Symptoms of motor alalia
With any type of alalia, vocabulary is the first to suffer. A child 3 years old and older retains forms of speech communication that his peers have long left in the past - syllables and even babble. Motor alalia manifests itself primarily in communications. Children with this disorder communicate mainly through facial expressions and gestures. They use no more than 10-40 words in which sounds are pronounced incorrectly, and replace complex sounds with simple ones. They construct their sentences incorrectly, preferring short, choppy ones. In addition to speech symptoms, it is important to pay attention to the accompanying ones. This:
- inability to maintain concentration for a long time;
- difficulty maintaining balance due to problems with gross motor skills;
- Poorly developed self-care skills due to deficits in fine motor skills.
Motor development disorders can manifest themselves in other ways. If violations of fine motor skills manifest themselves not only in everyday life, but also in play activities, this is a serious signal. The same applies to gross motor skills (aka coordination of movements). Assess how the child walks and runs, and whether he can play with the ball. If you feel like something is wrong, you need to discuss it with a specialist, even if your speech is fine.
There are also manifestations of motor alalia in the psycho-emotional sphere. In order for a non-specialist to notice or suspect them, it is important to observe the child’s interactions with peers and compare reactions to different situations. Of course, all children are different. You should think about a visit to a neurologist if you notice neurotic symptoms (unreasonable whims, night terrors, uncontrolled movements, etc.); lagging behind peers in the emotional-volitional sphere; difficulties with understanding the surrounding world; the desire to do without verbal communication (logophobia), up to the lack of response to direct appeals.
Sometimes motor alaliks have high speech activity. In such cases, anxiety and neuroticism are extremely pronounced.
Causes of the disease
The causes of motor alalia in a child lie in damage to areas of the cerebral cortex, which is responsible for speech in all its forms: listening, reading, writing and, of course, pronouncing phrases. There is a theory about a genetic predisposition to this disorder. It often turns out that at least one of the child’s parents had similar characteristics during childhood. In addition, the disease in its simple form occurs 14 times more often in boys than in girls, and twice as often in the variant complicated by intellectual impairment.
There has been a proven connection with the occurrence of motor alalia of conditions that cause hypoxia, which can damage the brain. Their range is wide: these are complications of pregnancy or chronic diseases of the mother, hypoxia during childbirth, traumatic brain injuries, infections and even frequent illnesses at an early age.
Another set of reasons is social. Motor alalia can occur in children who do not have enough contact with society, they do not have enough opportunities to develop speech in communication with older children or adults.
There is almost never just one cause for a violation. This is a complex, and there is no need to look for who is to blame for the child’s illness. You need to focus on treatment.
Alalia and childhood aphasia: their characteristics, similarities and differences, causes of occurrence.
Oral speech disorders include alalia and aphasia.
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech due to organic damage to the speech areas of the cerebral cortex in the prenatal or early period of development. With alalia, there is a late appearance of speech reactions, a poverty of vocabulary, a violation of the syllable structure, sound pronunciation and phonemic processes. There are several variants of alalia, depending on which speech mechanisms are not formed and which of their stages (levels) is predominantly affected.
Among alaliks there are children who, to a limited extent, understand the speech of others, but do not speak (motor alalia). In such children, the formation of conditioned connections is disrupted, mainly in the motor (kinesthetic) speech systems of the cerebral cortex. But since the auditory-speech analyzer is directly connected with the speech-motor analyzer, the understanding of speech among motor alaliks is sharply limited: they understand only specific things, mainly from the area of household use or kindergarten.
Other alaliks do not understand speech at all, and therefore do not speak, although their ability to form sounds is sufficiently preserved in the form of mechanical repetition. The basis of misunderstanding in this case is acoustic agnosia (phonemic hearing is impaired): the child hears speech, but does not understand it. There is no connection between the first and second signaling systems. This is a sensory (sensitive) alalia. There are no pure forms of alalia: in some, sensory impairments predominate, in others, motor impairments predominate. Motor alaliks speak slowly, heavily, with difficulty, they squeeze the words out of themselves with effort. Their speech is characterized by rearrangement of sounds and syllables and contamination.
In turn, aphasia is a complete or partial loss of speech caused by local brain lesions. A child loses speech as a result of traumatic brain injury, neuroinfection, or brain tumors after speech has already been formed; if such a disorder occurs at the age of 3 years, then researchers refrain from diagnosing aphasia. If it happened at an older age, then they talk about aphasia.
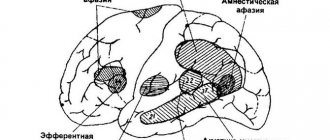
Depending on the location and degree of damage to brain tissue, there are two main types of aphasia: motor (expressive) and sensory (impressive, receptive). In accordance with the classification of A.R. Luria, three forms of expressive speech impairment can occur: afferent, efferent and dynamic motor aphasia.
Afferent motor aphasia leads to the replacement of some articulations by others, to the replacement of sounds - phonemes (instead of “l” is pronounced “n”, or instead of “sh” - “s”, etc.). The patient loses all types of oral speech - spontaneous, automated, repetition of proposed words, names of objects. Reading and writing are also affected.
Efferent motor aphasia is characterized by a violation of the processes of switching from one speech unit (sound, word) to another.
Attention!
If you need help writing a paper, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 authors are ready to help you right now. Free adjustments and improvements. Find out the cost of your work.
Cost calculationGuaranteesReviews
With dynamic motor aphasia, the patient cannot actively express a thought or ask a question, but he repeats individual words and sentences well and answers the question correctly.
Sensory aphasia is the loss of the ability to understand speech in general, that of others and one’s own. The basis for speech understanding disorders is phonemic hearing disorder.
Aphasia differs from alalia in that it always occurs in a child as a result of organic damage to certain areas of the cerebral cortex (pathological “foci”), moreover, during the period of more or less developed speech (after three years).
In aphasia, motor and sensory forms also differ.
We will help you write any paper on a similar topic.
- Essay
Alalia and childhood aphasia: their characteristics, similarities and differences, causes of occurrence.
From 250 rub.
- Test
Alalia and childhood aphasia: their characteristics, similarities and differences, causes of occurrence.
From 250 rub.
- Course work
Alalia and childhood aphasia: their characteristics, similarities and differences, causes of occurrence.
From 700 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project
Find out the cost
How to make sure of the diagnosis
Diagnosis of motor alalia in children is possible from 3 years of age. Until this age, its symptoms can be noticed, but in most cases this is only a reason for parents to be wary and an opportunity for the doctor to talk about the likelihood of a diagnosis.
The examination begins with a visit to a neurologist. He makes a preliminary diagnosis. In the differential diagnosis of motor alalia, it is necessary to exclude:
- sensory alalia (speech neurologist);
- hearing impairment (otorhinolaryngologist or audiologist);
- autism, intellectual development disorders (psychiatrist).
Delayed speech development, dysarthria, and aphasia are ruled out by a speech therapist. Based on the data obtained by this specialist and doctors, as well as the results of the examinations they prescribed, the neuropsychologist determines the level and location of brain dysfunction. As a result, the diagnosis of motor alalia is confirmed or refuted.
Article:
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech due to organic damage to the speech areas of the cerebral cortex in the prenatal or early period of a child’s development.
What is the difference between alalia and deaf-muteness?
With alalia, hearing function is preserved. Hearing research plays a decisive role. A deaf person is characterized by a complete lack of reaction to sound stimuli. You can call out to the child behind his back or hit a musical instrument. Alalik will give a normal indicative response. Important! Do not make sounds with additional vibration, do not knock, do not clap. The child is referred to an audiologist for an audiometric hearing test. Typically, deaf children use gestures without sound accompaniment, and speech does not appear without special training. Alalik gives a sound reaction to gestures (non-verbal vocalization). Unlike deaf people, Alaliks have perfectly preserved prosody.
The difference between sensory alalia and hearing loss.
Audiometric hearing test. If you increase the volume of your voice, a child with hearing loss will hear better and respond. For touch alik, volume will not improve speech understanding. Alaliks have a ringing voice, while children with hearing loss have a muffled voice. Children who are hard of hearing try to repeat words, but alalik does not.
For anarthria and dysarthria.
In children with alalia, the motor level of speech production is completely or relatively preserved. They can perform articulatory movements in full. In children with anarthria and dysarthria, articulatory motor impairments are leading in the structure of speech defects. With alalia, the entire language system is upset, with anarthria - only one of its subsystems is phonetic, due to the presence of paresis and paralysis.
Difference between alalia and aphasia
The difference is in the anamnesis: the effect of harmful factors is observed in the prenatal and early postnatal periods (up to 3 years). In childhood aphasia - after a period of intensive speech development. If a child ever spoke better than during the examination, this is aphasia. An aphasic person exhibits “splinters” of previous speech. With alalia, targeted intensive formation of the speech system is necessary. With aphasia, spontaneous restoration of speech is possible.
For severe speech delay
One of the most difficult cases of differential diagnosis. Alalia is characterized not only by delayed speech development, but, above all, by a pathological type of language acquisition. A child with a tempo developmental developmental disorder most often exhibits varying degrees of impairment of articulatory motor skills and a slight lag in the formation of language ability in expressive speech. With alalia, the motor sphere is preserved, but gross violations of the lexico-grammatical system are expressed, the manifestations of which are not characteristic of children's speech in the early stages of its development. Children with delayed speech development often spontaneously, without special training, master language, which does not happen in children with alalia. An important diagnostic criterion is the ability and speed of learning new words.
Difference from speech pathology caused by mental retardation.
Speech impairment in alalia occurs with relative preservation of nonverbal mental operations. Speech disorders in UI are the result of pathology of cognitive activity. The decisive role is the examination of thinking at the non-verbal level.
Motor alaliks understand spoken speech well and follow instructions, which three-year-old children with disabilities may not be able to do. At school age, alaliki try to express and understand complex cause-and-effect relationships. Children with ID either do not express them at all, or only the most elementary ones.
With alalia, there are language speech disorders in the form of agrammatism and phonemic disorders. In mentally retarded children, speech is primitive, but correct in formal linguistic terms.
Children with alalia have a large stock of “subject knowledge”. Children with intellectual disabilities easily update simple words, but when shown low-frequency object pictures, there will be errors and refusal.
Children with motor alalia have preserved nonverbal thinking and a higher degree of learning ability. During the examination, a training experiment is used. They show how to complete the task and see whether the child takes the hint or not. Children with motor alalia, unlike children with mental retardation, are critical of their speech impairment.
From early childhood autism
A condition similar to sensory alalia. Autistic people come across as children with sensory alalia. A child with early childhood autism does not respond to spoken language, does not make eye contact, avoids touch, or reacts to it by screaming and crying. Such children do not have the words mom and dad, and there may be constant mumbling, including a variety of sounds, including complex ones. Echolalia is characteristic of both categories. Pronounced psychopathological symptoms for early childhood autism: stereotypies, stimulation (tactile, olfactory). Changing the usual image leads to violent reactions. Coldness towards mother.
How to help your baby?
Specific treatment methods and prognosis for motor alalia depend on the results of the examination. The program is always compiled individually. A mandatory part of it is classes with a speech therapist, but sessions with a psychologist, treatment of the nervous system, and neurorehabilitation may be necessary. In our center, alalia treatment is carried out comprehensively, children receive all the help that is necessary in their particular case. Our center’s specialists work with both simple cases and those in which motor alalia is combined with other developmental disorders, focusing on the best possible result for each patient.