Stuttering
Includes several directions. The most typical are distraction, suggestion and relaxation. People who stutter are taught to speak simultaneously with rhythmic movements of the hand and fingers or in a slow, sing-song voice. The effect is often temporary.
Classical psychoanalysis and psychotherapeutic methods are not effective in treating stuttering. Modern methods are based on the view that stuttering is a form of learned behavior not associated with neurotic manifestations or neurological pathology. Within the framework of these approaches, it is recommended to minimize factors that increase stuttering, reduce secondary disorders, and convince a stutterer to speak, even with a stutter, freely, without embarrassment and fear, in order to avoid secondary blocks.
An effective self-therapy method is based on the premise that stuttering is a specific behavior that can be changed. This approach includes desensitization, which reduces emotional reactions and fear of stuttering. Because stuttering is something a person does, and a person can learn to change what they do.
Drug treatment is auxiliary in nature and is aimed at relieving symptoms of anxiety, severe fear, depressive symptoms, and facilitating communication interactions. Calming, sedative, and general restoratives are applicable (valerian, motherwort, aloe, multivitamins and B vitamins, magnesium preparations). In the presence of spastic forms, antispasmodics are used: mydocalm, sirdalud, myelostan, diafen, amizil, theophedrine. Tranquilizers are used with caution; Mebicar 450-900 mg/day is recommended, in short courses. Dehydration courses have a significant effect.
Alternative drug treatment options:
- 1) For clonic stuttering, Pantogam is used from 0.25 to 0.75 - 3 g/day, courses lasting 1-4 months.
- 2) Carbamazepines (mainly Tegretol, Timonil or Finlepsin-Reterd) with 0.1 g/day. up to 0.4, g/day. for 3-4 weeks, with a gradual reduction in dose to 0.1 g/day. as maintenance treatment, lasting up to 1.5 - 2 months.
Comprehensive treatment of stuttering also includes physiotherapeutic procedures, courses of general and specialized speech therapy massage, speech therapy, and psychotherapy using the suggestive method.
Examination of children who stutter
Stuttering in children is a form of speech pathology, the basis of which is a violation of verbal communication. To adequately plan a program of speech therapy and treatment work with children who stutter, it is necessary to comprehensively examine them, taking into account all the symptoms of this complex speech disorder. The examination of a child who stutters consists of two stages.
The first stage includes the study of anamnestic data, medical and psychological-pedagogical documentation.
The various negative factors of the natal and postnatal periods of the child’s development identified during the study of the anamnesis are analyzed and assessed by specialists in order to most fully study the etiology and pathogenesis of stuttering. Along with traditional data, the anamnesis includes information about the presence of stuttering in parents or other close relatives.
The study of psychological and pedagogical documentation complements the anamnestic data and allows us to identify the following features of upbringing and psychological manifestations in a child who stutters:
- the attitude of adults towards him;
— assistance in the formation of correct speech;
- time of stuttering onset, its first external signs;
— features of the manifestation of stuttering depending on the situation;
- the child’s attitude towards his speech impairment;
— whether help was provided to a child who stutters, what was recommended and what were the results.
The second stage is the study of the stuttering child himself.
After clarifying information about the child, the history of the occurrence and characteristics of his stuttering, the actual speech of the stutterer and extra-speech processes that have a direct impact on his speech activity are examined.
A study is conducted of sociability, motor skills, imitation, impressive and expressive speech, gaming, educational activities, and personality traits of a stutterer. There are primary (during the first month of a child’s stay in a speech preschool institution, in the first two weeks of stay in a sanatorium for children who stutter, at a school speech therapy center) and dynamic study of a stutterer in the process of correctional and educational intervention.
The materials for studying children's actual speech are pictures, children's books, and toys.
The objectives of a speech examination of a person who stutters are to determine:
— place of occurrence and form of speech spasms;
- the frequency of their manifestations and the preserved speech capabilities of the stutterer;
— concomitant speech disorders, motor disorders;
— the attitude of a stutterer to his speech defect, the presence of psychological characteristics.
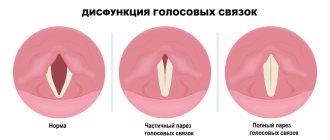
The place of occurrence of convulsions (respiratory, vocal, articulatory, mixed) and their form (clonic, tonic, mixed) are determined aurally or visually.
The frequency of seizures is of particular interest to the speech therapist, as it allows us to judge the intact areas of speech. The study of the level of free speech begins with identifying the dependence of the frequency of seizures on different degrees of independence of speech.
In order to study speech behavior and speech spasms, the following techniques are used:
- writing a story or describing the content of a picture;
- retelling the listened text;
- conjugate and reflected repetition of simple and complex phrases;
- a story of poetry or rhythmic prose.
To determine the dependence of speech spasms on the level of speech volume, the subject is asked to speak quietly, loudly, or in a whisper.
When examining a child who stutters, it is necessary to pay attention to concomitant speech and motor disorders. When studying children's play activities, the nature of games, relationships with peers, the degree of play activity, and emotional state are clarified.
During the entire examination, the psychological characteristics of a stuttering child are noted: the nature of contact with others, assessment of one’s own speech, in particular painful fixation on a speech defect, the presence of defensive reactions, speech behavior during the examination.
The information obtained during the examination is summarized in a speech therapy report, which takes into account:
- form of seizures (tonic, clonic, mixed);
— type of convulsions (respiratory, vocal, articulatory, mixed);
- degree of stuttering (mild, moderate, severe);
- rate of speech (slow, accelerated, presence of tachylalia);
— concomitant speech disorders (dyslalia, erased form of dysarthria, general speech underdevelopment);
— state of motor function;
— the presence and severity of mental symptoms of stuttering: fear of speech (logophobia), motor and speech tricks, embolophrasia, reaction to an emotionally significant situation.
The influence of the complexity of the speech situation, the individual psychological characteristics of a stuttering child, the nature of play activity, and attitude to learning are also noted.
A speech therapy report makes it possible to carry out a differential diagnosis and distinguish stuttering from other speech disorders (tachylalia, dysarthria, stumbling of a physiological nature), as well as distinguish between different forms of stuttering. Data from a comprehensive study of a stuttering child make it possible to establish the nature of stuttering.
Control questions
1. What is the purpose of a speech therapy examination?
2. What sections make up the content of a speech therapy examination?
3. What is the peculiarity of the examination of coherent speech?
4. What characteristic errors of coherent speech are observed with speech underdevelopment?
5. By what principle is lexical material selected for vocabulary examination?
6. How is the uniqueness of vocabulary expressed in speech underdevelopment?
7. What techniques are used to study the grammatical structure of speech?
8. What types of agrammatism are observed with underdevelopment of speech?
9. What is the peculiarity of examining the sound side of the language?
10. What parameters are taken into account when writing a speech therapy report?
11. What is the peculiarity of studying medical and psychological-pedagogical documentation when examining a child who stutters?
12. What are the objectives of a speech examination of a person who stutters?
13. What techniques are used to study the speech of people who stutter?
14. What characteristics are taken into account when writing a speech therapy report for a child who stutters?
Literature
Main
Volkova G. A.
Psychological and speech therapy study of children with speech disorders. - St. Petersburg, 1993.
Methods for examining speech in children / Ed. I. G. Vlasenko and G. V. Chirkina / Comp. T. P. Bessonova. - M., 1996.
Filsheva T. B., Cheveleva I. A.
Speech therapy work in a specialized kindergarten. - M., 1987.
Additional
Filteva T.E., Chirkina G.V.
Preparing children with general speech underdevelopment for school in a specialized kindergarten. - M., 1993.
Belyakova L.I., Dyakova E.A.
Stuttering: A textbook for pedagogical institutes. - M., 1998.
Speech therapy: Textbook for universities / Ed. L. S. Volkova and S. N. Shakhovskaya. - M., 1998.
Treatment of logoneurosis
Today, an integrated approach is most often used. The first step you need to start with is visiting a neurologist. The doctor will analyze the specific picture, assess the child’s condition and select treatment tactics. The examination of children with stuttering includes collecting information about the family’s lifestyle and the situation in which stuttering first appeared. The doctor will also assess the child’s general condition and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The treatment regimen for logoneurosis in children may include taking medications (for example, sedatives, nootropics), sessions with a psychologist, and logotherapy. The most important point is the elimination of stress, the formation and consolidation of non-convulsive speech skills.
Homeopathy performs an auxiliary function in complex treatment. The advantage of homeopathic remedies is that they are selected strictly taking into account the needs of a particular child.
Parents can provide invaluable assistance to a child in dealing with the problem. Even if your son or daughter sees the doctor regularly, home exercises are important. Be sure to follow your doctor's recommendations. For example, he may recommend daily performance of a set of special speech exercises. Singing lessons help some children get rid of stuttering - discuss this option with your doctor.
If you are looking for a clinic to treat your child's stuttering, look no further than Iris Medical Center. We have experienced neurologists who will help your baby achieve beautiful, fluent speech.