Causes of stuttering
Stuttering is a disorder provoked by psychological and physical factors. The medical name for this speech problem is logoneurosis; it is studied by both medical workers and psychologists, grouped into groups.
Biological prerequisites (heredity)
It is noted that if the mother or father suffered from stuttering, then the child’s chance of developing logoneurosis from early childhood increases. Also, this speech disorder can be transmitted through generations if the grandparents had mild or complicated stages of the pathology.
Physiology
In most cases, somatics influences:
- the brain is functionally affected;
- there were head injuries while in the womb;
- past infectious disease;
- disorder of the autonomic nervous system, etc.
In addition, stuttering is provoked by general physical or nervous exhaustion, a weakened immune system, defects in the formation of the speech apparatus, insufficient development of motor skills, etc.
Social influence
The social factor influencing a person disturbs and changes the general internal and external state. Children suffer from disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus due to communication problems:
- quarrels and misunderstandings in the family;
- any aspects of education are not covered;
- do not find a common language with their peers.
Psychology
Children and adults are susceptible to psychological factors that influence their future interactions with others. Logoneurosis can develop due to:
- psychological trauma;
- acute emotional experiences (they can be both positive and negative);
- severe fear;
- psychological fatigue;
- information exhaustion;
- stressful situations, etc.
These factors depend on the person; not all life circumstances can lead to disorders and problems. If you set your priorities correctly and cope with psychological barriers, then speech disorders can certainly be avoided.
Those who stutter are most often withdrawn, which prevents them from correcting and restoring correct speech skills. Logoneurosis, which arose due to psychological reasons, is treated faster and easier.
First, the prerequisites for the onset of the problem are examined, and then a comprehensive treatment method is prescribed. Logoneurosis must not only be eliminated physiologically, the psychological causes of stuttering must be eradicated so that in the future they do not again contribute to the development of pathology.
If a child stutters - recommendations
If a child in your family begins to stutter, help him by following these tips:
- Talk to him slowly, almost syllable by syllable, calmly pronouncing the words.
- Do not pull back or interrupt your child if he is excitedly trying to tell you something. Holding his hands will help him calm down and continue speaking at a normal pace.
- Read good fairy tales, retell them, discuss the plots, ask and answer questions. In a home environment with close, loving people, it will be psychologically easier for the child to cope with the problem.
- Be careful about his feelings. If he doesn't feel comfortable talking in a certain situation, don't force him.
- Create a calm, friendly atmosphere at home. It is unacceptable to tease, imitate stuttering, or be dismissive.
- Teach your child to work conscientiously and not miss speech correction classes in order to stop stuttering.
Statistics
Logoneurosis is considered a problem that arises more often in childhood than in adulthood. According to statistics, around one to three percent of children worldwide stutter. These statistics vary depending on location, age, and nationality.
Boys are four times more likely to develop a stutter than girls. Many people do not know what logoneurosis is and whether they have it, since the pathology can manifest itself in a milder form.
It has been proven that stuttering in adults, which they suffer from since childhood, is much more common in people who grew up in orphanages and boarding schools. It is obvious that early separation from parents and an unfavorable social climate affect the further psychological state and development of a person.
Also, people living in villages and towns are less susceptible to speech defects than those living in a metropolis. This is due to the calm environment. Adults who stutter account for only 1% of the population, which indicates the successful treatment of this pathology.
Siblings adopt this disorder in 18% of cases. Moreover, stuttering occurs in 32% of dizygotic twins, and in 77% of monozygotic twins.
Phases of pathology development
Phase I
Stuttering with short episodes, shortening the period of smooth speech regularity. Characterized by the following symptoms:
- Difficulty in pronunciation at the beginning of a word and when constructing a sentence.
- Stumbling in speech occurs in the pronunciation of short parts of speech, conjunctions and particles.
- Stuttering occurs as a result of “Communicative pressure” (excitement, a person is in a hurry to say something, etc.).
- There is no speech phobia observed.
II phase
- A chronic form of pathology appears.
- Pronunciation is difficult when speaking quickly and in complex word combinations.
- Awareness of a speech defect, but this does not interfere with normal communication.
III phase
- Obvious convulsive syndrome. But the person does not yet perceive this as a problem.
- Some sounds and syllables cannot be pronounced.
- Speech inhibition, as attempts begin to replace some words with others that are less problematic.
IV phase
- Stuttering develops into a major personal problem. The person understands that he has serious speech impairments and avoids contacts and difficult situations where communication is required. If at earlier stages words and expressions sometimes changed, now this happens all the time.
- Anticipation - a person waits for his speech errors.
- Chronic problem in pronouncing words. Development of fear of communication.
Types of stuttering
The division concerns convulsive forms, clinical manifestations and the course of the pathology.
Convulsive forms of stuttering in adults and children have the following divisions:
- The clonic form is a short-term spasm, followed by a second similar one, which leads to involuntary repetitions of phrases and letters.
- Tonic form - long-term or short-term muscle contraction. As a result, a person does not pronounce one word for a long time.
- Mixed stuttering in the form of parallel clonic and tonic forms.
In addition, in addition to the functionality of the speech apparatus, facial expressions suffer: they may be accompanied by cramps of the facial muscles and parts of the limbs.
Course of stuttering
- Long-term - when the defect manifests itself on a permanent basis in all words and in any situation.
- Intermittent - some psychological situations provoke stuttering (excitement, joy).
- Relapse - after treatment, the problem appears after some time. It doesn’t matter whether a person is cured completely or partially.
Clinical form of stuttering
Logoneurosis manifests itself in two clinical forms: neurotic and neurosis-like. Each of them has its own cause with a developing mechanism.
Neurotic stuttering
Stuttering in adults and children was not caused by birth or postpartum trauma. These are not physical disorders in the cerebral cortex. This form of disorder includes the psychological and social factors described above. With this type of pathology, the patient is easier to cure than with a neurosis-like form. The problem is mainly dealt with by a psychologist. Adults are more often susceptible to the chronic form of this pathology.
Characteristics of a person with neurotic stuttering:
- A person with a stutter is immediately visible: he is silent, timid and agitated, he invents worries, he is often offended, irritated, he is withdrawn, his far-fetched fears interfere with life. These are melancholic people.
- This patient has no physical developmental abnormalities.
Neurosis-like form
It appears unexpectedly, most often in the medical history there are birth problems. For example, the mother suffered a difficult pregnancy: complications, birth injuries. As a result, the functioning of the brain and central nervous system is disrupted, treatment takes longer, and a 100% guarantee of recovery is not always given.
Often, each part of the speech apparatus is susceptible to severe forms of convulsions. When talking, people can accompany their speech with sharp nods of the head, twitching of the hands, and contraction of the facial muscles. All this happens involuntarily.
A person gets tired after a long conversation, so such people are more silent. In addition to exhaustion, the patient complains of poor memory, orientation in space and time.
You need to work with a specialist in a comprehensive manner, taking special medications. The lengthy recovery procedure can take several years.
How does stuttering develop?
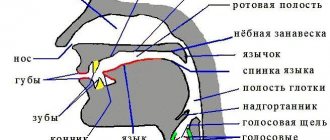
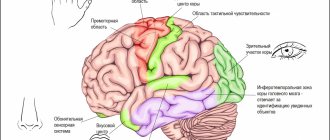
This process has not been fully studied; at the moment there is a version. Depending on the prerequisites for dysfunction of the speech apparatus, Broca's center is affected (the vocal center responsible for the work of the muscles and ligaments involved in speech). As a result of overexcitation of Broca's center, the speed of its work increases. The functioning of the so-called speech circle (Broca's center, Wernicke's area and associative center) is disrupted.
This causes a convulsive effect (tongue, lips, soft palate and others). A person develops stuttering due to impaired coordinated functions of the speech apparatus when reproducing words, syllables and phrases that are caused by a spasm. The spasm begins in one of the sections of the speech apparatus.
If Broca's center is highly overexcited, this is reflected in nearby areas of the brain. As a result, involuntary movements and spasms of the limbs, etc.
It is interesting that nerve impulses during an excited nervous system and consonant sounds (especially voiceless ones) are similar in frequency. Therefore, stuttering mainly occurs on consonants and is extremely rare on vowels.
Classes with stutterers, work with children who stutter
The child began to stutter . Often, instead of adequate effective treatment, parents send their child to a speech therapy kindergarten or wait until it goes away on its own. They naively think that classes with a speech therapist, speech therapy, speech therapy work with preschoolers and schoolchildren who stutter, speech therapy classes for stutterers can help if a child stutters. But a speech therapist can provide sounds, not treat stuttering. Classes with children who stutter are aimed at eliminating sources of excitation in the central nervous system. This hard, systemic work with children who stutter produces small positive results, which immediately disappear when exposed to provoking factors.
Specialists
Treatments for stuttering in children and adults are similar. Depending on the determination of the cause of the speech defect, the attending physician is appointed. There are several of them, sometimes two or more specialists deal with one patient.
- A neurologist and psychiatrist prescribe medication to solve the problem of stuttering.
- The psychotherapist prescribes psychotherapy depending on the characteristics of the person: hypnotization, training.
- A psychologist studies psychosomatics and human personality. First, the patient is removed from the psychological barrier. He is trained to be in society and make decisions in stressful situations.
A speech therapist is a specialist who corrects speech in parallel with the provision of assistance by another specialist. It helps improve speech, use breathing exercises, and pronounce letters and sounds.
The goal of his therapy is not to correct incorrect pronunciation, but to help in realizing that words can be constructed easily in a sentence, regardless of pathology. The patient reduces his fear of stuttering.
An acupuncturist works to improve blood circulation. The sessions used are responsible for a specific organ; in general, the technique helps with mild stages of stuttering. Stuttering is a fairly rare occurrence and can take a long time to correct. If you start to fight the pathology in time and diagnose the correct factor in the development of the problem, then the chances of getting rid of this speech disorder increase sharply.
Article:
CAUSES Scientists believe that logoneurosis occurs as a result of several factors.
An important role is played by the child’s developmental characteristics and genetic predisposition. It has been established that in children who stutter, the speech areas of the brain have their own structural characteristics. Disorders of speech development The formation of speech skills is a complex process. It involves developing connections between certain areas of the brain, the central nervous system, and the muscles responsible for breathing and speech.
If each part of this multi-level system works correctly, words are pronounced correctly and in the right order - speech has a certain rhythm with pauses and accents. A child learning to create simple sentences needs constant practice. This stimulates the development of the speech areas of the brain and nerve pathways (tracts).
Speech problems occur when the structures of the developing nervous system are not coordinated. This leads to repetitions and stops, especially when the child is excited or in too much of a hurry. As the brain continues to develop, some of these problems resolve or compensate for themselves. Therefore, many children “grow out” of stuttering.
Influence of gender and genes Stuttering is more common in boys than in girls. This is due, first of all, to differences in their development: girls first develop speech characteristics, and then psychosexual ones. In boys this happens almost simultaneously. Therefore, they are more vulnerable to speech and language problems.
Pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth The risk of speech disorders increases if during pregnancy the mother suffered from an infectious disease or fetal hypoxia was observed. Various intrauterine pathologies negatively affect the development of the central nervous system, which can subsequently cause stuttering.
Problems during childbirth and the use of obstetric aids also subsequently negatively affect speech development. Severe birth injuries can cause decreased intellectual abilities and stuttering.
Psychological stress Severe psycho-emotional stress, for example, the loss of a loved one, parental divorce can also provoke logoneurosis. Positive emotions have a similar effect. A noisy birthday with lots of gifts and clowns, and the next morning - stuttering. Possible triggers could be watching a TV show with scenes of violence or a horror movie.
Conflict situations in the family are another cause of speech disorders. In families of drinking parents, especially those who abuse children, cases of logoneurosis are not uncommon.
Somatic diseases Traumatic brain injuries (for example, concussion), previous encephalitis and meningitis rarely cause logoneurosis, however, nevertheless, they create the ground for its appearance. Any provoking factors (stress, improper upbringing) can lead to speech pathologies.
Sometimes stuttering develops after severe infectious diseases, such as influenza or measles. Diabetes with frequent hypo- or hyperglycemic states negatively affects the development of the child and can lead to speech disorders.
HOW EXACTLY IT IS TREATED How to stop a child from stuttering, what needs to be done to speak without stuttering or stuttering, how to quickly get rid of stuttering and stuttering in speech for a teenager and to recover for an adult?
The choice of treatment method for a speech defect is based on the individual characteristics of the person, his age, as well as the degree and form of the disease. Below is a description of the methods for treating the disease.
Speech therapy sessions with a child and stages of correction How to cope with stuttering, overcome the problem, unlearn stuttering? There are a huge variety of proprietary methods to combat this speech defect.
The most famous of them is the technique of doctor Smirnova. The essence of the treatment is as follows: a speech therapist conducts 20 minutes of lessons a day with a stuttering child (preferably in the morning) in a playful way.
Classes should begin with a warm-up for the hands. Then muscle tone relaxes, motor and speech coordination develops, and lastly, a sense of rhythm and tempo develops.
It is worth noting that this method of correcting, eliminating and overcoming stuttering is practiced only on preschool children.
Psychological and psychotherapeutic approach How to combat stuttering in adults and cure it in a teenager? One of the ways to get rid of the disease is hypnosis. Since ancient times, it has been given a special place in the fight against illness.
During the procedure, a person’s speech spasm is relieved by hypnosis. Hypnosis does not help to get rid of stuttering completely, but only to maintain the results obtained.
Medications Experts say that in order for the treatment to be most effective, it is necessary to take medications: Phenibut, Afobazol, Neurobion, Eglonil, Cytolopram.
The exact names of the tablets and doses should be prescribed by your doctor. Don't self-medicate!
Fighting with the use of various signals and currents How else to overcome and eliminate stuttering? Treatment of the patient with the use of various signals and currents inhibits the stuttering process. One such treatment method is the rhythmization method.
So, the patient puts on headphones, which allow him to hear his speech louder, so the person has to speak more quietly, which has a beneficial effect on the treatment of stuttering.
Biofeedback (BFE) How else can an adult stop stuttering and save a child from stuttering? Biofeedback (hereinafter referred to as biofeedback) allows a person to see how his body works. With the help of biofeedback, correct correction of speech and its deficiencies occurs, as well as its improvement.
This method includes the ability to breathe correctly when speaking, speak clearly, and develop fluent speech skills.
Physiotherapeutic How to correct stuttering in adults, which will help eliminate the disease in children? Physiotherapeutic methods improve and stabilize the functioning of the nervous system, improve the psycho-emotional state of the child.
If a child or adult stutters, a doctor may prescribe procedures such as:
therapeutic electrophoresis; electrosleep therapy; baths with nitrogen, iodine and bromine; acupuncture; aerotherapy; massotherapy. aerotherapy; Darsonvalization of the cervical spine. Osteopathy Scientists prove that the causes of stuttering lie in:
in violation of coordination of the muscles responsible for speech; in violation of hearing feedback; in insufficient control of speech function by the central nervous system. Osteopaths successfully solve these problems. How is stuttering treated in children and adults by an osteopath? Doctors:
relieve excitement of the nervous system; relieves spasms of speech centers; identify and solve problems of speech muscles; relieve nervous tics. After eliminating the causes of stuttering with the help of osteopathy, the disease usually goes away.
TYPES OF STUTTERING IN CHILDREN
Stuttering in children is not just a speech defect, manifested in a slower rate of speech and repetition of parts of words, involuntary pauses, but a neurological problem. All these difficulties in speech are caused by convulsions of the articulatory organs and are associated with the work of the central nervous system. Although non-specialists call these problems with one general word: stuttering, doctors and speech therapists distinguish these types of problems.
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, logoneurosis proper and neurosis-like stuttering are distinguished:
Logoneurosis or neurotic stuttering is caused by functional disorders of the nervous system and can be treated quite successfully. Neurosis-like stuttering is caused by organic lesions of the central nervous system. It's much more difficult to deal with. Based on physical manifestations, more than 6 species are distinguished. But since most of them are mixed, we will name only the main types. Clonic, which manifests itself in repetitions and stretching of sounds, syllables or words beyond the child’s control. Tonic, in which from time to time the baby is unable to pronounce sounds and words, involuntary pauses occur in his speech.
ADVICE FOR PARENTS If there is a child in the family who stutters, some adjustments will need to be made to the daily routine. It is advisable to exclude psycho-emotional stress (parental quarrels, loud music, etc.). The environment should be calm and friendly.
What matters is how parents respond to stuttering. This largely determines the child’s self-perception
Therefore, under no circumstances should you show your concern or irritation. Communication should always be calm and relaxed.
When talking with a child who stutters, you need to follow some rules. During the conversation you need to:
pronounce phrases slowly and calmly; use short sentences and simple language to reduce speaking demands; always ask one question and do not rush into an answer; do not speak too quickly, the child should have enough time to understand and develop an answer; Make time every day for one-on-one communication without distractions from other family members or homework. When parents listen to their child, they need to:
do not show anxiety, impatience, or try to correct or supplement the child’s speech; maintain natural eye contact; listen carefully and not be distracted by other stimuli; pause before answering a question; always try to encourage your interlocutor, you can say something like: “learning to speak correctly is very difficult, it takes time; are you all right". HOW TO PREVENT THE DEVELOPMENT OF SPEECH DEFECTS Preventing stuttering is a lot of work for parents and others. It includes:
Organizing your baby's daily routine. Creating a calm and friendly atmosphere in the family. Avoiding authoritarian parenting methods. Protecting the child from physical and psychological harm. Activities for speech development - reading, talking with the baby. Limiting the child’s contact with relatives or friends who stutter. Doctor pays attention
A stutterer needs to be under the supervision of a neuropsychiatrist and speech therapist at all times. Don't read too many books to your children, especially if they are not age appropriate. Do not read scary fairy tales at night, as this provokes a feeling of constant fear: fear of seeing Baba Yaga, the devil, the devil. Do not allow you to watch television programs for a long time. This overstimulates and tires the children's nervous system. Age-inappropriate transmissions have a particularly negative impact. Do not overload your baby with new experiences (reading, movies, watching TV) during the period of remission after treatment. Speak to a stutterer clearly, smoothly (without separating one word from another), take your time, but do not pronounce words in syllables or into a chant. Try to bring your baby closer to balanced, well-spoken peers so that he learns to speak clearly and expressively. It is impossible to involve a stutterer in a game that excites and requires speech performances from the participants. Dance and music classes are very important, which contribute to the development of correct speech breathing, rhythm, and tempo. Singing lessons are useful. What else to read
MAIN RULES OF CLASSES Speech rules for people who stutter:
Planning a statement. Impromptu speech when stuttering is challenging. At the initial stages of correction, it is better to avoid improvisations in speaking, so as not to provoke speech spasms. When the speaker knows what he wants to say, his psychological stress decreases, and with it the likelihood of a spasm. A good result is obtained by preliminary speaking “to yourself”. Monitor your breathing during the speech act. Speaking while inhaling air is unnatural. You need to pronounce the phrase while exhaling. Moreover, you need to breathe with your diaphragm. The air supply should be spent primarily on pronounced vowel sounds. Don't forget about stops in speech. Pauses give you the opportunity to gain air reserves and think about the next phrase. Make pauses not only between meaningful sections of text, but also within long sentences. Watch your movements. General rules of conduct when dealing with stuttering:
Do exercises and other activities to overcome the defect on your own every day. Introducing a daily routine will help with this. Planning for a day will allow you to distribute time so that work on combating stuttering becomes familiar.
Keeping fit
Speech depends on the general physical condition of the body, so it is important to get enough sleep, avoid stressful situations, get proper rest, and eat right. Certain sports help keep the body in good shape, and at the same time train the respiratory system. These include swimming, skiing, walking. Sudden movements and strong muscle tension are contraindicated in logoneurosis, so barbells, boxing, wrestling, jumping, football, and basketball will not be beneficial.
Give up bad habits.
Rules for a speech therapist - when preparing a lesson with children, you must:
Take into account the leading activity of a particular age. This is a game for preschoolers. All tasks and exercises should be carried out in such a way that the child finds it interesting. Otherwise, you may encounter a reluctance to engage and a loss of contact. Monitor the duration of classes. It should be no more than 20 minutes. When developing lessons, take into account the individual characteristics of the person who stutters. Give material and tasks with a gradual increase in complexity. REASONS Stuttering can be either congenital - if it appeared when the child began to speak, or acquired - if, for example, stuttering appeared for the first time in a 5-year-old child, and before that he spoke normally. They differ for reasons.
Congenital Causes of congenital stuttering in children:
Difficult pregnancy. If this stage is accompanied by fetal hypoxia - when it lacks oxygen, then this can affect the formation of its speech apparatus. Infectious diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy also have an impact. Birth injury. The formation of the articulatory apparatus can also be affected by hypoxia, but this does not arise in utero, but during a long, difficult birth. When you receive a birth injury, brain cells can be damaged. Early babies who are born prematurely often suffer. Heredity. Speech impairment is also inherited. And this is a fairly common reason. Features of temperament. Choleric children are more likely to stutter than melancholic or sanguine children. Their nervous excitability is much higher. If a little person spoke well until a certain age, and then suddenly began to stutter, this is a sign of an acquired disease.
Acquired Causes of acquired stuttering in children:
Experienced stress. This is the loss of a loved one, a sudden change of situation, severe fear. Psychosomatics also plays a role. Lack or excess of attention. Spoiled, capricious children often stutter. Increased demands from parents. Difficult home environment. Children from dysfunctional families often suffer, where there are often scandals, quarrels, and assault. Divorce of parents can also have an impact. Spending a long time at the computer or in front of the TV. This generally affects mental development. Diseases. Serious consequences include meningitis, encephalopathy, head injuries, influenza and other diseases. Pseudo-stuttering. This phenomenon occurs in families where one of the elders suffers from stuttering. Then the baby is able to adopt the manner of speaking from a loved one without suffering from any disorders. To determine what causes the speech disorder, you need to observe the child. Does the problem occur when you are nervous, in the presence of strangers, or in an unusual environment? Then, most likely, logoneurosis is acquired. If the child stutters consistently, in any environment, then the problem is congenital. However, only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the reasons.
BASIC METHODS OF TREATMENT AND CORRECTION What to do? How to treat the disease? Stuttering goes away without special treatment measures only in isolated cases.
Such a speech defect must be eliminated, and therapy should begin at the first signs of disruption in the child’s process of sound reproduction.
Speech therapy classes, breathing exercises, some types of special massage and computer programs will help correct the situation. In most cases, therapy involves the mandatory use of medications to normalize the functioning of damaged parts of the brain.
Speech therapy classes A set of speech therapy exercises is developed for each child individually. First, a comprehensive examination of the baby is carried out, the causes of the disease are determined, and the degree of pathology is determined.
Only after studying the clinical picture of the disease, the speech therapist chooses classes, the regular implementation of which will speed up the process of normalizing the child’s speech.
Examples of speech therapy exercises:
“Funny carousels” (the child slowly walks in a circle, saying with the speech therapist the phrase “we are funny carousels, opa-opa-opa-pa-pa, tatati-tata-tata”). “Chickens” (the child jumps on one leg, repeating the phrases “clap-top-clap”, “oof-iv-av”, “tap-tip-rap-rop-chick-chick”). “Conductor” (the speech therapist portrays a conductor; when raising his hands, the child chants vowel sounds, and when mixing, consonants). Breathing exercises Breathing exercises are carried out with the child based on the technique developed by A.N. Strelnikova. You can stand or sit while performing the complex. Inhalations are always made sharply, and exhalations are smooth and slow.
Exercises can be combined with games to make it more interesting for the child to reproduce them.
Examples of exercises:
“Cat” (the child should squat several times with the body turned to the side; when straightening the body, exhale; when squatting, inhale). “Pump” (the child takes deep breaths and exhales, while the lips must be pulled out with a tube). “Ears” (the child should tilt his head, trying to reach his ear with his shoulder; when tilting, inhale; when in the starting position, exhale).
“Palms” (arms should be bent at the elbows so that the palms are directed downwards; when straightening your arms, you need to exhale slowly; in the starting position – a sharp inhale).
“Pendulum” (the body is tilted forward while exhaling, straightening the body while inhaling sharply).
Acupressure Acupressure for stuttering in children is aimed at influencing certain areas of the speech apparatus.
Smooth massaging movements should be applied to the corners of the lips, the area near the sinuses, earlobes, the bridge of the nose, the middle of the chin and the tip of the nose. During the massage, you can turn on relaxing music or recite calm poems.
Computer programs For the treatment of stuttering in children, special computer programs are especially popular. They are approved and used by many specialists.
The programs can also be used for home treatment of speech defects in children.
Their main goal is to reproduce the correct intonation of speech and influence the child’s speech apparatus by playing with a simulator.
Examples of computer programs:
Demosthenes; Speak gentle; Dr. Fluence.
MAIN STAGES OF TREATMENT Work with a speech therapist Classes with a specialist are held for a long time, at least 8 months. The speech therapist teaches the child to pronounce difficult sounds, speak smoothly and rhythmically, and breathe correctly. Logorhythmics are often used - special musical exercises for children with speech impediments. In one form or another, a game of “silence” is offered, when children must restrain their speech for several days, and then gradually begin to communicate in short phrases. Different specialists work using different methods, the choice is up to the parents.
Breathing exercises Incorrect breathing and a weak diaphragm are frequent accompaniments of speech spasms in children. A set of actions combining movement, inhalation and exhalation allows you to eliminate this drawback.
Starting position: standing with your arms down. You need to lean forward, rounding your back, lowering your head. At the end of the tilt, you need to take a noisy breath, then rise not all the way and exhale. Repeat the exercise several times. Starting position – standing, arms down, feet shoulder-width apart. You need to turn your head from side to side, inhale at the end point, and exhale while turning. Repeat the exercise. Hardware methods for treating stuttering There are many computer programs that allow you to correct the functioning of the auditory and speech centers. This is more relevant for older children who are able to accurately complete tasks.
The hardware techniques (Speech corrector, Demosthenes) are based on the patient pronouncing a phrase, which the computer slows down a little and outputs to the headphones. An attempt to adapt to the device leads to smoothness and rhythm of speech. As a result, seizures lose their neurotic component (complexes and embarrassment disappear), which has a positive effect on the course of the disease.
Drug treatment Treatment of this disease with drugs (tranquilizers, anticonvulsants) has a very narrow scope of application. It is possible only when stuttering occurs against the background of severe brain damage or a serious mental disorder. All other treatment options for speech cramps do not involve any medications.
The duration of treatment for stuttering can vary from several months to several years. It all depends on the severity of symptoms and personality type. If a speech therapist, parents and baby work together as a team, then the chances of complete healing are very high
But even with insufficient results, it is important to help the baby adapt so that he feels loved and complete, despite the defect
WHAT IS STUTTERING Stuttering is a violation of the communicative function of speech, accompanied by a violation of tempo, rhythm and smoothness, caused by convulsions of the articulatory apparatus. Stuttering is one of the most common childhood neuroses.
The delay in the pronunciation of sounds and syllables is associated with convulsions of the speech muscles: the muscles of the tongue, lips, and larynx. They are divided into tonic and clonic seizures.
Tonic convulsions are difficulty pronouncing consonant sounds.
Clonic seizures are when a child repeats sounds or syllables at the beginning of a word or pronounces extra vowels (i, a) before a word or phrase. Tonic-clonic stuttering also occurs.
The first symptoms of stuttering can be of a different nature - these can be repetitions of the first sounds, syllables and the inability to further pronounce words. The child seems to begin to sing the first syllable. For example - “Ta-ta-ta slippers.” Or the impossibility of starting a phrase - tonic convulsions.
Vocal spasms appear - prolongation of a vowel sound at the beginning or middle of a word. The first symptoms of stuttering occur during the development of phrase speech. This age ranges from 2 to 5 years
If you notice that a child has trouble breathing during speech, voice difficulties, he cannot start a phrase, if he starts repeating the first syllables of words or prolonging vowel sounds, then these are alarming symptoms and you need to pay attention to them
If you do not pay attention in time, then such speech behavior can turn into real stuttering, causing not only problems with speech, but also difficulties in the social sphere. In adults, the process is sharply disrupted and more facial muscles, neck muscles, and the upper shoulder girdle work
The social picture is not pretty. But this speech defect is not an irreversible disorder and in most cases it can be cured. The efforts made to combat stuttering have made some people famous. These people: Demosthenes, Napoleon, Winston Churchill, Marilyn Monroe.
Fortunately, stuttering begins in a small percentage of children. According to statistics, only 2.5% of children have this defect. City children stutter more often than children from rural areas.
There are more boys than girls among children who stutter. This is associated with the structure of the hemispheres. The hemispheres in women are organized in such a way that the left hemisphere works better than the right. Thanks to this, girls usually begin to speak earlier, and they more easily overcome those speech difficulties that are usually expected at 2.5 - 4 years.
When a child begins to speak in phrases, he experiences difficulties in selecting words and coordinating them in number, gender and case. Sometimes we see that at this phase the child talks excitedly, with carelessness, he has difficulty finding words, he is in a hurry. And then we hear such specific hesitations in the child that qualify as a tendency to stutter.
In a 2-3 year old child, it is worth distinguishing stuttering from non-convulsive stuttering. When hesitating, there are no convulsions of the articulatory apparatus - neither vocal nor respiratory. Hesitations are always of an emotional nature. They happen because at the age of 2 - 5 years the child’s speech capabilities do not keep up with his thoughts, and the child seems to choke. This is called physiological iterations or hesitations. A child with a stutter, when asked to speak better, will worsen his speech, and a child with hesitation, on the contrary, will improve it.
CAUSES OF THE DISEASE The main reason for the appearance of neurotic hesitations is the influence of a traumatic situation or prolonged distress.
In the case of a one-time destructive psycho-emotional event, the disease may go away after some time; more serious consequences (up to transient mutism) are expressed due to prolonged stay in an environment unfavorable for the psyche.
Is it possible to start stuttering from fear? Examples of psychogenic causes of stuttering in children and adults:
stress, extreme fear, or extreme anger; excessive load when teaching spoken language; violation of family roles and family functionality in children; imitating the conversation of a stuttering relative or friend; loss of a loved one; love problems. Pathogenesis and development mechanisms The origin and formation of logoneurosis in modern medicine has not yet been sufficiently studied.
Presumably, when exposed to acute stressful situations, neurotic hesitations develop through the appearance of a stable pathology of conditioned reflex functions. And the final consolidation of the disease is the formation of motor automatism.
It can be assumed that at the age of 2 to 4 years, stuttering is influenced by the pathological consolidation of natural speech hesitations, characteristic of this age period of the formation of speech functions (so-called functional stuttering).
Statistics show that stuttering often begins to appear in the early stages among children aged 3-5 years. Complications of symptoms and accompanying neurotic reactions can be observed mainly among adolescents, in the period 15-17 years.
The complication process is associated with rapid age-related changes in the human body. Logophobia (fear of speech) is formed precisely during puberty, subdepressive mood changes also appear, and various kinds of asthenic and somato-vegetative disorders arise.