Dyslalia is a disorder of sound pronunciation in children with normal hearing and intact innervation of the articulatory apparatus. With dyslalia, there may be a violation and difficulty in pronouncing any phonemes of the child’s native language.
Dyslalia is characterized by replacement, confusion, distortion or absence of sounds in the child’s oral speech. Diagnosis of dyslalia involves a speech therapy examination of the structure and mobility of the speech apparatus, as well as diagnosis of the state of current sound pronunciation and phonemic hearing. In some cases, consultation with highly specialized specialists (dentist, neurologist, otolaryngologist) is necessary.
The causes of this speech disorder can be organic, hereditary, congenital or acquired factors.
Types of dyslalia
Dyslalia, as a form of speech pathology in children, has various types and forms. The classification depends on the reasons for which the sound pronunciation disorder occurs. Experts distinguish two forms of dyslalia: mechanical and functional.
Mechanical (organic) dyslalia is a form of speech pathology caused by the presence of defects in the structure of the articulatory apparatus.
The causes of functional dyslalia, in contrast to mechanical dyslalia, are associated either with social factors or with reversible neurodynamic disorders in the cerebral cortex.
Functional dyslalia has the following varieties:
- motor dyslalia: this pathology is characterized by imprecise and undifferentiated movements of the tongue and lips, which causes phonetic defects (distortion of sounds);
- sensory dyslalia: with this disorder, auditory differentiation of acoustically similar sounds (hard/soft, dull/voiced, etc.) is difficult, causing the child to mix and replace sounds in oral speech.
In addition, there are cases when experts identify the presence of sensory and motor speech insufficiency; this type of disorder is called “sensorimotor dyslalia.”
The lack of formation of certain signs of sounds and the nature of the speech defect allow us to distinguish the following types of dyslalia:
1. Phonemic dyslalia - the cause of this type of dyslalia is the immaturity of the operations of selecting sounds according to their articulatory characteristics. With this form of dyslalia, the articulatory base may or may not be fully formed. In the first case, the child simply selects the sounds incorrectly; the second option assumes that in the absence of the desired sound, the child replaces it with a simpler phoneme.
2. Phonetic dyslalia - the occurrence of this form of dyslalia is associated with the formation of incorrect articulatory positions. Such a speech disorder manifests itself in the fact that the child pronounces a sound that does not exist in the phonetic system of the language.
Taking into account the number of disrupted sounds, the following types of violations can be distinguished:
- simple dyslalia (monomorphic dyslalia) - characterized by incorrect pronunciation of one sound or several sounds from one group;
- complex dyslalia (or “erased” dyslalia, or polymorphic dyslalia) - characterized by incorrect pronunciation of several sounds from different groups.
Experts also distinguish physiological dyslalia (or age-related), which is characterized by disturbances in sound pronunciation up to 5 years of age, caused by insufficient development of the organs of articulation. This speech disorder goes away on its own after 5 years.
Sound pronunciation with dyslalia
Sound pronunciation with dyslalia is impaired in different ways. It all depends on the type of dyslalia. A large number of children suffer from deficiencies in sound pronunciation. In a small proportion of children, the disorders gradually smooth out with age. Physiological dyslalia ( physiological tongue-tiedness ) is registered in them In most children, dyslalia requires very serious complex treatment. In these cases, dyslalia manifests itself as an independent disease, an independent speech disorder. Dyslalia very often precedes diseases such as stuttering, general speech underdevelopment (GSD), dysgraphia, agraphia, and dyslexia.
Causes of dyslalia
The occurrence of speech impairment in a child can be due to a number of reasons. Somatic causes include physical and neurological weakness (due to long-term chronic diseases).
Mechanical dyslalia, as a rule, occurs due to organic or congenital defects of the articulatory apparatus (tongue, lips, teeth, jaws).
Social reasons (with functional dyslalia) for the occurrence of speech disorders are as follows:
- bilingualism (bilingualism in the family - in this case, the child inserts elements of one language into another);
- the child imitates the incorrect speech of adults (uses dialects, is in a hurry);
- adults, when communicating with a child, imitate baby babble (“lisp”);
- pedagogical neglect (parents do not correct deficiencies in their children’s speech and do not demonstrate examples of correct sound pronunciation).
In addition, factors such as:
- choice of incorrect articulation;
- underdevelopment of phonemic hearing (while physical hearing can be preserved).
How to treat dyslalia and get rid of tongue-tiedness?
At the first consultation, the doctor will tell you how to treat dyslalia in Saratov in preschoolers and schoolchildren, how to cure dyslalia in Russia in children of preschool and school age, how to get rid of tongue-tiedness , what is articulatory phonemic, articulatory phonemic and phonetic, motor and sensory, mechanical, monomorphic, phonemic, simple, complex dyslalia in preschool children. How is prevention, correction of dyslalia , speech therapy examination of children with dyslalia carried out? Does speech therapy psycho-correctional pedagogical communication work help? How does sound pronunciation suffer with dyslalia? Why is polymorphic dyslalia dangerous, what is cheiloplasty, uranoplasty? What is the etiology and causes of dyslalia, differential diagnosis, exercises, gymnastics, literature, conclusion? What is rhinolalia, dysarthria, FNR, FFN, speech card? What is the prevention of dyslalia ? Sarklinik knows how to treat dyslalia in children in Russia.
Sarclinic provides treatment for aphonia, dysphonia, bradylalia, treatment of stuttering, tachylalia, open and closed rhinolalia, dyslalia, treatment of alalia, dysarthria, treatment of aphasia, nasalization, treatment of speech delay, dysgraphia, treatment of general speech underdevelopment, hyperkinesis, synkenesia, treatment of speech development disorders, SPD, delays in speech and psycho-speech development, dyslexia in children and adolescents in Saratov.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Text: ® Sarclinic.com \ Ssrlinic.ru Photo: (©) (©) Gekaskr | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The children depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all coincidences are excluded.
Related posts:
Headache in children, treatment, how to get rid of it, how to relieve it
Bruxism, teeth grinding during sleep, odonterism: symptoms and treatment
Neuropathy, childhood nervousness, treatment, nervous child
Perinatal encephalopathy, consequences, treatment
Psychopathy, types, symptoms, treatment of psychopathy in children and adolescents
Comments ()
Dyslalia examination
Diagnosis of speech with dyslalia in children begins with collecting the following data:
- features of the course of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother;
- a list of diseases suffered by the child;
- whether there is early psychomotor and speech development;
- the condition of the child’s hearing, vision and musculoskeletal system.
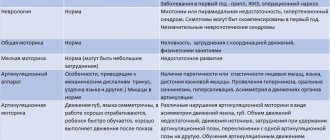
After collecting the necessary information, the speech therapist proceeds to study the structure and mobility of the organs of the articulatory apparatus (visual inspection and assessment of the performance of a series of imitation exercises).
Diagnostics of oral speech at the First Children's Medical Center includes examination of the state of sound pronunciation and identification of incorrectly pronounced sounds. A speech therapy examination for this speech pathology makes it possible to identify the nature of the disorder in various positions, words, phrases, and texts.
Dyslalia, correction of dyslalia, treatment of dyslalia in Saratov, Russia
Sarklinik provides treatment for dyslalia in Saratov , treatment for dyslalia in Russia in children, boys, girls, treatment for tongue-tiedness. Complex treatment allows you to normalize and improve the child’s speech, sounds are staged, special procedures are carried out. In the prevention of dyslalia, proper speech education in young children is important, when it develops most intensively. The younger the preschool child, the faster dyslalia is treated.
Correction and elimination of dyslalia
Methods for eliminating dyslalia depend on the form and type of disorder and include:
- work aimed at eliminating anatomical defects (with mechanical dyslalia);
- articulation gymnastics;
- speech therapy massage;
- individual lessons with a speech therapist.
Specialists at the First Children's Medical Center determine the treatment method individually for each little patient. All classes with a speech therapist are aimed at developing the baby’s speech motor skills, as well as the development of phonemic processes.
Please note that speech therapy sessions for the correction of dyslalia should be conducted on a regular basis. In addition, to achieve a positive result, it is important to complete the speech therapist’s tasks at home and do articulatory gymnastics.
By contacting our Center, you will receive qualified help from a speech therapist who will pay special attention to your child and give answers to all your questions. We are happy to help you! First Children's Medical Center: Children's health - parents' peace of mind!
Share on social networks:
To make an appointment with a doctor
Choose a doctor
Prevalence of the problem
The disease is a common occurrence, most common in the practice of speech therapists.
According to various estimates, the average number of children with such problems in preschool age is 25-30%, in elementary grades – 17-20%, and in older age – 1%. Classes with a speech therapist are also required for adults who have suffered strokes, TBI, or multiple sclerosis. Most often, there are combined disorders of sound pronunciation that prevent further mastery of written speech. At the same time, the vocabulary can be replenished according to age, all cases are used correctly, the structure of syllable formation is not disrupted, speech is developed at a high level.
Forecast
With timely and competent correction, in 95% of children the disorder is completely corrected within 4-6 months. The main condition for success is regular classes and strict adherence to the recommendations of the doctor and speech therapist.
Is dyslalia dangerous? Unfortunately, some parents may even be touched by a child with a lisp, and they wait for the child to “outgrow” and magically cope with this problem on his own. But the disorder is dangerous because against its background more complex mixed speech defects easily develop, which require difficult and lengthy correction.
Publication date: 03/10/2020. Last modified: 07/07/2020.
Diagnosis of the disorder
In the case of dyslalia, an extremely accurate diagnosis of the disease is necessary. It is not enough to diagnose Dyslalia; you need to determine the reasons for its occurrence. Sometimes a complex of reasons is immediately discovered. This is possible when, against the background of an unfavorable environment and improper upbringing, the child exhibits delays in speech and/or development due to past illnesses, birth injuries or other reasons.
Several specialists are involved in diagnosing the disorder:
- Speech pathologist-defectologist;
- Speech and/or behavioral neurologist;
- neuropsychologist.
If necessary, specialists are involved who perform surgical correction. Without such an approach, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis and carry out correction.
Diagnostic rules
To identify a speech defect, the following is studied:
- facial expressions;
- work of articulatory muscles: tongue, palate, lips, lower jaw.
To do this, the child is asked to open his mouth as wide as possible several times. Then smile, form your lips into a tube (these tasks alternate), stick your tongue forward, lowering it onto your lower lip (“shovel”), then make the tongue as narrow as possible (“needle”). Alternate tasks for the language. Say “a” abruptly and clearly, then yawn, opening your mouth as much as possible. Repeat.
Causes
- defects and features of the development of speech organs;
- pedagogical neglect;
- violations of the mechanisms of perception, analysis and reproduction of speech (as a result of hearing loss, injury, etc.);
- the presence of a person around the child who cannot pronounce certain sounds well;
- abuse by parents of distorted “children’s” pseudo-words, such as “kisya”, “vava”, etc.
- use of two or more languages in the family.
The child usually pronounces most sounds and syllables correctly; the only difficulties for him are sounds that are similar in place and method of formation. The violation can manifest itself as one defect or a combination of them.
Functional dyslalia
The problem is completely dealt with by a speech therapist. In some cases, a visit to a neurologist and neuropsychologist is required. Parents will need to do “homework” - study with the child at home, developing correct pronunciation. The program and intensity of classes is developed by a speech pathologist-defectologist individually depending on the severity of the disorders.
Treatment of dyslalia is necessary - in the vast majority of cases, without correction, the disorders do not go away (after all, the brain “remembers” the incorrect pronunciation), but only get worse, which can lead to difficulties in the child’s socialization, stuttering and other various psychological disorders. It is easier to teach correct pronunciation than to reteach.
Timely correction is the best solution to the problem.
Diagnosis of speech disorders
To identify defective sounds, the speech therapist asks the child to repeat the words after him or her to name what is shown in the picture. This material is selected in such a way that it covers all groups of sounds. Moreover, the sound must be in different positions: at the beginning, at the end, and in the middle of the word, soft and hard consonants are also taken into account.
Parents should prepare for the fact that the speech therapist may need information about the presence or absence of pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth. The specialist may prescribe additional examinations from other specialists (vision, hearing, mental development tests). When a child is diagnosed with hearing loss, in addition to a speech therapist, he will need the help of an otolaryngologist.
Diagnostics includes a number of phonemic tests, which are aimed at testing the ability to distinguish sounds that are close in pronunciation. In the mechanical form of the pathology, it is impossible to get rid of the defect in the pronunciation of certain sounds unless the source of their appearance is eliminated. Therefore, the treatment of dyslalia begins with this.
Causes of the disorder and mechanism of development
Provoke the appearance of a defect:
- Physiologically incorrect formation of the maxillofacial system, mouth and nasopharynx. Anatomical abnormalities lead to incorrect articulation of entire groups of sounds. Children with an anterior bite have problems pronouncing sibilant consonants because it is difficult to hold the tongue behind the teeth.
- Despite normal physiological hearing indicators, children with acoustic-phonemic dyslalia have not developed a sensory understanding of oral speech. There is no recognition function, comparison of common and different features of phonemes, as a result of which the child perceives words incorrectly.
The main reason for such a speech disorder is the immaturity of phonemic hearing.
The child does not distinguish between sounds, so he replaces one with the other when pronouncing. Usually, the sounds of one acoustic group are replaced: sonorant, whistling, hissing, voiced or voiceless.