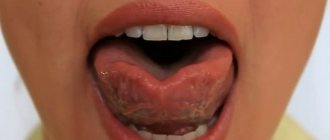
We help with dyslalia. We work with children of all ages. We develop correction programs based on the child’s characteristics and try to avoid drug treatment.
Dyslalia is the most common type of speech disorder that occurs in both children and adults. If the disease is observed in an adult, then the “root” of the disease should be sought in childhood. Dyslalia is expressed in the incorrect pronunciation of sounds and words: distortion of words, replacement of letters and sounds, omission of letters. At the same time, the child hears perfectly and has a good vocabulary.
There is a clear division of possible causes of dyslalia into two groups:
Functional - anomalies and disorders in the structure of the tongue, jaw, palate and teeth. Such defects can be acquired (knocked out tooth, dislocated jaw, malocclusion, etc.), or they can also be congenital (short frenulum of the lip, cleft lip, palate defect). Many such defects can be corrected surgically: a timely operation will help correct speech disorders, or minimize them.
Another cause of dyslalia is a delay in psycho-speech development. It can be caused by social isolation, lack of attention from parents, excessive “lisping” with the baby, and the child’s desire to imitate adults with speech impediments.
Many years of experience show that mechanical dyslalia is treated much faster than phonemic dyslalia. To correct the first, it is enough to eliminate the cause of incorrect pronunciation, while for phonemic it is necessary to involve a larger number of specialists.
Phonemic dyslalia also includes acoustic dyslalia - the child pronounces speech as he hears it. If a child has hearing problems, then the sounds are often mixed. Thus, instead of the word “fish” the child says “lyba”, and instead of “car” - “mafina”). This shows the difference between adult and child dyslalia: an adult hears correctly, but has an articulation disorder, and a child, in most cases, hears incorrectly and, accordingly, speaks with errors.
The next type of deviation is articulatory-phonemic dyslalia, which occurs when the speech organs are incorrectly positioned during pronunciation (tongue, teeth). Incorrectly acquired articulation leads to the development of articulatory-phonetic dyslalia.
Simple violations, for example, incorrect pronunciation of whistling sounds only, require 2-3 months of regular sessions with a speech therapist. Sometimes this period can increase to six months. But the treatment of complex dyslalia, where the pronunciation of 5 or more groups of sounds is impaired, can take a long time and requires more painstaking work of a speech therapist.
Dyslalia can be age-related in preschool children. In this case, it does not require correction and goes away on its own. However, you should not relax and you need to carefully monitor the development of speech of minors. It is in the first years of life that the communication foundations are formed.
Diagnosis and treatment of dyslalia
Only an experienced speech therapist can correctly diagnose the form of dyslalia. After collecting the necessary data, the doctor makes a diagnosis, based on which a further course of correction is prescribed. If necessary, the small patient is referred to a dentist or neurologist, as well as other related specialists. To form a child’s correct speech, it is necessary to regularly show him to a specialist even before he reaches 4-5 years of age. Severe dyslalia occurs much more often in school-age children than in preschoolers, because early diagnosis and correction make it possible to solve the problem faster and more effectively. The main position that parents should be guided by is concern and attention to the child’s development, which will help avoid many complications in the future.
Ways to identify and overcome dyslalia in preschool children
Content
Introduction 3 Chapter 1. Theoretical aspects of the concept of dyslalia as a speech disorder 5 1.1. Types and forms of dyslalia 5 1.2. Causes of dyslalia in preschool children 7 1.3. Sound pronunciation disorders in preschoolers 10 Chapter 2. Identifying and overcoming dyslalia in preschoolers 15 2.1. Analysis of methods for speech therapy examination of preschool children with dyslalia 15 2.2. Description of correctional work to overcome dyslalia in preschool children 19 Conclusion 27 References 28
Introduction
Speech is the most important factor in the successful integration of an individual in society. Speech is both a means of communication and a means for an individual to master the diversity of social and mental life. In this regard, it is very important to develop in a person the skills to fully use his speech abilities in society. This is often hampered by common deviations and disorders in speech development, in particular in sound pronunciation. One common type of speech disorder is dyslalia. This term was introduced in 1827. At the moment, different forms of dyslalia are detected in a fairly large number of children, and in a certain number of adults. To a greater extent, this speech disorder concerns preschool children. Data from foreign and Russian researchers indicate that pronunciation deviations are observed in 25-30% of children aged 5-6 years. This issue was studied by Levina R.E., Pravdina O.V., Rau E.F., Smirnova A.M., Khvattsev M.E. etc. The most important direction in developing the problem of dyslalia is the study of effective tools for correcting the pathological aspects of the disease, in particular the development of phonemic hearing. The choice of an effective tool is determined by the developmental characteristics of an individual in a specific period of his life, taking into account the mental and psychophysiological characteristics of his development. This topic is relevant due to the fact that in science at the moment there are not enough theoretical and practical comprehensive works devoted to the study of the problem of diagnosis and correction of dyslalia in preschool children. Most of the studies cited consider individual aspects of this issue in the form of separate publications of a methodological nature or a description of the private experience of speech therapists. Purpose of the study: to study the problem of dyslalia in preschool children. Objectives: 1. Study psychological, pedagogical and methodological literature on the research problem; 2. Analyze methods for studying dyslalia in preschool children; 3. Describe the features of correctional work to overcome dyslalia in preschool children; Object of study: dyslalia, as a form of speech impairment in preschoolers Subject of study: speech therapy work to overcome dyslalia in preschoolers. The theoretical significance of the work is determined by the possibility of using the results of this study as methodological recommendations for organizing correctional work with preschool children.
List of sources used
1. Vanyukhina G.A. Ecologization of the speech therapy process from the standpoint of the principle of conformity with nature / G.A. Vanyukhina // Speech therapist: scientific method. magazine - 2005. - No. 2. - P.4-8 2. Volkova G.A. Methodology for psychological and speech therapy examination of children with speech disorders. Issues of differential diagnosis: Educational and methodological manual, - M.: CHILDREN'S PRESS, 2004 - 144 p. 3. Volosovets, T.V. Organization of the pedagogical process in a compensatory preschool educational institution: a practical guide for teachers and educators / T.V. Volosovets, S.N. Sazonova. - Moscow: Vlados, 2004. - 232 p. 4. Gomzyak O.S. Development of Coherent Speech in Six-Year-Old Children, Lesson Notes. M.: Creative. 2007 – 108 p. 5. Kolesnikova, E.V. Development of phonemic hearing in children 4-5 years old. Scenarios for 32 educational and game activities. 2nd edition, add. and correction. -M.: Publishing house GNOM and D, 2001. - 96 p. 6. Speech therapy. Textbook for students of defectology faculties of pedagogical higher educational institutions / Ed. L.S. Volkova, S.N. Shakhovskaya. — 3rd ed., revised. and additional - M.: VLADOS, 2003. - 357 p. 7. Rau, F. F. Techniques for correcting deficiencies in the pronunciation of phonemes. Fundamentals of the theory and practice of speech therapy, M.: Enlightenment, 1968. – 181 p. 8. Reznichenko, T. S., Larina, O. D. Speak correctly: sounds, words, phrases, speech. : Album for a teacher. - M.; Vlados, 2000. - 96 p. 9. Rosenthal, D.E. Golub, I.B. Telenkova, M.A. Modern Russian language. - M., 2000. - 448 p. 10. Sergeev, F. P. Speech errors and their prevention. - Volgograd: Teacher, 1999. - 96 p. 11. Smirnova L.N. Speech therapy in kindergarten./M.: “Mosaika-Sintez”, 2009. – 60-61 p. 12. Shapoval, I.A. Methods for studying and diagnosing deviant development: Textbook. - M.: TC Sfera, 2005. - 320 p. 13. Shevtsova E.E., Vorobyova E.V. Speech development of a child from one to seven years old./M.: “Sphere”. 2007. – 3 p. 14. Shatskova A.M. Differential diagnosis of minimal manifestations of speech pathology in children with similar disorders of the pronunciation side of speech: dissertation ... candidate of pedagogical sciences: 13.00.03 - Moscow, 2009. - 220 p.
Total volume: 28 pages.
Year: 2015
Price : 500 rub.