Article:
Dysorthography is the inability to apply the known rules of the native language in writing.
At the same time, the student’s oral speech and intellectual abilities can be at a fairly high level. In some cases, dysorthography is part of the symptoms of such a complex speech disorder as general speech underdevelopment. It is difficult for a person who cannot competently express his thoughts in writing to achieve success in many areas of professional activity. However, the number of children with this problem is growing from year to year. A child with dysorthography can make up to 80 mistakes in one written work. Moreover, he does not see his mistakes and cannot correct them, although he may know the rules very well. In this case, experts say that the student lacks spelling vigilance.
Causes
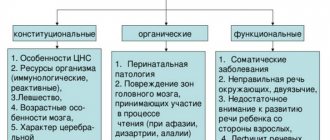
All possible causes of spelling disorders are divided into 3 groups:
- Medical.
- Mental.
- Pedagogical.
Typically, dysorthography occurs due to the impact of several negative factors on the child. The most common reasons include:
- Erased dysarthria, dyslalia.
- General speech impairment of 1-4 degrees.
- Dysgraphia.
- Lesions of the central nervous system of various etiologies.
- Pedagogical neglect.
- Psychosomatic weakness.
- Attention deficit.
- Delayed mental development.
- General lethargy.
- Mental overload.
The risk group consists of children who have a history of:
- Dysphagia and dyslexia (during primary school).
- Prenatal and postnatal pathology - disorders that arose from the moment of fertilization of the egg until the birth of the child or from the time of maturation of gametes until their fertilization, and complications that arose during the period of breastfeeding the child.
- Minimal brain dysfunction, encephalopathy, accompanied by neurological symptoms.
- Phonetic underdevelopment of speech, phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment of speech.
The essence of the problem
Dysorthography is a disorder of written language.
Schoolchildren's mistakes begin to appear at the end of the second grade and at an older age. It is during this period that schoolchildren master the rules of the Russian language, become familiar with the basic principles of spelling, and begin to apply the rules of grammar in writing.
You should know!
Experts have conducted numerous studies in which it was found that 80% of second-grade students, 90% of third-graders and older students suffer from dysorthography. This problem is the main reason for failure to learn the native language, has a negative impact on personal development and leads to a lack of adaptation at school, so dysorthography must be eliminated.
Classification
Dysorthography is usually divided into 3 forms:
- Morphological , in which the child more often makes spelling errors and finds it difficult to check unstressed vowels. The child knows the rules, remembers them, but is not able to apply the knowledge in practice. The greatest difficulty in the learning process comes from the rules for writing words with double consonants and unpronounceable sounds.
- Syntactic – errors are common when placing punctuation marks, identifying parts of a sentence, the child makes systematic syntactic errors. Children have difficulty expressing texts independently.
- Mixed - the child’s written work is not complete without syntactic and spelling errors.
According to severity, dysorthography is divided into:
- Easy – when writing, 15 or fewer errors are detected, the child copes well with completing tasks.
- Average – the number of errors reaches, but does not exceed 30, tasks are completed at an average level.
- Hard – the written work of a child in primary school usually contains 50-80 errors. Tasks are performed at an extremely low level.
What is this
Dysorthography is a persistent underdevelopment of the skill of correct writing. The child theoretically knows how to write, but cannot apply the rule. He makes the same mistakes, but does not understand how to correct them, does not notice them in the written text. In this case, teachers talk about a lack of spelling vigilance.
A feature of dysorthography is the increase in literacy problems during schooling. In grades 1-2, a student makes 30-40 errors in one text, and by grade 5, more than 80. This is due to the resistance of speech disorders to correction, a decrease in the child’s self-esteem due to awareness of his own shortcomings, and an increase in the level of complexity of speech material.
Symptoms of dysorthography
Signs of violations can be identified already in first-graders, but writing errors appear more often and more intensely in the second year of study, and steadily increase in grades 3-4.
Clinically, dysorthography is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The child cannot remember the meaning of the concepts “word”, “sound”, “syllable”.
- Difficulty in mastering spelling rules (if these are also present in other school students, the phenomenon is even more pronounced in representatives with dysorthography).
- Lack of developed skills to make inferences and determine the sequence of actions when performing written language tasks.
- By giving incorrect examples of previously learned rules.
- Misunderstanding of grammatical features of spellings, their confusion.
- Ineffectiveness of completing self-test tasks.
- Failure to use capital letters at the beginning of sentences when writing names.
- Errors related to word hyphenation and stress placement.
- Incorrect use of soft and hard signs.
- Forming your own false rules (zhIlezo - because ZHI, SHI is written with the letter I).
Schoolchildren with speech impairments usually act according to the principle: “As I hear, so I write.” The objective conditions of writing by non-children are not taken into account, they do not distinguish the semantic load of lexical units, and to check words they use consonant, not related ones.
Children with dysorthography have difficulty moving from one activity to another.
Nonspecific symptoms include:
- decreased auditory-verbal memory;
- unclear diction, poor articulation;
- violation of dynamic praxis of the hand (fine movements).
Children with dysorthography have difficulty developing ways of productive educational and practical activities; they have an inadequate attitude towards their abilities and the results of the work performed, which is why over time their attitude towards learning becomes careless. Children themselves can be unbalanced.
Treatment
The presence of dysorthography in a child should not be regarded as an excuse for making mistakes when writing.
This learning disorder can be corrected by practicing proper writing and reading skills. A child can learn the rules of spelling words.
Necessary for this is control by an adult, who must motivate the child to work and correct possible mistakes in order to avoid their consolidation. Frequent reading of books is very important. Thus, the child visually learns new words and remembers their spelling.
Working from home with a child requires patience and understanding of his situation. Often or sometimes his mistakes cause laughter, which makes him feel frustrated and rejected.
Exercise should stimulate both the intellect and the emotions. Good exercises for a child with dysorthography are puzzles, crosswords and funny drawings that allow you to distinguish the correct spelling of words from the incorrect one.
Didactic games are used that were created based on many years of work specifically to prevent dysorthography. Also, poems and songs whose content is centered around grammatical rules are beneficial. Melodies are easily reinforced in memory, thanks to which the child will remember their fragment in the event of a spelling dilemma, which will help make it easier for him to make a decision.
Each type of dysorthography benefits greatly from reading books. Experts agree that constant reading reduces the severity of all writing disorders.
The effectiveness of treatment for dysorthography depends, first of all, on systematic correction work, an individual approach and the formation in the child of the ability to concentrate and remember new rules.
Diagnostics
The examination of schoolchildren with dysorthography is carried out according to the developed methodology in 2 stages:
- Determination of the clinical picture. At this stage, the speech therapist analyzes the work of primary school children (dictations, essays, etc.). The specialist will have to carry out differential diagnostics and assess the number and nature of errors in the work of the subjects.
- Identification of the mechanisms of dysorthography. Primary school students are asked to complete a series of oral and written assignments and exercises. The study allows us to identify the severity of dysorthography and violations of the mastery of the leading principles of spelling.
It is necessary to distinguish dysorthography from dysgraphia - a partial violation of the writing process, manifested by persistent, repeated errors not related to the acquisition of spelling rules.
The specialist examining the child should pay attention to the subject’s school attendance, recent transfer to another teacher, or change in curriculum to another. In this case, violations of spelling rules will be unstable and will disappear as the necessary material is explained to the child and spelling rules are mastered.
Dysgraphia agrammatic
In this case, during writing, the grammatical structure of speech is disrupted:
- the connection between words in a sentence is disrupted, phrases are not consistent with each other;
- nouns are put in the wrong number, case or gender;
- prefixes and suffixes are replaced;
- the structure of the sentence itself changes.
The problem becomes noticeable in the 3rd grade, when mastery of grammar becomes a prerequisite for learning. Parents should be careful.
Example: “Beautiful car”, “Katya and Lena are driving a car”.
Correction methods
Speech therapist Olga Ivanovna Azova highlights the following areas of speech therapy work to eliminate dysorthography:
- Improving the phonetic-phonemic aspect of speech. At this stage, the child needs to improve sound pronunciation and the sound-syllable structure of the word, develop syllabic analysis and synthesis, work on stress, develop phonemic perception (auditory differentiation of voiced and voiceless, hard and soft consonants).
- Formation of the lexical component. In this direction, the goal of the classes is to enrich the school student’s vocabulary, find out in detail the meaning of the words learned, and work on antonyms, synonyms, paronyms and ambiguous words.
- Differentiation of meanings of different parts of speech. The child learns to distinguish parts of speech (also by pictures, word endings), then to transform words from one part of speech to another.
- Clarification of the grammatical meaning of words. The direction includes the study of the number of nouns, adjectives, their gender and case, and animation.
- Formation of morphological generalizations and inflections.
- Differentiation of related words.
- Formation of word-formation models.
- Development of morphemic analysis.
- Formation of the syntactic structure of simple and complex sentences.
- Development of attention, memory, thinking.
- Formation of spelling vigilance.
- Mastering the relationship between phonemic, morphological, syntactic, word-formation competence and spelling knowledge, skills and abilities.
This author uses the principle of “quantization” of the spelling rule. The essence of the principle is that the child learns several operations (quanta), which must become part of the skill before he begins to study a particular rule.
Example of the “separating soft sign(s)” rule:
- I quantum – we teach the child to quickly conduct morphemic analysis;
- II quantum - differentiate vowels and consonants;
- III quantum – we learn to distinguish oppositional sounds by hardness and softness.
During a speech therapist session with a child, this may look like this: the child is given pens of three colors - blue, red and green. The first is necessary for writing a whole word, and the other two are for highlighting the parts we need. We ask the child to highlight the soft sign in green, and the vowel separating it in red.
Examples of exercises
When working with a child, speech therapists can use the following exercises:
- Make up and say the words. An equally important element in the correction of dysorthography is the development of sound pronunciation and understanding of the syllabic structure of a word. We give the child cards with the inscriptions: KO, VA, FOR, RO. The student’s task is to make as many words as possible from them (goat, cow, etc.). The exercise helps children form correct articulation.
- Selection of adjectives for nouns (the car is red, fast, bright).
- Search for all cognate words in the picture (white, whitewash, blond, squirrel, whiteness).
- Guess what is shown in the picture and explain what the guessed expression means (“nod off”).
- Selection of nouns for the verb (assemble a puzzle, leaves, construction set, toys) and vice versa (the orange is ripe, the pear is ripe, the fruit is ripe).
- Combining words into phrases.
- Combining objects into pairs, selecting generalizing words for them (camel, scorpion - desert animals).
- Name the place of work (teacher - school, doctor - hospital) or tool (scissors - hairdresser).
- Writing as many words as possible with the same vowels (banana, ram, boar).
- Name an object, knowing its parts (kitchen, bathroom, bedroom - house, legs, arms, torso, neck, head - person).
- Arrange the pictures under gender symbols (cat, giraffe - masculine, turtle, dog - feminine, sea, sky - neuter).
- Forming adjectives from nouns (plum jam is plum, not plum or creamy).
- Find the extra word - an exercise to differentiate parts of speech. The child is offered a set of words from one part of speech and an extra word. The child’s task is to find the latter and explain his choice (milk, cottage cheese, sour cream, bread or spoon, plate, pan, bag).
- One is many. The student is shown pictures of one pencil and five. The child needs to be shown where there are many objects, and where he is alone and why.
- Make a proposal according to the diagram. We give the child a piece of paper or a card on which it will be written which components need to be used to construct a phrase. For example: Noun, verb, adjective and noun – Mom bought big apples. And so you can add more and more members of the sentence so that the child continues to work effectively.
- I'll check myself. We give the student a dictation with the condition that he skips spellings that are incomprehensible to him (you can start an exercise with a few words, moving on to small phrases and sentences).
- Spelling reading. The child is asked to read words in the same way as he will write them, clearly pronouncing all unstressed, voiceless sounds, etc. The exercise will also help develop visual and auditory memory.
- Find a dangerous place. The speech therapist pronounces the words, and the child claps his hands if he hears a sound that cannot be trusted when writing. The “Traffic Light” game is considered similar, when the student needs to be shown a red traffic light when a dangerous place in a sentence is heard.
The process of consolidating skills and abilities is very long. It takes several years for severe dysorthography. Automation of competent writing occurs in any type of work with a speech therapist and parents.
Pay special attention to the written work of primary school students, especially cheating.
Working with word-formation models is considered effective:
- Visual perception of word structure based on a drawing model. The peculiarity of the tasks is the graphic presentation of the word-formation model; the root void is filled with a picture that provides information about the meaning of a given morpheme in the word. At the same time, students visually perceive the morphemic structure of the word as a whole.
- Accumulation of groups of single-structure words. Gradually, children accumulate a certain number of word-formation models and lists of roots corresponding to them.
- Search for a given word using a guessing model. Children are presented with a riddle; a word-formation model can serve as a clue. You can invite the child to find the “hidden” word using the specified model and the selected single-root word, which tells the child which root needs to be “inserted” into the graphic model to get the hidden word.
- Comparative analysis of words that are externally similar in composition. During the lesson, the ability to parse the composition of words of the same model, as well as words that have an external similarity in structure, is developed.
- Graphic representation of nests of cognate words using word-formation models. It may take the form of various tasks: we invite the child to carefully examine the record and find the words hidden in it, writing them down in letters, paying attention to the correct spelling of the roots. We can also invite the child to write down the encrypted words and explain what unites them and what their differences are.
In order for a child to increase his vocabulary, speech therapists recommend writing his own texts, reading other people’s works, examining and describing pictures, images, selecting synonyms, antonyms, and paronyms for known words.
Tips for parents
A favorable psychological climate will give the child everything necessary to master written language. It is necessary to exclude quarrels with the child, between adults, as this negatively affects his development, aggravating the fact that the child is under pressure from the presence of violations in the assimilation of spelling rules and other material.
Articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia
This option occurs when there are problems with sound perception and pronunciation of sounds. That is, the child “writes what he hears.”
- arbitrarily uses voiced and voiceless consonants in writing, changing their places;
- alternates between whistling and hissing sounds;
- skips a soft sign;
- mixes affricates and their components;
- randomly changes vowels of the first and second rows.
The problem cannot be solved until the speech therapist establishes the correct articulation of all sounds and masters phonemic hearing skills.
For example: “cat” - “koska”, “swing” - “rollers”.
Prevention
Main preventive rules:
- Our task as parents is to be attentive to our child. Take an interest in his school life, relationships with friends and teachers.
- Make sure he follows the curriculum and does his homework regularly.
It will be a plus if the school has a well-established collaboration between primary school teachers, speech therapists and child psychologists. Early identification of deviations in the acquisition of spelling rules and further work with the child by the last two specialists will allow the child to quickly overcome problems and return to effective learning on a par with peers.
Dysorthography, along with other disorders of the writing process, is increasingly being diagnosed in children of primary school age, but timely correctional and pedagogical assistance will prevent children from further failure to master the material, reduce the number of errors and compensate for school failure.
Tips for parents
The main thing that parents can do for their child is to create a favorable psychological climate for him during correctional work. The schoolchild is already under the pressure of the situation, and his mood is often not the most rosy, and then adults traumatize the child by constantly pointing out his speech errors.
The consequence of this may be that the child will become withdrawn, and instead of the communication he so needs, speech will slow down its development, will not improve and be enriched, which will lead to problems of social adaptation in the team. Therefore, it is important to show patience and forbearance to resolve the situation successfully.
Optical dysgraphia
Letters consist of a certain set of elements - hooks, sticks, circles, ovals, etc. If there are problems with visual-spatial perception, the process of analysis and synthesis, schoolchildren may experience typical errors:
- letters are written in mirror image;
- extra elements appear in the letters (“porridge” - “kashshsha”);
- the details of the letters “come off” from each other or a gap appears between the written
- letters in one word;
- visually similar letters are replaced (v - d, t - p, i - sh).