Card index
The card index is used to manage the cards of children who have passed or will be tested. To go to the file cabinet, you need to left-click on the “Card Index” tab at the top of the program window. The user card stores all test results, basic data, and dynamics. You can manually enter answers from test forms into the card. The results of tests that were passed in the program are saved automatically.
Technical requirements
- DVD drive built-in or external
- Operating system Windows 7, 8,10 and higher
- Office suite (Word, Excel) with an active license for editing reports
- Availability of a local network in the classroom for network versions of the software
The program can be installed on any number of computers, but it will only run if there is a disc in the DVD drive.
Please note that this product is intended for use for non-medical purposes as part of the provision of socio-psychological, socio-pedagogical services during psychological and pedagogical correction classes. The product is not intended for use for medical purposes or for the provision of medical services.
Study of sound pronunciation based on the “Album for speech therapist Inshakova.”
⇐ PreviousPage 4 of 4
1 - Andrey
2 – Alena
3 – Sveta
| WITH | wheel pine nose | 1 - kaleto, totna, note 2 - wheel, pine, nose 3 - kolefo, fofna, nof |
| With | lilac letter goose | 1 - tyren, drink, gut 2 - seat, letter, goose 3 - firen, pifimo, guf |
| 3 | castle goat star | 1 - castle, goat, star 2 - castle, goat, star 3 - castle, goat, star |
| 3 | strawberry newspaper | 1 - zemyaniya, newspaper 2 - strawberries, newspaper 3 - zamyanika, newspaper |
| w | hat cat mouse | 1 - hat, cat, mouse 2 - hat, cat, mouse 3 - fapka, kofka, myfka |
1- Andrey
1 – Alena
2 – Sveta
| WITH | wheel pine nose | 1 - kaleto, totna, note 2 - wheel, pine, nose 3 - kolefo, fofna, nof |
| WITH ' | lilac letter goose | 1 - tyren, drink, gut 2 - seat, letter, goose 3 - firen, pifimo, guf |
| 3’ | castle goat star | 1 - castle, goat, star 2 - castle, goat, star 3 - castle, goat, star |
| Z | strawberry newspaper | 1 - zemyaniya, newspaper 2 - strawberries, newspaper 3 - zamyanika, newspaper |
| w | hat cat mouse | 1 - hat, cat, mouse 2 - hat, cat, mouse 3 - fapka, kofka, myfka |
| sch | brush box raincoat | 1 - theta, yati, dress 2 - brush, box, cloak 3 - feta, yafi, plaf |
| l | boat saw table | 1 - boat, saw, table 2 - boat, saw, table 3 - ftol, loda, saw |
| l | ribbon pipe shoes | 1 - ribbon, tvire, shoes 2 - ribbon, witness, shoes 3 - lena, firel, shoes |
| R | hand cow ax | 1 - hand, cow, ax 2 - duka, kodova, ax 3 - hand, koroa, ax |
| R' | radish rope door | 1 - redita, rope, ter 2 - dediska, vedevka, door 3 - redita, rope, - |
Based on the research, conclusions were drawn in the form of tables and diagrams (see Appendix No. 1). From them it is clear that phonemic hearing is not developed, the vocabulary is very poor and sound pronunciation is impaired. It is also clear from the results of the study that all children have a large stock of nouns, but there are big problems with knowledge of other parts of speech to varying degrees. But all subjects have a main problem: ignorance of numerals (children practically do not know this part of speech). Despite all the deviations in the development of these children, they easily come into contact with both adults and children. They understand speech addressed to them well, but at an everyday level.
Conclusion.
The purpose of the work was to study the level of speech development in mentally retarded preschoolers during play activities. And the tasks are to reveal psychological and pedagogical characteristics, as well as to reveal the characteristics of speech development and the specifics of gaming activities and conduct a confirmatory experiment to identify the level of speech development of mentally retarded preschoolers. The purpose and objectives are disclosed in the theoretical and practical parts of the course work. In the first chapter
The psychological and pedagogical characteristics of a preschool child with mental retardation, concepts, causes and forms of mental retardation, features of the mental and physical development of children with mental retardation are considered. Many definitions of mental retardation are also considered, and the author considers the following to be more correct and generalized:
Mental retardation
- this is a developmental atypia in which not only the intellect suffers, but also emotions, will, behavior, and physical development. The complex structure is due, first of all, to a primary disorder that directly arose under pathogenic influence, and then to secondary deviations. That there are many classifications of mental retardation. And that during mental development there is a persistent disruption of many body functions. And that physical development is influenced by the severity of the intellectual defect, concomitant disease, and secondary disorder. And, despite the fact that mental retardation is an irreversible phenomenon, this does not mean that it cannot be corrected. The gradualism and accessibility of didactic materials during physical exercise creates the prerequisites for children to master a variety of skills for the development of physical qualities and abilities necessary in the child’s life.
The features of speech development and play activity of mentally retarded preschoolers are also considered. It is said that a mentally retarded child lags behind in speech development from the first months of life. In the future, this lag progresses even more. And by the beginning of preschool age, the child has not formed the prerequisites for speech development: objective activity, lack of interest in the environment, insufficient emotions, phonetic hearing has not been formed, and the articulatory apparatus is poorly developed. Many mentally retarded children do not begin to speak not only by preschool age, but also by four to five years. And also that in a child with mental retardation, both auditory differences and the pronunciation of words and phrases arise much later. His speech is poor and incorrect. And that one of the main reasons for this condition is the weakness of the closure cortex, the slow development of new differentiated conditioned connections in all analyzers.
It is also said that play activity is the main activity of children in preschool age and contains all development trends; she is the source of development and the creator of the zone of proximal development; behind the game there are changes in needs and changes in consciousness of a general type. It was also found that the most important aspects of the psyche, in particular the formation of a child’s personality, develop mainly in play. Thanks to it, socially accepted ethical standards of behavior are highlighted and comprehended in the mind of a preschooler, and the main driving motive of personal development is formed - to be like an adult. A new form of motives develops in the game, a transition occurs from motives that have a form to conscious, affectively colored immediate intentions.
Research by Soviet psychologists and teachers revealed the relationship between a child’s play and his mental development.
And on the basis of theoretical research, a confirmatory experiment was carried out, which was described in the second chapter of the course work. It describes the empirical basis of the study and gives characteristics of the subjects. The following is a description of the experiment itself and its results. It is said that phonemic hearing is not developed, the vocabulary is very poor and sound pronunciation is impaired. Also in the experiment it was necessary to prove the hypothesis: if we study the level of speech development in mentally retarded preschoolers, we can determine ways of correction using game exercises. As a result of the experiment, the level of speech development of mentally retarded preschool children was revealed. And thanks to the results of the study, it is now possible to determine ways of correction using game exercises. Thus, the hypothesis is proven.
In the process of studying this problem, the author of the course work learned a lot of new and interesting things: he learned what mental retardation is and its concepts, causes and forms of development, about the psychology of preschoolers, about their speech development and about the specifics of the play activity of mentally retarded preschoolers. The author also learned how to conduct a statement experiment and describe the empirical basis of the study.
Bibliography.
1..Wiseman N.P.
Psychomotor skills of mentally retarded children. – M.: Agraf, 1997.
2. Wenger L.A.
Perception and learning (preschool age) - M., 1969.
3. Vinarskaya E.N.
Early speech development of a child and the problem of defectology - M., 1979.
4. Issues of training and education of mentally retarded children. Collection of scientific papers. – M., Moscow State Pedagogical Institute named after. Lenin, 1980.
5. Raising and teaching children in a auxiliary school: A manual for teachers./ Ed. V.V. Voronkova. – M.: School – Press, 1994.
6.Vygodskaya G.L., Sokolova N.D.
On the play activities of mentally retarded children. –
"Defectology", 1974, No. 5
7. Guseva G.M.
Methodological developments on the basics of special preschool pedagogy. – M. 1983.
8.Efimenkova L.N., Sadovnikova I.N.
Formation of coherent speech in oligophrenic children. – M. 1983.
9.Zabramskaya S.D.
Psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of mental development of children. – M. Enlightenment. 1995
10..Kataeva A.A., Strebeleva A.E.
Didactic games and exercises in teaching mentally retarded preschoolers. – M., “Buk – Master”, 1993.
11. Kataeva (Wenger) A.A., Davydova S.N.
Teaching mentally retarded preschoolers in a playful way using demonstration and verbal instructions. – M., “Defectology”, 1976, No. 1
12. Kataeva A.A.
Sensory development and sensory education of abnormal preschool children. – M., 1983.
13. Correctional pedagogy: Fundamentals of training in raising children with developmental disabilities. Textbook, ed. B.N. Puzanova. – M., Publishing House, 1999.
14. Lerner D.
Oligophrenopedagogy. – Priston, 1993.
15. Speech therapy. Textbook, ed. B.N. Puzanova. – M., Publishing House, 1999.
16.Martsinovskaya E.N.
The importance of substantive and practical activities for the training and education of abnormal preschoolers. – M., “Defectology”, 1982, No. 3
17.Morozova N.G.
Formation of cognitive interests in abnormal children. – M., 1969.
18. Mahler A.R.
A child with disabilities: A book for parents. – M.: Pedagogy – Press, 1996.
19. Mukhina V.S.
Speech impairment in preschool children. – M., Education, 1969.
20. Nepomnyashchaya N.I.
The role of preschool age in the psychological development of the child // Preschool education. – 1979. – No. 7
21. Education of children with severe intellectual underdevelopment: Programs, methodological recommendations/Under. Ed. L.B. Baryaeva and others - Pskov, 1999.
22. Features of the development and education of preschool children with hearing and intelligence impairments: Sat. scientific Tr. – M., 1988.
23.Program for training and education of mentally retarded children of preschool age//Defectology. – 1986. – No. 6
24. Psychological Dictionary/Under. Ed. V.V. Davydov, A.V. Zaporozhets and others, Scientific Research Institute of General Pedagogical Psychology Academ. Ped. Sciences of the USSR. – M.: Pedagogy, – 1983.
25. Rubinshtein S.Ya.
Psychology of mentally retarded preschool children. – M.: Education, 1986.
26.Trubnikova N.M. Practical speech therapy: Educational and methodological manual / Ural. State Ped. University. - Ekaterinburg. 2002
27. Shishkova O.B. Speech therapist's album. – M., 2000.
28. Tsvetkova L.S. On the question of methods for examining children with speech underdevelopment // Defectology. – 1971. – No. 3
Application.
№1
SOUND PRONUNCIATION
| Name | sizzling | whistling | sonorans |
| Andrey | + | replacement with "T" | + |
| Alyona | + | + | |
| Sveta | replacement with "F" | - (interdentally) | + |
PHONEMATIC HEARING
| Name | whistling-hissing | voiced-voiceless | hard-soft |
| Andrey | + — (not differential whistle.) | + | — |
| Alyona | + | + — (not differential explosive) | + |
| Sveta | — | — | — |
№2
Basic, key definitions of course work:
Preschool age
– childhood period from 3 to 7 years. During this period, the processes of maturation of the child’s body take place. All major tissues and organs develop. There is a transition from activities carried out jointly with adults to activities carried out to a certain extent independently.
A game
- one of the activities of humans and animals.
Children's game
- a historically emerged type of activity, which consists in children reproducing the actions of adults and the relationships between them and aimed at understanding the surrounding reality, serving as one of the most important means of physical, mental and moral education of children.
Speech development
– Possible understanding of speech and its pronunciation at an early age when communicating with adults, subsequent enrichment of vocabulary, grammatical and stylistic structures of speech in preschool age in the process of communication and under the influence of training and education.
Speech
- a historically established form of communication between people through language.
The term “mental retardation”
denote a persistent, pronounced impairment of cognitive activity due to the diffusion of organic damage to the central nervous system.
Mental retardation
is a generalized group diagnosis for a developmental anomaly. A characteristic feature of mental development is the underdevelopment of the most differentiated phylo- and ontogenetically young functions of the brain and the relative preservation of elementary, evolutionary older ones.
Mental retardation
- this is a developmental atypia in which not only the intellect suffers, but also emotions, will, behavior, and physical development. The complex structure is due, first of all, to a primary disorder that directly arose under pathogenic influence, and then to secondary deviations.
⇐ Previous4
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Possibilities
The software “Speech therapy examination of children” provides the opportunity to:
- Maintaining individual cards containing anamnestic data, examination results, as well as the dynamics of the correction process
- Automatic database formation, sorting and searching of cards according to specified parameters
- Carrying out step-by-step speech therapy diagnostics
- Recording, saving and analyzing received data
- Formation of speech cards
- Formation of graphs of individual dynamics of speech development
- Creation of group protocols based on survey results
- Printing speech cards, graphs of individual dynamics of speech development, protocols with group data.
Results
The level approach implemented by the technique significantly simplifies the examination procedure and the formulation of a speech therapy report. During the analysis of the results obtained, the specialist has the opportunity to substantiate the conclusion within the framework of the psychological and pedagogical classification (NPZ, FNR, FFNR, LGNR, ONR (I - IV levels)) and draw up a scheme of individual correctional work. Specially designed tables for recording results and the ability to print them significantly simplify reporting and allow you to track the dynamics of correctional work.
Protocol for examining the level of speech development
I. Preliminary interview
1. What is your name? ______________________________________________________________
How old are you? ______________________________________________________________
What are your parents' names?________________________________________________________________
What city do you live in?______________________________________________________________
What floor do you live on?______________________________________________________________
What days of the week do we rest?________________________________________________
Who is congratulated on March 8?________________________________________________________________
What holiday does Santa Claus congratulate us on?_________________________________
What fairy tales do you know?__________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
2. Volodina's album
1) Forms (p.4)-________________________________________________________________________________
Colors (p.4) -______________________________________________________________________________
2) “The fourth odd one” (p. 11) -__________________________________________________________
3) Seasons (pp. 12-13) -__________________________________________________________
4) Days of the week: today _____________yesterday________________tomorrow_________________
5) Time of day (p. 14): morning __________day__________evening__________night___________
II. Sound culture of speech
1. Sound pronunciation (Inshakova’s Album)
| WITH | WITH’ | Z | Z’ | C | Sh | AND | H | SCH | L | L’ | R | R’ |
| N | N’ | M | M’ | j | T | T’ | D | D’ | TO | TO’ | G | G’ | X | X’ | IN | IN’ | F | F’ |
| A | ABOUT | U | Y | E | AND |
| S/N | Salary | S/C | T '/H | R/L | Р/ j | P '/ j | L /j | L '/j |
| SASHA____ HIGHWAY___ SIX___ | MALE___ CITRUS___ HOTEL___ | ROLL___ THROAT___ DEN___ | RAIL___ LOIN___ CROSSROADS__ | RULER___ HIVE___ ALLEY___ |
| CLAMP___ WAND___ LIGHTER___ | BIRD___ FIRST KIT___ CHICK___ | PARADISE___ FAIR___ DISTRICT___ | LAIKA___ APPLE___ Puff___ |
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
2. Phonemic hearing
| syllables | 4 years | syllables | 5 years | 6 years | syllables | 5 years | 6 years |
| BA-PA | BA-BA-BA | SA-SHA-SA | |||||
| PA-BA | PA-BA-BA | SHA-SA-SHA | |||||
| GA-KA | DA-TA-DA | SA-CA-SA | |||||
| KA-GA | DA-DA-TA | CA-SA-CA | |||||
| TA-DAH | GA-KA-GA | CHA-CHA-CHA | |||||
| DATE | KA-GA-KA | Cha-cha-cha | |||||
| MA-BA | FOR-SA-FOR | SHA-SHA-SHA | |||||
| BA-MA | SA-ZA-SA | SYA-SHA-SIA | |||||
| VA-KA | ZHA-SHA-ZHA | PA-PA-PA | |||||
| KA-VA | SHA-ZHA-SHA | PY-PA-PY | |||||
| NYA-NA | TA-TA-TA |
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3. Syllable structure of the word
STRAWBERRY_________________________________________ ESCALATOR_____________________________________________ ESCAVATOR_____________________________________________ ARCHITECT________________________________________ PLUMBER______________________________ CONTROLLER_________________________________ AIRPORT_____________________________________________ AIRFIELD_____________________________________________ DRAFTSMAN_____________________________________________ BARRIER_____________________________________________ SHIP TURNING______________________________ TYPE WRITING___________________________
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
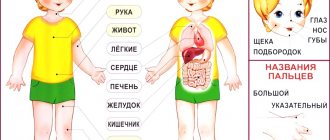
III. Vocabulary (lexis) album by Inshakova
| 1. Body parts | 15. Tools | — |
| 2. Toys | 16. Technique | — |
| 3. Dishes | 17. School supplies | — |
| 4. Clothes | 18. Sports equipment | — |
| 5. Shoes | 19. Construction machines | — |
| 6. Vegetables | 20. Berries | |
| 7. Fruit | 21. Birds | |
| 8. Furniture | 22. Mushrooms | |
| 9. Wild animals | 23. Pisces | |
| 10. Pets | 24. Hats | |
| 11. Trees | 25. Professions | |
| 12. Flowers | 26. Musical instruments | |
| 13. Products | 27. Insects | |
| 14. Transport | 28. Weapons | — |
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
IV. The grammatical structure of speech (Volodina’s album)
1. Understanding prepositions (p. 18-21)_________________________________________________
2. Plural of a noun (p. 22-23)_________________________________
3. Plural of the verb (p.24)_____________________________________________
4. Formation of prefixed verbs (p. 25)_____________________________________________
5. Formation of the diminutive form (p. 26-27)_________________________
6. Formation of adjectives from nouns (p. 38-39)________________________
7. Cases (p.40-46):
Accusative________________________________________________________________
Prepositional_________________________________________________________________
Dative___________________________________________________________________
Instrumental________________________________________________________________
Genitive unit. and plurals_______________________________________________
8. Agreement of a noun with a numeral (p. 46-47)_____________________
9. Antonyms (p.56-57)__________________________________________________________
10. Formation of possessive adjectives (p. 58-59)________________________
11. Sound analysis of words (p.69)_______________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
V. Coherent speech (Volodina’s album)
1. Compiling a story based on a picture (p. 72)__________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. Retelling (p.74)______________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. Compiling a story based on a series of pictures (p. 77)___________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
Note:___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Conclusion:__________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Personal data
F.I. child ________________________________ Date of birth ___________________
Attending kindergarten ____________________ at what age ____________________
Presence of other children in the family ___________________________________________________
Peculiarities of speech of parents and close relatives in the family _______________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Anamnesis
Pregnancy (what kind)__________________________________________
Course of pregnancy (toxicosis: 1st half, 2nd half; falls, injuries, psychoses, chronic somatic diseases, infections, intoxications, hemolytic disease)______________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Childbirth (early, urgent, fast, rapid, dehydrated)__________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Stimulation (mechanical, chemical, electrical stimulation)______________________
Anesthesia (local, general, epidural anesthesia)________________________
When the child screamed_______________________________________________________________
Presence of asphyxia (white, blue)________________________________________________
Weight and height at birth_______________________________________________________________
Breastfeeding until ____________________________________________________________
Early development
Began to hold his head____________(N-1.5 months), began to sit____________________(N-6 months)
Began to walk________________(N-11/12 months), first teeth appeared___________(N 6-8 months)
Used the pacifier until __________________________
Past illnesses
(severe somatic illnesses, infections, bruises, injuries, convulsions at high temperatures, fears)
Up to a year__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
From one to three years_______________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Sharkist's conclusion_______________________________________________________________
Otolaryngologist's report______________________________________________________________
Psychiatrist's report______________________________________________________________
Early speech development
Buzzing________________________________________________________________(N-2/3 months)
Babbling_______________________________________________________________________________(N-4/8months)
First words__________________________________________________________________________ (N-12 months)
First phrases_________________________________________________________________(N-1.5-2g)
Replacing words with gestures______________________________________________________________
The child’s attitude towards a speech defect__________________________________________
We worked with a speech therapist at the age of _______________________During ________________
Results of speech therapy work________________________________________________________________
Anatomical structure of the speech apparatus
Lips: N, procheilia (thick v.), cleft, scar Teeth: N, outside the maxillary lip, absent, absent, double row Hard palate: N, cleft, scar, high Soft palate: N, shortened, forked, sedentary, absent small tongue Bite: N, prognathia, progenia, lateral open (right-sided, left-sided) Tongue: N, macroglassia, microglassia Frenum: N, shortened, thickened, absent, trimmed
Author of the material: Yurieva Natalia Ivanovna