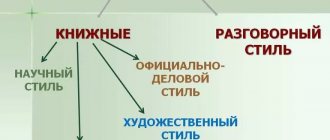
Informal communication in an informal setting is the most common description of this functional style. Examples of conversational style texts contain colloquial vocabulary, and the information in them is presented mainly on everyday issues.
The oral version of the style is used in everyday speech. That is why writing is often implemented in dialogues.
This article gives the corresponding definition, talks about the features, and also examines examples of texts in a colloquial style of speech.
Peculiarities
The style in which each of us expresses our thoughts, emotions and feelings is conversational. It is characterized by the absence of language selection. This is due to the fact that most people “speak first and think later.”
At the same time, the conversational style always contains shades of the speaker’s personality - it allows for slang, jargon, and other things that are not inherent in such strict styles as business or scientific.
An example of a conversational style of speech, small text:
-Have you tried it? — I pointed at the cheese. — Dad said it was delicious. “Of course it’s delicious, since he devoured it yesterday on both cheeks!” “But now you don’t act like you’re having lunch for the last time,” I laughed.
It clearly highlights slang expressions that are not applicable anywhere else than in everyday dialogue.
It should be taken into account that the conversational style is largely influenced by extra-linguistic factors: facial expressions and gestures, as well as the surrounding environment, etc. are of significant importance.
Signs of conversational style:
- simplicity;
- specifics;
- saturation with emotions, sometimes excessively, expression;
- imagery.
Examples of conversational style texts can be obtained by simply recording an everyday conversation, for example, between neighbors or a buyer and seller in a bakery.
Scientific style
What features are inherent in the scientific style? It is the language of encyclopedias, textbooks, dissertations, monographs and scientific articles. As O. Stycheva, candidate of pedagogical sciences, notes, the scientific style is easy to recognize by the following features:
- professional terminology;
- evidence - the presence of facts, figures;
- strict adherence to spelling or pronunciation standards;
- objectivity and completeness of information.
There is no room for the author's subjective opinion here. The purpose of the text, presented in a scientific style, is to prove the truths revealed through research.
By the way, O. Stycheva’s article also serves as an example of such a text:
A characteristic feature of the style of scientific works is their saturation with terms, including international ones. L.V. Shcherba wrote that on average, terminological vocabulary in scientific information is about 25%, however, the collections of scientific works we analyzed indicate that, in general, the scientific style of Russian speech tends to increase this percentage
.
A. P. Chekhov, “Revenge”
The features of the style under consideration are well illustrated by Anton Pavlovich Chekhov in his work “Revenge” - this is a clear example of a conversational style of speech. A small text of a monologue can already say a lot on this topic.
The character in the story begins to speak expressively: “Open it, damn it!” Please note that no other style allows swearing. His next sentence is no less revealing: “How long will I have to freeze in this through wind?” Its construction is abrupt, the manner of conveying information is simple and unpretentious. This is a conversational style of speech. It was not for nothing that examples of texts from literature began with Chekhov’s “Revenge”.
Literary and colloquial speech
Conversational speech in its primordial manifestation is oral. In works of art, it requires special means of imitation. The author himself may write in a speech close to conversational, but more often he uses it in conversations between characters. Thus, each hero acquires individuality.
A short text of a colloquial style of speech (examples from Bulgakov’s “Heart of a Dog”): “Indecent apartment. But how good. Why the hell did he need me? Will he really let him live? What an eccentric. But if he only blinked an eye, he would have such a dog that he would gasp.”
We have fully considered the colloquial style of speech and examples of texts. The 5th grade of the school curriculum involves the study of functional styles of speech, but conversational is the style that is encountered constantly, every day, both in works of art and in the environment (primarily in it).
In order to display the colloquial style of speech, examples of texts from literature have already been given above. Simply demonstrative sentences were placed equally with them.
Letter from A. S. Pushkin to his wife
The letter that Alexander Sergeevich wrote on August 3, 1834 to his wife, Natalya, is also a short text of a colloquial style of speech (examples are divided into sentences for consideration in greater detail).
The famous poet begins it with these words: “It’s a shame, wife.” This address is clearly colloquial vocabulary that is used in everyday life. Sentences: “What kind of desire is there to drag yourself to a nasty provincial town to see bad actors playing a bad old opera badly?” and: “I asked you not to drive around Kaluga, yes, apparently, you have such a nature,” - contain all the elements of a conversational style of speech, such as:
- evaluative derivational suffixes (gorodishko);
- inversion of word order in sentences;
- the use of a plural form for a word that, in fact, according to the rules of the Russian language, does not contain it (Kaluga - according to Kaluga);
- most verbs are used in the present tense.
Journalistic style
What are speech styles? These are its functional varieties that are used in one or another area of life:
- journalistic - media style;
- artistic - literature;
- business style is the language of documentation;
- colloquial is used in everyday life;
- scientific - in professional literature.
The scope of application is not the only thing that distinguishes the five existing styles from each other.
How to determine speech styles? Evaluate the text based on several criteria:
- his goal is what idea he wants to convey;
- vocabulary and genre;
- form - oral or written.
Lexical means
The conversational style of speech (short text examples will be discussed later in the article) uses the following lexical means:
- phraseological units;
- diminutive suffixes;
- expressive-emotional coloring of vocabulary;
- words-contractions and truncations;
- suffixes of subjective evaluation.
Standard designs and typed forms
In everyday life, spontaneous, unprepared speech prevails - people are used to expressing themselves without caring about word forms and without thinking about them. Therefore, it is not uncommon, and even frequent, to hear standard constructions, certain stereotypes for each specific daily situation. If we consider a short text of a colloquial style of speech, examples from the store will be as follows: “Three hundred grams of cookies... Weigh it by ten. Please give me a package of butter.” From public transport: “Are you leaving at the next one? To the Airship stop, where should I get off? Will you take me to Tractors?”
Forms of etiquette are also required. After all, if the speech is unprepared and less formal, this does not mean that it is rude and extremely impolite.
“Hello, good afternoon, how are you, what’s new,” these are still well-established constructions that do not lose relevance in conversations. An example of a conversational style of speech - a small text-dialogue between comrades who have just met - will contain these expressions in 99% of cases.
Individuality
For the same reason of spontaneity described in the previous paragraph, speech acquires individuality and originality. Thus, even there are countless stereotypical forms and designs, and at different times one or another comes into fashion in certain circles or, on the contrary, goes out of it, becomes obsolete, and then, however, sometimes returns. But the informal setting of communication does not set formal boundaries - people can use or not use familiar and established expressions as they choose. Untyped means are what convey the nature of the speaker’s speech.
Phonetics
The linguistic means that are used at the phonetic level of the language in a conversational style include two main features:
- Simplification, truncation, compression, that is, an incomplete type of pronunciation. This is not a necessary property that a conversational style of speech can have. Examples of texts (5th grade, by the way, in some regions study this book as part of the school curriculum) are “Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone,” “Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets” and the rest of this series. The vernacular trait is clearly expressed in the character Hagrid. Quote from “...Prisoner of Azkaban”: “The first thing he did this morning... was his resignation. I can’t, I say, put it at risk if... well, this happens again.” Unfortunately, Russian translators did not fully convey all the simplified word forms; this is more evident in the original text, but even in this quote one can already distinguish “grit,” which means “says.”
- Intonation is a purely individual feature that emotionally colors any, even stereotypical, construction. An example of a colloquial style of speech is a small text of the story “A Hypothetical Case” by the author O'Henry: “Will you be Mr. Phineas K. Gooch?” - said the visitor, and in the tone of his voice and intonation there was at once a question, a statement and a condemnation.
What makes your conversational style unique?
Another name for colloquialism. The word "conversational" comes from the Latin colloquium, meaning "conference" or "conversation".
As a literary device, colloquialism refers to the use of informal or everyday language in literature. All expressions tend to be geographical in nature, as colloquial expressions often refer to a regional or local dialect.
These can be words, phrases or aphorisms. Native speakers understand and use colloquial expressions without realizing it, while non-native speakers may find colloquial expressions difficult to translate. This is because many colloquial expressions are not literal uses of words, but idiomatic or metaphorical statements.
Colloquialism is similar to slang, but the definition of colloquialism has some key differences. The vocabulary of speech allows you to expand its standard potential.
Vocabulary and phraseology
Linguistic means related to the lexical and phraseological level:
- The percentage of speech is clearly dominated by neutral, specific, commonly used vocabulary, also called interstyle. It is the basis of the language. Neutral vocabulary states a fact and therefore has no emotional and/or expressive overtones. This makes it a universal option for use in any style: both colloquial speech and business, scientific, journalistic. Examples of texts of a colloquial style of speech in which there is neutral vocabulary (essentially, the author’s language of literary texts, except, perhaps, fairy tales and similar genres, for the most part only contains interstyle words) are “Chameleon” by Anton Pavlovich Chekhov and “Teddy » Yuri Pavlovich Kazakov.
- Neutral colloquial vocabulary. It includes words like “doctor’s wife”, “understand” and others.
- Terminology: socio-political and general scientific, nomenclature.
- Emotional-evaluative colloquial vocabulary. It can carry a negative or positive assessment. All words from it are divided into three groups, of which: 1) the assessment is included in the very meaning of the word; 2) in a figurative sense; 3) the word contains subjective evaluative suffixes. The epithet “expressive” is also applicable to this vocabulary.
- Standardized figurative means. These include metaphors, phraseological units, hyperboles and litotes. “We drink from the cup of existence with our eyes closed” (M. Yu. Lermontov). This is an artistic metaphor, while colloquial ones have a shade of the same vernacular. An example of a conversational style of speech, text-dialogue: “What is he? - And he, as usual, says, we’ll break through! “Who else would I be worried about, but this one will really break through.” - Otherwise! Cunning like a fox! He’ll fool anyone!”
- Professionalisms and jargons. It is worth considering that each example of a piece of spoken language in fact often contains most of the devices given here: it cannot illustrate only one property. Thus, the above dialogue, in addition to the metaphor “cunning as a fox,” also has the jargon “will deceive.”
Art style
How to distinguish an artistic style? Most often it is used in literary works. Its task is to create an artistic image, to evoke emotions and experiences in the reader.
The artistic style is characterized by:
- emotional speech, enhanced by literary devices - epithets, comparisons, metaphors, inversions;
- stylistically colored vocabulary;
- careful description of details;
- individual style of the author;
- direct speech;
- use of various tropes.
Additionally, artwork can incorporate elements from other styles (such as conversational or formal) to create more vivid images.
The imagery of this style is well demonstrated by an excerpt from the book “The Life of Arsenyev” by Ivan Bunin:
Silence and shine, the whiteness of roofs thick with snow, a low winter garden, drowned in snow, reddishly blackened by bare branches, visible from both sides behind the house, our treasured hundred-year-old spruce, raising its sharp black-green top into the blue bright sky from behind the roofs of the house, because of its steep slope, like a snowy mountain peak, between two calmly and high smoking chimneys...
Morphology
- The nominative case is most common.
- Personal and demonstrative pronouns predominate, as well as adverbs and particles.
- The participle is rarely used, the gerund is almost never used.
- The boundaries of temporary forms are blurred. This means that they are freely changed and used for purposes other than their intended meaning.
- There are verbal interjections.
An example of a conversational style is a small dialogue text that illustratively illustrates the morphological linguistic level of the topic under consideration:
“He went there,” Petya waved his hand. -Where is this going? - I asked him. - Well, there’s a store there. Products. Mom asked me to be stingy, so I decided to run away quickly. “That’s how the skunk ran away?” That’s exactly what happened.”
Syntax
- In conversational style, simple sentences are more often used than compound or complex sentences. Their construction is characterized by a certain “stringing” on top of each other, the specificity of the transmitted information.
- There are often incomplete sentences, in particular, they lack main members.
- The structure is nonlinear, sometimes fragmentary. Interruptions in intonation and phrases rearranged on the fly are the consequences of spontaneity of speech. The conversational style fully allows for the active use of connecting structures, expressed in introductory words and all kinds of particles.
- Interjective phrases as one of the ways to express thoughts in a conversational style.
- Free word order - in this case, the important is usually expressed first (however, this is not a prerequisite).
List of used literature:
1. Psychology and ethics of business communication. Ed. Lavrinenko V.N. 4th ed., revised. and additional - M.: Unity-Dana, 2005. - 415 p.
2. Business communication: Chernysheva L.I. Publisher: Unity-Dana, 2011. – 414s.
3. Business communication - Titova L.G. — Textbook, 2006. – 271s.
4. Borozdina G.V. Psychology of business communication: Textbook.— M.: INFRA-M, 2006. — 224 p.
5. Vvedenskaya L.A., Pavlova L.G., Kashaeva E.Yu. Russian language
and speech culture. – M.: Phoenix, 2011. – 511s.
Attention!
If you need help writing a paper, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 authors are ready to help you right now. Free adjustments and improvements. Find out the cost of your work
Free estimate
0
Size: 26.64K
Downloads: 110
06/01/13 at 11:30 Author: Svetlana_Skots
Liked? Click on the button below. It's not difficult for you
, and we
are pleased
).
To download test papers for free at maximum speed, register or log in to the site.
Important! All submitted Tests for free downloading are intended for drawing up a plan or basis for your own scientific works.
Friends! You have a unique opportunity to help students just like you! If our site helped you find the job you need, then you certainly understand how the job you add can make the work of others easier.
Add a job
If the Test work, in your opinion, is of poor quality, or you have already seen this work, please let us know.