Article:
The sound [l] normally appears in a child at the age of 5 years.
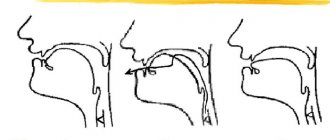
But the sound [l'-l] normally appears independently earlier from 3 years. If a child at 5 years old does not have the sounds [l], [l'], be sure to contact a speech therapist. If in a child’s speech the sounds [l], [l'] appear in a distorted version (maybe even earlier at 3 or 4 years), contact a speech therapist as soon as you notice it. Distorted sounds are never restored on their own. How to pronounce the sound [l].
- teeth are brought together to a distance of 2-4 mm;
- neutral lip position;
- a weak stream of air passes along the sides of the tongue;
- vocal folds are closed - produce voice.
- the tip of the tongue is raised and pressed against the base of the upper incisors;
- the lateral edges of the tongue do not meet the molars;
- the back of the tongue is raised towards the soft palate;
- the root part is raised - “saddle”;
- the back of the tongue is lowered.
Articulatory features of the sound [l].
[l] – mouth sound. The soft palate is raised, the uvula is pressed against the back wall of the pharynx, air enters the oral cavity; [l] – consonant sound. The air escaping from the oral cavity encounters a barrier; [l] – ringing sound. When pronouncing the sound [l], the vocal cords are closed, vibrate, and a voice is formed; [l] – stop-pass sound according to the method of formation. The tip of the tongue forms a connection with the alveoli or upper teeth, the air stream passes along the sides of the tongue, between the tongue and the cheek; [l] – anterior lingual sound at the place of formation. A barrier to the outgoing air stream is formed by the front part of the back of the tongue.
Acoustic signs of sound [l].
[l] – sonorant (sonorous) sound – its quality is determined by the nature of the sound of the voice, which plays a major role in the formation of sound, and noise participates to a minimal extent; [l] - hard sound - the middle part of the back of the tongue does not take an active part.
Sound disturbances [l].
- The sound [l] is absent in the child’s speech - lambdacism.
- The sound [l] is replaced - paralambdacism: - with [a], [u], [s] and other vowels; — on [l'] – softening; — on [c] – labiodental paralambdacism; - on [n] – lingual-dental paralambdacism; - on [g] – posterior palatal paralambdacism; - on [th] - midpalatal paralambdacism.
- The sound [l] is distorted: - nasal pronunciation (nasal lambdacism); - interdental pronunciation (interdental lambdacism).
How to pronounce the sound [l'].
When pronouncing the sound [l'], the position of the organs of articulation is similar, but:
- lips are open, stretched more to the sides;
- the back of the tongue rises a little higher towards the hard palate and forward, and the back of the tongue is moved forward and lowered.
Articulatory features of the sound [l'].
[l'] – consonant sound. The air escaping from the oral cavity encounters a barrier; [l'] – mouth sound. The soft palate is raised, the uvula is pressed against the back wall of the pharynx, air enters the oral cavity; [l'] – ringing sound. When pronouncing the sound [l'], the vocal cords are closed and tremble, a voice is formed; [l'] – anterior lingual sound at the place of formation. The barrier to the outgoing air stream is formed by the front part of the back of the tongue; [l'] – stop-passive sound according to the method of formation. The tip of the tongue forms a bridge with the alveoli or upper teeth, the air stream passes along the sides of the tongue, between the tongue and the cheek.
Acoustic signs of sound [l'].
[l'] - soft sound - the middle part of the back of the tongue is additionally raised towards the hard palate; [l'] - sonorant (sonorous) sound - its quality is determined by the nature of the sound of the voice, which plays a major role in the formation of sound, and noise participates to a minimal extent.
Sound disturbances [l'].
- The sound [l'] is absent in the child’s speech - lambdacism.
- The sound [l'] is replaced - paralambdacism: - with [a], [u], [s] and other vowels; - on [c'] – labiodental paralambdacism; - on [n'] – lingual-dental paralambdacism; - on [g'] – posterior palatal paralambdacism; - on [th] - midpalatal paralambdacism.
- The sound [l'] is distorted: - nasal pronunciation (nasal lambdacism); - interdental pronunciation (interdental lambdacism).
The sound L at the end of a word in a series of words
List of words: Hall, canal, glass, basement, Ball, pencil case, coral, jackal.
List of words: Table, cauldron, goat, goldfinch, Ox, donkey, football, cover.
We fix the pronunciation of the sound L at the beginning of words:
varnish shop lama lamp noodles bast weasel patch palm avalanche swallow lamp forehead crowbar dexterous boat elbow elk vine catch break chunk tray meadow moon puddle meadow Luka lawn bow splint magnifying glass bast crafty
Exercise “Listen. Remember. Repeat"
Bench - paw - lamp. Delicacy - boatman - shopkeeper. Elbow - spoon - boat. Bow - magnifying glass - puddle. Lusha - hole - ray.
Correction of sound pronunciation. Album “Automation of the sound “L””
Articulation gymnastics for the sound “L”.
Automation in syllables.
Automation in words (beginning of a word)
Walk along the path and say the words.
Help Luntik find friends. Say all the words slowly and clearly pronouncing the sound “L”.
(varnish, lamp, palm, bench, lily of the valley, noodles, flippers, swallow, bast shoes, camp, loto, husky, doe, burdock, llama, shovel, lotus, curls, elk, horse, boat, slices, spoons, meadow, puddle , moon, magnifying glass, rays, bow, skis, skier)
Automation in words (middle of a word)
Walk along the path and say the words.
Help the little bun return home to his grandparents.
(spinning top, saw, robe, salad, closet, school, bee, shark, village, saddle, oar, hollow, swamp, cap, well, salt shaker, dove, acorns, naughty, shelf, needle, bun, fork, jump rope, soldier )
Automation in words (in confluences)
Walk along the path and say the words.
Help Lusha get home.
(pilaf, raft, scarf, plan, crying, cloak, flame, dress, square, patch, parcel, elephant, clown, ball, flowerbed, strawberry, bug, doll, treasure, heel, notepad, clouds, eggplant, apple, eyes , globe, capercaillie, felt-tip pens, flag, bottle, firecracker)
Game "Let's play and count."
Count and cover with chips: one squirrel, two squirrels, three squirrels, four squirrels, five squirrels.
Coloring game “On the contrary”.
(fixing antonyms)
Game “What we saw, we won’t say, but what we did, we’ll show”
The girls sent Mila photographs. Tell me what the girls did.
(rolled, jumped, sat, swayed, walked (walked), swam, read, ate, wrote, danced, put on shoes, swept, sunbathed (lying down),
Slept, washed, drank, ran, watered)
Game “What Mom Can Do.”
Have you noticed how much mom has to do? Tell me what mom did.
(washed, sewed, knitted, embroidered, dressed, hugged, bathed, laid, calmed, washed, ironed, washed, cooked, covered)
Automation of the “L” sound at the end of a word.
Dunno collected photographs of what the boys can do.
(dressed, looked, drew, played football, ate, sang, slept, played (built), rode, swung, dug, brushed teeth, caught, swam)
Game “What Dad Can Do”
Dad talked about his activities.
(read, dug, worked, drove (managed, got stuck), collected (repaired), built, caught, ate, sat, (talked), rode, played, vacuumed, swam, lay, walked, drew, sawed, cooked)
Game "Coloring".
White page
Yellow Page.
Say the phrases:
(yellow robe, yellow raincoat, yellow T-shirt, yellow dress, yellow gold, yellow shovel, yellow skis, yellow tent, yellow spoon, yellow fork, yellow moon, yellow ear, yellow butter, yellow cap, yellow tie, yellow lamp, yellow boat, yellow chair, yellow table, yellow acorns, yellow plate)
Automation in connected speech.
Tell poems based on pictures.
Retell it using pictures.