4.6
Average rating: 4.6
Total ratings received: 728.
4.6
Average rating: 4.6
Total ratings received: 728.
The branch of the science of language, called stylistics, studies functional styles of speech. What it is and how they differ, we will tell you in this article.
The material was prepared jointly with the highest category teacher Lyubov Alexandrovna Koroshchup.
Experience as a teacher of Russian language and literature - 30 years.
Introduction
The stylistic organization of speech is a system of linguistic elements within a literary language, characterized by the conditions and tasks of communication; the form of our statements depends on where, with whom and why we are talking.
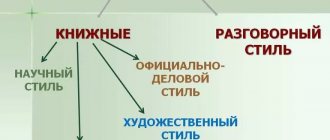
There are five styles: four book styles: scientific, business, journalistic, fiction and colloquial. Each style is characterized by certain linguistic means: Words, their forms, combinations of words, types of sentences, their belonging to a conversational or book style are realized in comparison with neutral means.
Language styles are implemented in certain forms or types of text, the so-called language genres. Language genres are a typified form of speech organization that defines types of texts that are distinguished by a certain nature of speech activity and the form of speech use. In principle, each genre of language belongs to a certain style of language, but there are also overlapping genres, such as: article, essay, essay.
general characteristics
Functional speech styles are a type of literary language in which some task is realized. Hence the name. Most scientists prefer to divide them into five types:
- colloquial;
- journalistic;
- official business;
- scientific;
- art.
Each style reflects linguistic flexibility with expression and diversity of thought. Through language:
- the law is written;
- a concept is given;
- a table is compiled;
- a scientific fact is stated;
- a poem is composed and so on.
Thus, semantic functions of an aesthetic, business and scientific nature are performed. Phrases and individual words are selected from the language; designs that better suit their exterior style.
There are semantic contexts. Conversational style is characterized by discussion of everyday or everyday topics. Journalism touches on topics of politics and public opinion, and the system of official business speech is used in diplomatic activities and lawmaking.
Different language styles
Scientific style is one of the book styles used in scientific papers, textbooks and teaching aids, and oral presentations on scientific topics.
The purpose of the scientific style is to provide scientific information and explain it by presenting a system of scientific argumentation. Used in an official environment, it is characterized by logic, objectivity, and semantic accuracy.
In the scientific style, the following options can be distinguished:
- current scientific style (inherent in scientific works - monographs, dissertations, articles in scientific journals, books, encyclopedias, scientific reports)
- popular science style (inherent in texts intended to popularize scientific knowledge, i.e. popular science literature, articles in non-specialized magazines, newspapers, speeches on radio and television, public lectures for a mass audience)
- scientific and pedagogical style (used in textbooks, teaching aids, reference books for students).
The scientific style is characterized by the use of the following language tools:
at the vocabulary level:
- Saturation with the concepts of this science;
- Using words with abstract meaning: law, number, limit, property; verbal nouns with the meaning of action: processing, planting, using;
- Use of words in direct meanings, lack of imagery (metaphors, metonyms, hacking, exclamation marks);
at the morphological level:
- rare use of personal pronouns “I” and “you”, as well as verbs in the 1st and 2nd singular forms.
- special methods of authorization: “we” of the author, indefinitely distinct (you mean that ...) and impersonal constructions (it is known that ...; it seems that it is necessary ...).
- the use of participles and separate parts and turns with them;
at the syntactic level:
- use of complex sentences with compounds indicating connection;
- no exclamation marks, little use of question marks;
- frequent quotes, links;
- use formulas, diagrams, diagrams as components of the text.
The main types of speech are argumentation and description.
Main genres: textbook, article, report, dissertation, scientific monograph, encyclopedic article, patent application, abstract, review.
As an example, we can cite an excerpt from a linguistic work written in the scientific style of its own scientific orientation - a monograph on linguistics:
“Rule 3 (optional coloring of presumptions). If a component with a potential hypothesis P is the syntactic act of a fresh predicate, then there are two possibilities: a) P is a hypothesis in the relevant world that can be converted into a hypothesis in the real world (or at least into a proposition that is true in the real world). world) with a corresponding change in content - modal “coloring” (the term “coloring” is according to Schiebe 1979); b) P remains a hypothesis in the real world. The difference between the terms a) and b) has no regular semantic expression.
This section reflects the following characteristics of the scientific style:
- linguistic terms: opportunistic, syntactic, actor, predicate, modal, semantic;
- Symbol P (assumption) as a text component;
- Words with an abstract semantic component, possibility, judgment, change, understanding, expression;
- Absence of words in a figurative sense: The word "coloring" is used as a term, enclosed in quotation marks and having an appropriate reference;
- Words indicating objective criteria for assessing a situation: potential, actual, true, regular;
- Absence of appeals, hacking, modal particles, question and exclamation marks and other visual aids;
- a complex set with a conditional subordinate conjunction if... ...which then indicates a cause-and-effect relationship;
- To make the text more understandable, divide it into a) and b).
- reference to another work of scientific literature, a full description of which is included in the bibliography: Schiebe 1979.
Functional speech styles. general characteristics
Stylistics (the word “style” comes from the name of the needle or stiletto with which the ancient Greeks wrote on waxed tablets) is a branch of the science of language that studies the styles of literary language (functional styles of speech), the patterns of language functioning in different spheres of use, the peculiarities of the use of linguistic means depending on the situation, content and purpose of the statement, the sphere and condition of communication. Stylistics introduces the stylistic system of the literary language at all its levels and the stylistic organization of correct (in compliance with the norms of the literary language), accurate, logical and expressive speech.
Stylistics teaches the conscious and purposeful use of the laws of language and the use of linguistic means in speech.
There are two directions in linguistic stylistics: stylistics of language and stylistics of speech (functional stylistics). Language stylistics examines the stylistic structure of language, describes the stylistic means of vocabulary, phraseology and grammar.
Functional stylistics studies, first of all, different types of speech, their dependence on different purposes of utterance. M. N. Kozhina gives the following definition: “Functional stylistics is a linguistic science that studies the features and patterns of language functioning in various types of speech corresponding to certain spheres of human activity and communication, as well as the speech structure of the resulting functional styles and “norms.” “selection and combination of linguistic means.”
At its core, stylistics must be consistently functional. It should reveal the connection between different types of speech with the topic, the purpose of the statement, with the conditions of communication, the addressee of the speech, and the attitude of the author to the subject of speech. The most important category of stylistics is functional styles —varieties of literary speech (literary language) serving various aspects of social life. Styles are different ways of using language when communicating.
Each style of speech is characterized by the originality of the selection of linguistic means and their unique combination with each other.
Thus, five styles of the Russian literary language are distinguished:
- conversational;
- official business;
— scientific;
- journalistic;
- artistic.
Conversational speech serves for direct communication, when we share our thoughts or feelings with others, exchange information on everyday issues. It often uses colloquial and colloquial vocabulary. The conversational style is characterized by emotionality, imagery, concreteness, and simplicity of speech.
In colloquial speech, the emotionality of a statement, unlike artistic speech, is not the result of creative work or artistic mastery. She is a living reaction to events, to the actions of people around her.
Unforced communication leads to greater freedom in the choice of emotional words and expressions: colloquial words (stupid, rotozey, talking shop, giggle, cackle), colloquial words (neighing, rokhlya, ahovy, klutz), slang words (ancestors - parents) are more widely used.
In colloquial speech, words with evaluation suffixes, especially diminutives, are often used: candle, candle (neutral candle), window, window (neutral window), etc.
The conversational style is characterized by simple sentences, a dialogical form of speech, and addresses. The content of colloquial speech heard during direct communication is supplemented by the context of the speech. Therefore, the conversational style is characterized by incomplete sentences: they express only that which supplements the interlocutor’s remarks with new information that develops the topic of speech.
Example of colloquial speech: A month before leaving Moscow, we ran out of money - it was dad who was preparing for fishing... And then the fishing began. The father sat down on the shore, laid out all his belongings, lowered the fishpond into the water, threw out the fishing rods - there were no fish.
Scientific style is the style of scientific communication. Its genres are scientific articles and educational literature.
The scientific style of speech is characterized by the use of terms and abstract words; emotional vocabulary of a colloquial nature, phraseological units, etc. are completely excluded; widespread use of verbal nouns, participles and gerunds, the predominance of the genitive and nominative case of the name, verbal forms of the present tense of the 3rd person, etc.; the use of complex sentences, including multi-component ones, etc.
The main purpose of a scientific text is to describe phenomena, objects, name them and explain them. Common features of scientific style vocabulary are: the use of words in their literal meaning; lack of figurative means (epithets, metaphors, artistic comparisons, hyperboles, etc.)? extensive use of abstract vocabulary and terms. For example: The most important economic and biological characteristics of varieties are: resistance to growing conditions (climate, soil, pests and diseases), durability, transportability and shelf life. (G. Fetisov)
The official business style is used for communication and information in an official setting (the sphere of legislation, office work, administrative and legal activities). Within the framework of this style, various documents are drawn up: laws, orders, regulations, characteristics, protocols, receipts, certificates.
In an official business style there is no room for the manifestation of the author's individuality, therefore its main stylistic feature is formality and precision. Business style is characterized by special vocabulary (decree, protocol, resolution, etc.) and stable combinations (make a decision, consider invalid, should be indicated, should be kept in mind, etc.).
An example of a formal business style of speech:
SYSTEM MENU
The system menu is called up by the button located in the upper left corner of the window. The commands in this menu are standardized for all applications in the Windows environment. The system menu is available in each document window. It can be called even if the window is minimized to an icon by clicking on the icon once with the mouse button. There is also a way to open the system menu using the keyboard - using the [Alt-space] key combination.
System menu commands are selected using the mouse, cursor keys, or by entering the underlined letters in the command name along with [Alt]. (V. Pasko)
Journalistic style is the style of newspapers, magazines, literary critical books and articles, speeches on socio-political topics in any audience in direct contact with the addressees of the speech, as well as speeches on radio, television, etc.
The main task is to influence the listener or reader in order to motivate him (them) to action, reflection, etc. The main topics are socio-political, moral and ethical problems.
Speeches on socio-political topics contain a lot of specific vocabulary and phraseological units: society, debate, parliament, tough measures, social explosion, stand on guard, etc.
In order to influence the listener or reader, journalism widely uses words and expressions that have a positive evaluative connotation (valiant, wonderful, etc.) and a negative evaluative connotation (deceitful philanthropy, thugs, yellow press, etc.).
The journalistic style is freer in the choice of linguistic means than the scientific and business style. Proverbs, catchphrases, phraseological units, artistic and visual means (comparisons, metaphors, etc.), colloquial vocabulary are appropriate in journalism; Interrogative (often rhetorical questions) and exclamatory sentences, appeals and other techniques are widely used.
An example of a journalistic style of speech:
Needless to say, Russia is rich in natural resources and mineral reserves - everyone knows about it. But its real wealth is people, their intelligence, knowledge and experience. Outside Russia they have long understood what the truly inexhaustible source of our wealth is. Many young scientists are still trying to go to the West. And the reason for this is not always money. Laboratories often lack the necessary equipment and working conditions. How to fix the situation? First of all, you need to learn how to correctly evaluate knowledge - as they do in all developed countries (according to V. A. Makarov)
Artistic speech is the speech of fiction (prose and poetry). Artistic speech, influencing the imagination and feelings of readers, conveys the thoughts and feelings of the author, uses all the wealth of vocabulary, the possibilities of different styles, and is characterized by imagery and emotionality.
The emotionality of artistic speech differs significantly from the emotionality of colloquial and journalistic styles, primarily in that it performs an aesthetic function.
Elements of other styles easily penetrate into artistic speech if they are necessary to achieve certain goals and objectives, therefore it is distinguished by its diversity and stylistic multicolor. Thus, to recreate a historical era, writers use historicisms (or archaisms), to describe the life of people in a particular area - dialectisms, etc.
An example of artistic speech:
“Everything you meet on Nevsky Prospekt is full of decency: men in long frock coats, with their hands in their pockets, ladies in hats. Here you will find the only sideburns, worn with extraordinary and amazing art under a tie, sideburns velvet, satin, black, like sable or coal, but, alas, belonging only to one foreign board...
Here you will meet a wonderful mustache, impossible to depict with any pen or brush; a mustache, to which the better half of life is dedicated, is the subject of long vigils during the day and night, a mustache on which the most delicious perfumes and aromas are poured out... Thousands of varieties of hats, dresses, scarves - colorful, light, ... - will dazzle anyone on Nevsky Prospect. (N. Gogol)
Formal business style
Official business style is one of the book styles used in business relations, business papers, i.e. in laws, documents, acts, contracts, regulations, charters, official correspondence, etc.
The purpose of this style is to provide information and instructions. Officially, business style is characterized by accuracy, unambiguity, impersonality, standardization of text structure, and the mandatory nature of the text.
Official business style is characterized by the use of the following language tools:
at the vocabulary level:
- use of full names, exact dates;
- Book dictionary (due to, during, due to characteristics);
- use of words with direct meaning;
- Insufficient expressiveness and evaluative vocabulary;
- frequent use of verbal nouns (statement, use, performance);
- the presence of standardized transactions (come into force after expiration in the prescribed manner);
- limited possibilities of synonymous substitution, frequent lexical repetition;
- morphological
- The absence of personal pronouns, in particular 1st and 2nd persons, in the place of which proper names, surnames or special designations are used (manager, performer), as well as verbs in the form of 1st and 2nd persons;
at the syntactic level:
- complicating a simple sentence with isolated phrases, homogeneous members
- clear division of text into semantic blocks, usually using subheadings and digital paragraph layout
- The official business style is characterized by monologue methods of speech formation, as well as dialogue (a conversation between two people) or polylogue (a conversation between several people).
- Main genres: monologue - order, instruction, statement, statement, request, complaint (claim), recommendation, report, review; genres - polylogistics - assembly, meeting, negotiations, interviews.
As an example, here is an excerpt from a standard contract.
Anna Ruzheva, a citizen of the Russian Federation, hereinafter referred to as the “Author”, on the one hand, and, hereinafter referred to as the “Company”, represented by its General Director Sergei Ivanovich Bozin, acting on the basis of the Charter, on the other hand, have concluded this Agreement as follows .
Official or business
The official style of speech is used in managerial, administrative, legal and diplomatic spheres of human activity. It is used in documents and contracts, legislative regulations, business and some specific genres of literature, such as autobiography. There are 5 main substyles:
- legislative;
- business correspondence;
- clerical;
- diplomatic.
The style differs from others in that its features and rules of application are enshrined in official manuals and GOSTs for the purpose of standardization and unification. Therefore, it develops slowly and is little subject to change, regardless of time, location, cultural and other characteristics of the population. Distinctive features of the style:
- standardization;
- language that leaves no room for ambiguity or misinterpretation;
- conciseness;
- a combination of neutral, bookish and special vocabulary, the use of professional terminology;
- use of official speech stamps;
- the presence of archaisms (outdated words), absence of slang and neologisms;
- unambiguity of information, confirmed by references to its sources (articles in codes, clauses of the contract, and so on);
- abundance of verbal nouns (application, confirmation) used to reduce volume;
- direct word order;
- sentences with complex grammatical construction, use of participial and participial phrases;
- a large number of enumerations, homogeneous members of the sentence;
- use of passive designs (accepts board instead of accepts board);
- speech without any expressiveness, emotional or figurative coloring;
- narrative nature of the presentation;
- abundance of details and clarifications.
In colloquial speech, business style is rarely used and under specific circumstances. It can be found in courts, at diplomatic negotiations, in communication between entrepreneurs and business partners. The rules of formal speech in oral communication are less strict than in written documents.
Definitions used in the contract
The work is “Russian language for students and freshmen”, created by the author. Description of the work - the manual contains the basic theoretical concepts of the school course of the Russian language and explains the procedure for analyzing language material addressed to students and especially graduates of secondary schools, due to the lack of a single set of textbooks in Russian for secondary schools.
This section reflects the following features of official business style:
- no personal pronouns;
- full names of the characters and their social status;
- Replace them later with special names such as author, company;
- Standardized Sales: This Agreement, hereinafter referred to as the “Agreement”, is based on the following
- exact indication of the place and time of conclusion of the contract;
- complication of a simple sentence of several isolated members;
- Dividing text into blocks using subheadings and numeric characters.
Scientific style
It is widely used. This style has a serious impact on the language. With progress, new terms are introduced into mass use, previously found only on the pages of specialized publications. Thanks to this, new genres are formed.
Scientific language protects itself from amateurish methods. He is intelligent and therefore logical. This is expressed in thinking through, presentation of information and sequence of transfer of material. Science is objective in nature, so the author has a minor role. The main thing is the material itself, research and their actual data.
Requirements also determine the use of language. Scientific vocabulary is characterized by:
- Common usage. Use of words used in scientific texts.
- General science. The immediate area that describes objects and events.
- Terminology. The closing, internal layer, which embodies the main differences that scientific language carries.
Journalistic style
Journalistic style is one of the book styles used in journalistic and literary criticism, in the media, at meetings and rallies.
The task of this style is to influence mass consciousness through socially significant information. The characteristic features of the journalistic style are logic, visual language, emotionality, evaluativeness, and attractiveness.
Journalistic style is characterized by the use of the following language tools:
at the vocabulary level:
- widespread use of socio-political, economic, general cultural vocabulary;
- Use of solemn vocabulary (dimensional, see, radiating, incomparable), often in combination with colloquial language;
- Use of pictographic means: epithets, comparisons, metaphors, phraseology and “catchphrases”;
- Emphasis on the author’s personal assessment of the situation;
- frequent language games, puns, parodies (especially in titles);
at the level of morphology and syntax:
- Active use of person 1 and 2 personal pronouns and corresponding verb forms
- Failure to utilize participating and non-private sales and replace them with applications;
- the use of persuasive and exclamatory sentences, rhetorical questions;
- use of appeals;
- frequent lexical and syntactic repetitions.
Main genres: public speech (speech, report), discussion, critical remark, report, interview, article, review, essay, sketch.
Artistic or literary
Artistic style is used in literature. Its task is not only to convey information, but also to create accurate visual and emotional images in the reader, to make him experience certain feelings. Divided into three substyles:
- poetic - poems, poems;
- prose - stories, novels, novellas, short stories, fables;
- dramatic - plays, dramas, comedies, tragedies, tragicomedies.
The artistic style is expressive. It is believed that it is in it that the beauty of language is most clearly revealed. Its main features:
- expressiveness;
- constant use of artistic techniques - metaphors, comparisons, allegories, epithets, contrasts;
- figurative phrases;
- aesthetic significance;
- use of the author’s individual style;
- playing with sentence length and pacing to create emotional effect;
- the use of syntax as a means of expression;
- deviations in sentence structure;
- the use of speech means from other styles to achieve an emotional impact on the reader;
- freedom, lack of strict text structure.
Artistic style can be used in descriptions, discussions and narratives. It is considered the freest, since it practically does not limit the writer. The quality of information delivery largely depends on his talent, experience, abilities and diligence.
Art style
The artistic style is used in works of art and refers to book speech.
The task of style is to paint a picture with words, express an attitude towards what is depicted, and influence the feelings and imagination of the reader. The peculiarity is the unity of communicative and aesthetic functions, high pictorial quality.
The artistic style is characterized by the following means of expression:
- Paths are phrases in which a word or phrase is used in a figurative sense: metaphor, metonymy, personification, simile, epithet, etc.;
- Phrases: Anaphora, antithesis, gradation, inversion, parallelism, rhetorical question;
- Rhythm, rhyme, mainly in poetry.
A broader concept is the language of fiction: the style of fiction is usually used in the speech of the author, and other styles, such as conversation, may also be used in the speech of characters.
As an example, let us give an excerpt from a poetic text - a poem by A. Blok:
- Autumn is late. The sky is open
- And the forests intersect in silence.
- Lying on the shore blurry.
- Mermaid head.
The following linguistic techniques characteristic of the artistic style are used:
- Rhythm, rhyme;
- Inversion - an adjective after a noun: late autumn, the sky is open, the shore is blurry, the mermaid is sick;
- Paths: open sky, silent forests, the mermaid's head lies on the shore;
- syntactic parallelism in the first line;
- so-called sentences that create a feeling of static and stillness.
Journalistic style
Journalism is sometimes called a chronicle or chronicle of modern life. It reflects the pressing issues of today. It is close to the artistic language, but at the same time different from it. This style is fact-oriented. And artistic speech is imaginary. The topics and vocabulary in the journalistic style are varied. Journalism invades life and contributes to the formation of public opinion. This style performs two important semantic functions:
- reporting;
- influencing.
Genres stand out among them:
- Reportage. The reader is given a general idea of the event that occurred.
- Feature article. The reproduced story contains the author's thoughts.
- Feuilleton. Reflects reality in a satirical light, ironically analyzes facts, actions, participants.
Conversational style
The conversational style is the opposite of the book style and is used in everyday conversations, often in informal contexts. The main form of existence is oral, but it can also be written (music notes, personal letters, recording the speech of characters, and sometimes the speech of the author in works of art).
The purpose of speech is to communicate and exchange impressions. Characteristic conversation styles are informal, relaxed, unprepared, emotional, with facial expressions and gestures.
Journalistic style is characterized by the use of the following language tools:
at the phonetic level:
- greater vocal reduction, compression of word pronunciation (now [shshs], hello [(z)dras't'i]);
- different intonation with a relatively free sequence of speech;
at the level of vocabulary and word formation:
- Use of colloquial language and vocabulary, jargon (workaholic, training, meticulous, gentle, soft, gentle);
- Preferential use of concrete vocabulary, little use of abstract, terminological words;
- Expressiveness and value in vocabulary and word formation (big, boo, big book);
- frequent use of phraseology;
at the morphological level:
- the most common of all styles is the use of personal pronouns
- the predominance of the use of verbs over the use of nouns;
- Rare use of participles and short adjectives, no use of individual parts;
- slope of complex numbers, slope of acronyms;
- use of particles, feuds;
- Frequent figurative use of morphological devices (for example, the use of tense and slants in meanings not typical for book style).
at the syntactic level:
- use of separate and incomplete sentences;
- Lack of complex syntactic structures;
- unification of a complex sentence;
- frequent use of persuasion, questions and exclamation marks;
- use of links.
As an example, here is a statement about one of the characters in Chekhov’s story “Revenge”: Open this damn door! How much longer do I have to walk in this? If you knew that your corridor is 20 degrees below zero, you wouldn't have made me wait so long! Or do you have no heart?
This small excerpt reflects the following features of the conversational style:
- Question mark and exclamation mark,
- Conversational style interaction, damn it
- Personal pronouns 1st and 2nd person, verbs in the same form.
Another example is an excerpt from a letter to N.N. Pushkin’s wife dated August 3, 1834.
"It's a shame, woman." You are angry with me, not knowing who is to blame, me or the post office, and you leave me for two weeks, knowing nothing about yourself or the children. I was so ashamed that I didn't know what to think. Your letter reassured me, but it was not consolation. The description of your trip to Kaluga, no matter how funny it may seem, is not funny to me at all. What kind of chase is this that drags you into an evil provincial town to see evil actors playing a wicked old wicked opera? <…> I asked you not to drive around Kaluga, yes, I see that you are so natural.”
The following linguistic features of conversational style appeared in this passage:
- Use of colloquial and simple vocabulary: Wife, drag, evil, ride around, what is for hunting, union yes in the sense of “but”, there is no particle at all, the introductory word should be visible,
- a word with the suffix of the rating word “city”,
- Reversing word order in some sentences,
- lexical repetition of the word “bad”,
- treatment,
- there is a dubious phrase,
- Use of personal pronouns 1 and 2 singular,
- using verbs in the present tense,
- the use of the word Kaluga (travel around Kaluga), which does not appear in the language, to refer to all small provincial towns.
Journalistic texts
The task of this functional style of literary language is not only to convey information to the reader or listener, but also to have a certain psychological impact on him and to arouse public interest . It is divided into five substyles:
- newspaper and journalistic - informational articles, notes and reports, interviews;
- propaganda - leaflets, posters, appeals;
- political-ideological - official substyle used in party resolutions;
- mass political - used at rallies, public speeches and other public events of a similar nature.
In the classification table, the journalistic style occupies an intermediate place between official and artistic everyday styles. From the former he adopted standardization and rigor, from the latter - expressiveness and emotionality. Other features of this style:
- information saturation;
- simplicity and accessibility of presentation, targeting the general public;
- elements of appeal, declarativeness;
- a combination of imagery and brevity in the expression of thoughts;
- constant use of emotional amplifiers;
- commitment to a certain position or idea, value judgments;
- motivational words and phrases;
- the presence of speech cliches characteristic of business and newspaper language;
- use of socio-political terminology, including labels (pseudo-democrats, fascists);
- first person presentation;
- addressing the reader directly;
- use of rhetorical questions and exclamatory sentences;
- reverse order of parts of speech in sentences;
- minimal use of negative words;
- an attempt to play on the reader’s feelings, an attempt to hurt his emotions.
When writing a journalistic text, it is important to interact with the reader and motivate him to action. Therefore, all information posted must be understandable and accessible to a wide audience.
Choosing the right speaking style is important to convey information completely and accurately to readers. The use of syntactic and morphological structures, intonation, speech stamps, artistic means and other language tools is necessary to fulfill the main task of the text.
Bibliography
- Greek V.F. and others. Handbook for Russian language lessons. Moscow, Education, 1968 - 201 p.
- Kostomarov V.G. Russian language on a newspaper page. Moscow, 1971 — 291 p.
- Russian language and culture of speech: Textbook / ed. prof. IN AND. Maksimov. -Moscow: Gardariks, 2003. -413 p.
- Russian language and culture of speech: Textbook for universities / A.I. Dunaev, M.Ya. Kozhevnikov et al., eds. V.D. Chernyak. - M.: Vysh. Shk.; St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after A.I. Herzen, 2003 - 509 p.