is preschool.
Correction almost always takes a long time, during which all necessary medical and speech therapy procedures are carried out.
During this period, it is important not to discourage the child from studying, so the professionalism of the speech therapist and the support of parents are important here.
Prevention of mechanical dyslalia should begin at the stage of pregnancy planning, because many developmental anomalies are associated with the mother’s poor lifestyle, especially during the first trimester.
Preventive measures include timely contact with specialists.
For example, the first visit to the dentist should be planned for when the baby is 6 months old, so that you can anticipate possible problems with teeth or bite in the future.
If possible, artificial feeding should be avoided. If this is not possible, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician for prevention; from the moment the first words and phrases are uttered, take the child to a speech therapist.
Parents can do exercises and games aimed at expanding vocabulary, pronunciation and speech development at home on their own.
Mechanical dyslalia can be prevented from early childhood. This is a common pathology that becomes more and more noticeable over time for a child, teenager, or adult.
If the disease is left to take its course, in the future it can lead to conditions that are practically impossible to correct. To avoid serious complications, you need to pay attention to the child’s speech from early childhood and not ignore incorrect pronunciation, burrs and nasal sounds.
Related posts:
- Dyslalia - from diagnosis to effective treatment Dyslalia in childhood leads to negative consequences of speech development...
- Dyslalia - functional form Dyslalia is the most common speech disorder. This deviation...
- Rhoticism in speech - complete information Rhotacism (problem with the sound [P]) is the most common disorder in children...
- How to cope with dyslalia? There are different types of speech defects. Let's consider the features of dyslalia and its methods...
Correction and elimination of dyslalia
Methods for eliminating dyslalia depend on the form and type of disorder and include:
- work aimed at eliminating anatomical defects (with mechanical dyslalia);
- articulation gymnastics;
- speech therapy massage;
- individual lessons with a speech therapist.
Specialists at the First Children's Medical Center determine the treatment method individually for each little patient. All classes with a speech therapist are aimed at developing the baby’s speech motor skills, as well as the development of phonemic processes.
Please note that speech therapy sessions for the correction of dyslalia should be conducted on a regular basis. In addition, to achieve a positive result, it is important to complete the speech therapist’s tasks at home and do articulatory gymnastics.
By contacting our Center, you will receive qualified help from a speech therapist who will pay special attention to your child and give answers to all your questions. We are happy to help you! First Children's Medical Center: Children's health - parents' peace of mind!
Share on social networks:
To make an appointment with a doctor
Choose a doctor
Complications
Complications of mechanical dyslalia include difficulties with socialization in childhood, which leads to inability to build relationships in the future.
Burr and nasality can cause ridicule from peers, and this is very painful for children. Psychological trauma underlies subsequent nervousness and complexes.
Mechanical dyslalia at school age causes difficulties with reading and writing, which, combined with psychological discomfort and self-doubt, lead to academic failure, refusal to learn, antisocial behavior and social maladjustment.
Signs of pathological deviation
1) prognathia; 2) progeny; 3) anterior open bite
The main symptoms of the disease are unclear pronunciation of sounds, replacement of rows of phonemes (especially similar in articulation). Separately, the emphasis of the voice on whistling and hissing sounds and the pronunciation of “r-r-r” are assessed.
Classification of defects by bite:
- Prognathia is a disorder in which the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. As a result, the teeth do not close together.
- Progeny - characterized by the opposite picture, when the lower jaw protrudes.
- Open bite, a defect in which a gap forms between the upper and lower incisors when closed. It can be anterior or lateral, depending on the location of the resulting space. Gaps between individual teeth can also lead to dyslalia. When speaking, the tongue will fall into it and distort speech. Too full lips or a short lower lip distort lip sounds (“cleft lip”).
The patient has difficulty pronouncing vowels and his speech is incoherent. It is difficult to produce mixed sounds that involve the entire vocal apparatus. Upon visual examination, disturbances in the structure of the jaw region may be noticeable: distal or mesial bite. Normally, with the jaws closed, the upper row of teeth covers the lower row by about a third.
If phonemic perception deviates from the norm, the child is not able to distinguish by ear parts of a word that are similar in sound or articulation. As a result, there are no phrases with difficult-to-distinguish letters in his dictionary. This leads to falling behind peers. For the same reason, writing is violated: some prepositions and unstressed endings of words are not taken into account.
Diagnosis of pathology
During the first examination, pay attention to breathing through the mouth, not the nose. This leads to jaw deformation. Due to malocclusion, the child's nasal passages are underdeveloped. The timbre of the voice is distorted, the cartilaginous septum of the olfactory organ is deformed. External signs that may indicate this speech defect:
- half-open mouth;
- narrow shoulders;
- sunken chest;
- pale skin;
- due to drying of the mucous membrane, the child licks his lips;
- getting the tongue into the gap between the teeth during a conversation.
Diagnosis of the disorder is carried out by an orthodontist or dentist. During the speech therapy examination, the degree of mobility of the articulation organs is checked, for example, they are asked to reach the nose or chin with their tongue, fold their lips into a tube, etc. They evaluate not only the reproduction of exercises, but also the speed of transition from one to another.
Did you know! In mentally retarded children, in more than 50% of cases, incorrect production of sounds is noted.
Pathology can be manifested either by the absence of sounds, or some may be replaced by others or be distorted (“yba” instead of “fish”, “pipes” instead of “beep”, etc.). Dyslalia can be simple or complex, which is marked by the presence of less or more than 4 defective sounds in words, respectively.