Dial-Dent speech therapist T. B. Tsukor shares his experience in staging and automating the sound of R.
Producing the sound R in a child is one of the most common wishes of parents of preschool children during consultations with a speech therapist. Although, objectively speaking, in addition to the phoneme R, a number of other sounds may be impaired in the child, but parents often do not notice this. There is nothing surprising. The fact is that R is a very bright, energetic sound, and its absence in speech or its replacement with the sounds L, L, V, G, D, Y, the throat sounds R and R, and even N are very noticeable. The first thing a speech therapist is interested in is the child’s age. It is important to understand that the sound R in a child’s speech does not appear immediately and is formed by the age of 5. There is no need to teach a child to pronounce the sound R, for example, at 3 years old! Often, a parent’s attempt to “evoke” this sound in a child ends with the baby developing a guttural sound R, which is then very difficult to get rid of. The fact is that the muscles of the tongue are not yet ready to pronounce P or P, and parents, wanting to achieve clear speech in their child, ask him every now and then: “Say fish, say mouth, say hands,” and the child tries to phonetically adapt to the sound adult. The most similar and simplest is the throat sound R. Therefore, do not rush things, but also do not lose vigilance, since not only the age of the child can cause the absence or disturbance of the sound R.
Massage method in the correction of speech disorders
Indications for the use of massage
Speech therapy massage is an active method of mechanical action that changes the condition of muscles, nerves, blood vessels and tissues of the peripheral speech apparatus (techniques and methods of speech therapy massage are taken from the book by E.A. Dyakova). Speech therapy massage is part of a comprehensive medical and pedagogical system of rehabilitation of children, adolescents and adults suffering from speech disorders. Massage is used by those diagnosed with speech disorders such as dysarthria, including its minimal manifestations: rhinolalia, stuttering, voice disturbance, as well as for the prevention of speech disorders in children of the pre-speech period of development who have various types of motor disorders.
The main goals of speech therapy massage:
- Normalization of muscle tone of general, facial and articulatory muscles;
- reducing the manifestation of paresis and paralysis of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus;
- reduction of pathological motor manifestations of the muscles of the speech apparatus (syncinesia, hyperkinesis, convulsions, etc.);
- stimulation of proprioceptive (body sense, posture, movement) sensations;
- increasing the volume and amplitude of articulatory movements;
- activation of those muscle groups of the peripheral speech apparatus that had insufficient contractile activity;
- the formation of voluntary, coordinated movements of the organs of articulation.
Brief anatomical and physiological information:
Speech therapy massage is performed mainly in the area of the muscles of the head, neck, and shoulder girdle. Particular attention in the process of speech therapy massage is paid to the muscles of the peripheral speech apparatus, which include the muscles of the tongue, lips, cheeks, and soft palate. The speech therapist must have a good understanding of the structure and functions of the muscles in the area of which speech therapy massage will be performed. .
Reasons for development
Dysarthria is not an independent disease, although often this speech disorder is the main manifestation of various pathologies of the central nervous system. In most cases (up to 85%), dysarthria accompanies cerebral palsy. Malformations of the nervous system can be caused by a variety of reasons:
- pathological conditions of the fetus during intrauterine development. These include severe toxicosis and the pathological course of pregnancy, chronic maternal diseases and intrauterine infections, hypoxia, asphyxia or ischemia of the fetal brain, Rh conflict, etc.;
- genetic predisposition (presence of severe hereditary pathologies);
- head injuries and illnesses suffered by a child in the first few years of life. These include hydrocephalus, meningitis and other neuroinfections, purulent otitis media, as well as poisoning with toxic substances and intoxication due to infectious diseases.
The above reasons lead to damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, the cerebellum, basal ganglia, brain stem, nerve fibers and their connections with muscles.
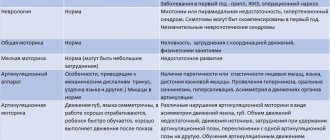
Manifestations of dysarthria are different, and they depend on which part of the central nervous system is affected.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSTICS
The appointment of speech therapy massage should be preceded by a medical diagnosis carried out by a doctor. The medical report contains an indication of the presence of neurological symptoms, including an indication of the form of paresis (or paralysis), local disorders of muscle innervation, etc. As a rule, speech therapy massage is recommended only on the recommendation of a doctor. Before starting correctional work, the speech therapist must determine the form and structure of the speech defect, guided by the clinical and pedagogical classification, and then raise the question of the need for massage. As a rule, the main indication for massage is a change in muscle tone, which can be observed both in the general muscles and in the organs of the speech apparatus. However, even with a medical report, the speech therapist must independently diagnose the condition of the muscles. This will help him determine massage tactics in each specific case. The speech therapist should determine the condition of the muscles: the upper half of the torso, neck, facial expression, articulation. This is established by inspection, palpation, and observation when performing dynamic and static exercises.
Inspection. When examining a child, you should pay attention to the position of the head in relation to the body, and note whether there are any habitual asymmetrical postures. When examining the face, one must remember about possible asymmetry in the form of a smoothed nasolabial fold, drooping corner of the mouth, widened or narrowed palpebral fissure, as well as the presence of a constantly slightly open mouth, drooling (this is important). Skin coloration, skin rashes, skin hemorrhages.
Palpation. Palpation of the muscles involved in articulation allows the speech therapist to more accurately determine the nature of muscle tone disorders. The following characteristics are determined by palpation. Skin elasticity, skin swelling, condition of lymph nodes, condition of muscles.
Types of massage used in speech therapy practice
Several types of massage can be used in speech therapy practice. The main thing is differentiated (strengthening or relaxing) massage, based on the techniques of classical (manual) massage. In addition, speech therapy practice uses massage of biologically active points (BAP), massage using special devices (speech therapy probe, spatula, vibrating massager, cupping, etc.), as well as elements of self-massage.
Contraindications for massage
Contraindications for massage are any somatic or infectious disease in the acute period, conjunctivitis, acute and chronic skin diseases, gingivitis, stomatitis, the presence of herpes on the lips or other infections of the oral cavity, the presence of enlarged lymph glands, pronounced pulsation of the carotid arteries. Before conducting a massage course, it is necessary to obtain a conclusion from a neurologist and pediatrician about the absence of contraindications.
Preparing for a massage
To carry out a massage, the speech therapist must have the following materials: 1) medical alcohol (for disinfecting probes, spatulas. 2) sterile napkins 30 x 30 cm (for examining the state of muscle tone of the articulatory apparatus), 3) hexoral (after massaging the muscles of the oral cavity, the child can for hygiene purposes, rinse your mouth with the solution), 4) sterile medical rubber gloves (can be used when performing massage in the oral cavity), 5) ammonia and 3 percent hydrogen peroxide (can be used if necessary to provide emergency care), 6) protective mask (use it is advisable to avoid droplet infection). The skin of the person being massaged should be clean, the hands of the speech therapist should be clean and warm, without abrasions or scratches or any areas of inflammation, with short-cut nails, without jewelry that would interfere with the massage. Before massaging your face or neck, you can lightly lubricate your hands with baby oil or use baby powder. When massaging the muscles of the oral cavity, it is recommended to use sterile medical rubber gloves or sterile napkins.
General recommendations for massage.
Speech therapy massage is carried out in a clean, comfortable, warm and well-ventilated room. On average, two or three procedures per week, performed in a row or every other day, may be sufficient. Typically, massage is carried out in a cycle of 10 - 20 procedures. These cycles can be repeated at intervals of two weeks to two months. In case of severe disorders of muscle tone, massage can be carried out for a year or more. The duration of one procedure may vary depending on the degree of damage, the age of the patient, etc. The initial duration of the procedure is usually 5 - 7 minutes, and the final duration is 20 - 25 minutes.
Body positions during massage.
Before starting the procedure, the child must take the correct position - a resting position. Adopting the correct posture helps relax muscles, makes breathing free, and also provides a comfortable position for the speech therapist when performing a massage.
The following body positions are optimal for speech therapy massage: 1. The person being massaged lies on his back, arms extended along the body, legs lying freely, socks slightly apart. Under the head is a small flat pillow that reaches the upper edge of the shoulder blades. The speech therapist takes a position behind the patient's head. 2. Pose - half-sitting in a chair with a high headrest. The speech therapist takes a position behind the patient's head.
BASIC MASSAGE TECHNIQUES.
- Stroking: superficial; deep grasping; rake-shaped.
- Trituration.
- Kneading.
- Vibration and effleurage.
- Firm pressure
Stroking. This is a mandatory technique with which every procedure begins. It is alternated with other techniques and ends each massage complex.
Trituration. This technique is carried out, as a rule, in small, limited areas (the subcutaneous fat tissue is slightly shifted into the fold).
Kneading . This technique is performed in the same way as rubbing, in the area of individual muscle groups, maximally activating muscle function. It consists of grasping, sliding, pulling, squeezing, squeezing, pinching and rubbing tissue.
Vibration and effleurage . Vibration changes interstitial metabolism and improves tissue condition. Strong, hard vibration increases muscle tone, and light, weak vibration reduces their tone.
Press firmly . As a rule, this technique, which improves blood circulation, lymph circulation, and metabolic processes, is used at the exit points of bundles of nerve endings.
Guidelines for conducting a relaxing massage.
- The massage is performed at a slow pace.
- The main techniques are stroking and light vibration.
- A relaxing massage should cause only pleasant feelings of warmth and peace in the child.
- The speech therapist's hands must be warm.
- Muscle relaxation is facilitated by the sound of quiet music with a slow, smooth rhythm or by the speech therapist performing the massage pronouncing calm formulas for autogenic training.
- To enhance the relaxing effect, a warm compress can be placed on the face of a teenager or adult a few minutes before the massage. This can be a terry towel soaked in warm water (40-45°C) and wrung out well. The compress is applied for 3 - 5 minutes.
- The sequence of effects on the massaged areas during one relaxing massage session can be as follows:
- muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle,
- facial muscles,
- lip muscles,
- muscles of the tongue.
Methodological instructions for carrying out activating massage.
- This type of massage is used for decreased muscle tone.
- The speech therapist's hand movements should be quite rhythmic.
- The main technique is stroking, which alternates with rubbing, kneading, and strong vibration.
- The force on the massaged tissues should increase gradually.
- Vigorous effects are contraindicated on the front surface of the neck, since the thyroid gland is located in this area.
- When the massage is performed correctly, the baby's breathing is even.
- The massage should not cause significant pain in the person being massaged.
- The sequence of effects on the massaged areas during one strengthening massage session can be as follows:
- facial muscles,
- lip muscles,
- tongue muscles,
- muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle.
Cost of tongue massage at Dial-Dent. Specialist in speech therapy massage.
At the Family Dental Tongue Massage or speech therapy massage, speech therapist-myofunctional therapist Tatyana Borisovna Tsukor is engaged. Graduated from Moscow Pedagogical State University. Lenin. Work experience more than 15 years. Speech therapist teacher of the highest qualification category. Laureate of the competitions “Heart given to children 2008” and “Heart given to children 2010”.
The cost of a session with a speech therapist is 3,500 rubles. The duration of the session is from 30 minutes to 50 minutes depending on the task and the age of the patient. If necessary, the session also includes speech therapy massage.
Being a unique speech therapist who has been collaborating with dentists for a long time and successfully, Tsukor T.B. conducts training courses for both orthodontists and speech therapists. The course covers all aspects of speech therapy massage. Of course, every orthodontist should know about the capabilities of such a powerful tool as speech therapy massage. Training is carried out both as part of presentations at congresses, and individually or in small groups.
Our speech therapist also conducts classes via Skype. The cost of such a lesson is 2500 rubles. As you understand, speech therapy massage cannot be done via Skype, so if you need a massage, you will still have to come to Dial-Dent.
You can make an appointment with the Family Dental speech therapist Tatyana Borisovna Tsukor by calling the clinic +7-499-110-18-01 or using the form on the website. You can ask questions about speech therapy, as well as massage training, to T.B. Zukor on her page in.
SHOULDER AND NECK MASSAGE
Relaxing massage. Relaxation of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck expands the physiological capabilities of the respiratory apparatus, while the tone of the root of the tongue reflexively decreases, which helps to intensify movements of the lower jaw. The person being massaged should be naked up to half the chest.
- Slowly stroke the front of the neck with the palms of both hands (alternately with the right and then with the left hand) from top to bottom along the side areas of the throat (avoid pressing on the thyroid gland area)
- Slowly stroke the side of the neck, alternately on the right and then on the left.
- Place both hands on the back of the neck, towards the back of the head, this massage technique relieves tone from the trapezius muscle.
Invigorating massage. Massage movements are performed in the direction from bottom to top, using stroking and rubbing techniques. Tapping, kneading and vibration of these sections are contraindicated. 1. The movement is carried out simultaneously or alternately with both hands, up the side surface of the neck to the corners of the lower jaw. 2. The movement begins from the area of the shoulder blades along the posterolateral surface of the neck up to the back of the head.
Forehead massage
Relaxing massage.
- Stroking movements with the palmar surface of all fingers (except the thumb) in the direction:
- from the middle of the forehead to the temporal areas. Circular stroking in the form of a spiral is carried out on the temples
- from the middle of the forehead to the tragus of the auricle, ending with light pressure
- Stroking in the direction from bottom to top, from the brow ridges to the scalp. The movements are carried out alternately by the palmar surface of all fingers of the right and left hands or simultaneously by the pads of the 2nd–4th fingers of both hands.
Invigorating massage.
- Rubbing, i.e. semicircular or spiral movements in the direction from the midline of the forehead to the temples.
- Kneading, squeezing a fold of skin with two fingers - thumb and forefinger, or intermittent pressure.
- Intermittent vibration, or puncturing (tapping), with the pads of the index and middle fingers alternately at a fast pace.
Massage in the eye area
The massage affects the orbicularis oculi muscle and the corrugator muscle. The massage is performed with eyes closed. Massage movements in the area of the eye sockets should be very gentle, carried out without much pressure or moving the skin.
- Stroking with the pads of the middle fingers of both hands. Movement from the temporal fossa along the lower edge of the eye to the inner corner of the eye; then up to the eyebrow and then stroking is carried out with the index and middle fingers along the eyebrow to the temple; in this case, the middle finger lies under the eyebrow, and the index finger above the eyebrow
- Stroking the orbicularis oculi muscles. Using the pads of the fourth fingers of both hands, they simultaneously stroke from the temple along the lower eyelid to the inner corner of the eye. Then they smoothly move to the upper eyelid and stroke it very lightly, without pressing on the eyeball.
Massage in the cheeks and chin area
The massage affects the zygomatic, cheek, chewing, and chin muscles, as well as the muscles that change the position of the lips (the laughter muscle, the levator anguli oris muscle, the depressor anguli oris muscle, the depressor of the lower lip muscle). Particularly important is the effect on the masticatory, pterygoid and temporal muscles, since the quality of movement of the lower jaw, the position of the mouth at rest, and the function of chewing depend on their condition.
Relaxing massage.
- The index fingers of both hands are located under the lower lip, and the rest are under the chin.
- The index fingers of both hands are located above the upper lip, the middle fingers under the lower lip, and the rest under the chin.
- Movement of all fingers (except the thumb) starts from the back of the nose, passes through the zygomatic arch to the auricles, fixing the fingers in the recesses at the tragus and earlobe.
- The movement is carried out with three fingers (index, middle, ring) of both hands from the midline of the forehead down through the temporal cavities to the middle of the chin.
Invigorating massage.
- Circular rubbing in the cheek area is carried out with the dorsal surface of the terminal and middle phalanges of the four fingers in the direction from the edge of the lower jaw to the edge of the zygomatic bone.
- In a similar way, circular rubbing is carried out from the middle of the chin up to the wings of the nose.
- In the area of the masticatory muscle, kneading is performed with spiral movements and circular rubbing.
- The back surface of the middle phalanges, clenched into a fist, shakes the cheeks both longitudinally and transversely.
Star Smile plates to help a child’s healthy bite
The standard Star Smile plate is more often used as a preventative when there are no changes in the bite and tongue position yet, but factors predisposing to this have already appeared. The child's need to suck often continues until school age and is sometimes unwisely encouraged by parents who want “a little peace.” Research has shown that more than 20% of children starting primary school still suck their thumb. But the older the child, the more firmly his bad habits are ingrained, and the more difficult it is for him to give up sucking his finger, tongue, or foreign objects. The authority of the dentist or orthodontist will help convince the child that the habit of sticking out the tongue and keeping a finger in the mouth can lead to serious problems. And only in this case will the treatment be successful if the doctor’s authority works. Treatment even in adulthood can always be successful, but it will simply take more time and money.
Massage of the inner cheek
Massage of the chewing, cheek and zygomatic muscles, and especially the pterygoid muscles, can be carried out with the speech therapist’s fingers positioned inside the child’s mouth. When massaging the left cheek, the speech therapist places the thumb of the right hand in the mouth, the remaining fingers remain outside. Massage movements are carried out with the thumb on the inner surface, and with the remaining fingers on the outer surface of the cheek. When massaging the right cheek, the index and middle fingers are inserted into the oral cavity, the thumb is on the outer surface of the cheek, performing the basic massage movements. Massage of the inner surface of the cheek can be carried out in different positions of the mouth: open and wide open - and with the jaws closed. The main techniques used are rubbing and kneading.
- Circular movements along the cheek from the periphery to the center and vice versa.
- Spiral rubbing and kneading with fingertips in a circle.
- Kneading in a circular motion and rubbing in the area of the masticatory muscle.
- Rubbing movements from the cheekbone down to the corner of the mouth. All fingers, except the thumb, are located at the edge of the zygomatic bone. Thumb - on the inside of the cheek.
- Rubbing spiral movements. All fingers, except the thumb, are located in the area of the tragus and earlobe, gradually moving towards the corner of the mouth.
- Spiral rubbing of the temporomandibular (zygomatic) joint area. In the open mouth position, find the “hole” at the earlobe. Massage the pit area with your index and middle fingers. The thumb serves as a support on the inside of the cheek.
How do physical therapy sessions work for speech delay?
Magnetic therapy and medicinal electrophoresis procedures are prescribed in a complex manner . Initially, the session time is specially shortened in order to monitor the child’s reaction. On average, a course of treatment consists of 10–12 procedures . Physiotherapy procedures for delayed speech development at the First Children's Medical Center are carried out under the supervision of specialists in a separate room. All hardware is certified and approved for use. The medical staff will help the child feel safe and able to tolerate painless procedures. If parents wish, they can be present during medicinal electrophoresis or magnetic therapy.
Additional methods include working with defectologists and correctional specialists, increasing the time spent with the child, activating social skills, and communicating with peers. Physiotherapy for delayed speech development can be prescribed at intervals of 2–3 months in the absence of contraindications. After courses of magnetic therapy and medicinal electrophoresis, improvements are noticeable in coordination of movements, motor function, as well as in psychological development: speech reserve increases, activity in communication with other children appears, and the range of knowledge expands.
To make an appointment with a doctor
Choose a doctor
Lip muscle massage
Relaxing massage.
- Using the palmar surface of the index fingers, make stroking movements along the upper lip from the corners of the mouth to the middle.
- The same movements are made along the lower lip from the corners of the mouth to the middle.
- The movement is performed with the pads of the index and middle fingers alternately with the right and left hands. The movement begins from the tragus of the auricle, the fingers easily slide along the cheek and then around the lips. In this case, the index finger slides over the skin of the upper lip, and the middle finger over the skin of the lower lip, coming together at the opposite corner of the mouth.
- Using the pads of the index and middle fingers, stroke the nasolabial folds, moving from the wings of the nose to the corners of the mouth.
- With the same fingers, lightly tap around the lips in a clockwise direction. Massage movements can be carried out with the mouth in different positions: closed and slightly open.
Invigorating massage . Rubbing techniques are used in the form of semicircular and spiral movements, kneading in the form of rubbing and vibration.
- The palmar surface of the index fingers makes movements along the upper lip from the middle to the corners of the mouth. The same movements are used on the lower lip.
- With the thumbs of both hands, make movements from the middle of the upper lip to the corners of the mouth and slightly down, and then with the index fingers - from the middle of the lower lip to the corners of the mouth and slightly up. The movements alternate.
- Stroke the nasolabial folds, moving from the corners of the lips to the wings of the nose.
- Using your thumb and forefinger, grab your upper lip into a vertical fold, squeeze it and rub it between your fingers. The capture is carried out in the central part of the lip.
- Use your thumb and forefinger to grab the skin around your lips and perform a pinching technique.
- The ends of the index and middle fingers are tapped intensively around the lips.
- Rubbing movements carried out by the thumb and forefinger in the direction from one corner of the mouth to the other along the upper and then lower lip.
- Spiral movements made with the thumb and forefinger along the upper and then lower lip.
- Spiral kneading of the nasolabial fold area. The phalanx of the thumb is located in the oral cavity under the nasolabial fold, the index and middle fingers are located on top.
- Point squeezing of the lip between the thumb and index finger. Localization of points.
- The speech therapist places his index fingers on a point located between the middle of the upper lip and the corner of the mouth on both sides. A movement is made towards the middle so that the upper lip is gathered into a vertical fold. A similar movement is carried out on the lower lip.
- The specialist places the index and middle fingers near the corners of the mouth and slightly stretches the lips, as if smiling; with a reverse movement, the lips return to their original position. Movements are light and smooth. These exercises can be performed with the mouth closed or open.
Tongue muscle massage
Violation of muscle tone is always more pronounced in the muscles of the tongue. Increased tone of the tongue muscles is observed much more often than decreased tone. There may also be cases of uneven distribution of muscle tone in the muscles of the tongue; for example, tone can be reduced only in an isolated group of muscles (one half of the tongue, root, tip, etc.). Massage of the lingual muscles, which have a complex structure and produce subtle, precise movements during the process of articulation, is the most complex procedure. In addition, performing massage movements on the tongue, as a rule, causes discomfort in the person being massaged. One should also take into account the fact that the tongue is a rather intimate part of the human body. Massage of the tongue muscles requires the speech therapist to have extreme precision of movements, accuracy and a certain correctness. When performing a massage, the following guidelines should be taken into account: differentiated massage of the tongue muscles is carried out either with rubber gloves, or through a gauze cloth, or through a sterile cambric handkerchief; When massaging the tongue, various devices can be used: probes, spatulas, toothbrushes, etc.; To do this, the speech therapist pulls the tongue forward as follows: grabs the tip of the tongue (through a handkerchief or gauze) so that the thumb is on top, the index and middle fingers are on the bottom, and slightly pulls it forward. The tongue is grasped with the left hand, and massage movements are carried out with the right. massage movements should be carried out in three directions, according to the location of the tongue muscles: horizontal, transverse and vertical.
Relaxing massage.
The most difficult is a relaxing tongue massage. With increased tone, it is difficult to keep the tongue out of the mouth; the velopharyngeal (gag) reflex can also make massage difficult. In this regard, when carrying out a relaxing massage of the tongue, it is necessary to strictly follow a number of rules: relax the muscles of the tongue only after relaxing other muscles, especially the muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle and muscles that provide movement of the lower jaw, since these muscles are closely related to the muscles of the tongue, especially its root; movements in a relaxing massage are mainly directed from the tip to the root of the tongue; Before the massage begins, the “border” of the velopharyngeal reflex is established. To do this, you need to gradually touch the surface of the tongue with a spatula, moving along the midline from the very tip towards the root of the tongue. The location that is associated with the appearance of the gag reflex is considered the “border” of the gag reflex. With increased tone, the “border” of the gag reflex can approach the middle part of the tongue, and in severe cases even to its tip. In these cases, the massage should be performed extremely carefully, gradually going beyond the “border” of the gag reflex; if, due to severe spasticity of the muscles, especially the root of the tongue, it is not possible to keep the tongue outside the oral cavity, tongue massage begins inside the oral cavity. Gradually, as muscle tone normalizes, the tongue is moved to a position outside the oral cavity; Before a relaxing massage of the tongue muscles, it is advisable to carry out special exercises to help relax its root: use your index finger or thumb to make light vibrating movements in the area of the submandibular fossa.
After this, they move on to the actual massage of the tongue muscles.
- Using the thumb and forefinger of the right hand, make stroking movements on one side, then on the other side of the tongue, from the tip to the root of the tongue and back. In this case, the index finger is under the tongue and serves as a support.
- Make stroking movements with the thumb and forefinger from side to side (from the midline to the side of the tongue and back), gradually moving from the tip to the root. The movements are performed first on one half of the tongue, and then on the other.
- The thumb and index fingers are on the lateral surfaces of the tongue - right and left. Stroke the side surfaces of the tongue from tip to root.
- Lightly knead the muscles in a horizontal direction. The thumb of the right hand is on top, the middle and index fingers are on the bottom of the tongue. Rubbing movements are carried out with gradual advancement from the tip of the tongue to the root and back, first on one side of the tongue and then on the other. The movements are very light without pressure.
- With the same position of the fingers, make circular rubbing movements easily, without pressure.
- Grasping the tip of the tongue with your right hand, lightly shake it.
- Apply light tapping of the tongue and light rhythmic pressure with a spatula (wooden or plastic).
- The thumb is on top, the middle and index fingers are on the bottom of the tongue, in its middle part, turn the tongue to the right and pull it slightly, as if slightly pulling the root part of the tongue outward. Then a similar movement to the left.
Invigorating massage.
When performing an activating (strengthening) massage, you should pay attention to the following points: movements during a strengthening massage are active, intense and directed mainly from the root of the tongue to the tip; the techniques of kneading and grinding are mainly used; as a rule, with reduced muscle tone of the tongue, the gag reflex is also reduced, so massage movements in this case can be quite active even in the area of the root of the tongue; if a decrease in muscle tone is observed only in some part of the tongue (for example, only on one half of the tongue), massage movements are performed mainly on the affected side; with reduced muscle tone, as a rule, hypersalivation (increased salivation) is observed, therefore, before performing the massage and during the massage, the speech therapist suggests that the child swallow saliva.
An energizing massage may include the following movements.
- Grinding in the longitudinal direction. Thumb on top, middle and index finger on bottom. Rubbing the muscles of the tongue from root to tip on one side of the tongue, then on the other.
- The position of the fingers is the same. Rubbing the tongue muscles with spiral movements, the pressure gradually increases. The movement is directed from the root to the tip of the tongue on one side, then on the other.
- The position of the fingers is the same. Rubbing the muscles of the tongue in a transverse direction on one side of the tongue, then on the other.
- The thumb and index fingers are on the sides of the tongue. Squeeze the tongue from the sides. Hold your tongue in a compressed position for 1 - 2 seconds, move your fingers a little and repeat the movement.
- The position of the fingers is the same. With your right hand, squeeze the tongue from the side surfaces, and with your thumb and forefinger, carry out rubbing movements, gradually moving from the root to the tip of the tongue.
- Using your thumb and index finger, make pinching movements along the edge of the tongue.
- Patting the muscles of the tongue with a spatula (or the grooved surface of a handle or toothbrush).
- Vibrate the tongue using a wooden spatula, which is applied to the tip of the tongue for 10-15 s. You can place a gauze roller on the child’s lower teeth to avoid damaging the mucous membrane of the lower surface of the tongue.
Treatment of dysarthria
Since dysarthria can be a manifestation of a variety of nervous system disorders, there is no single treatment regimen for this pathology. The child, first of all, should be examined by a neurologist. He also carries out the treatment. Classes with a speech therapist are auxiliary in this case; they are part of a complex of treatment measures, which also includes:
- drug treatment. After making a clinical diagnosis, the neuropathologist determines the order of treatment measures, prescribes medications, etc. All this is carried out taking into account the severity of the underlying neurological disease, as well as the age of the child. It should be remembered that there is no pill for dysarthria . The medications used in therapy eliminate the main symptoms of the pathology and alleviate the condition of the small patient, making him more susceptible to other methods of correction;
- massage. Manual procedures can reduce the severity of muscle paralysis;
- breathing exercises. Dysarthric children often experience difficulties with speech breathing. Special exercises help them learn to control the exhaled flow, which allows them to normalize the tempo and rhythm of speech;
- physiotherapy.
If you notice symptoms of dysarthria in your child, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. The sooner doctors and speech therapists begin to deal with dysarthric, the higher the chance of normalizing speech and avoiding difficulties with learning at school.
Even a mild form of dysarthria requires correction, primarily due to the fact that the child himself feels constrained. He is aware of the mistakes in his speech and is offended when others do not understand him. All this leads to the fact that a dysarthric child withdraws into himself and completely stops communicating with the people around him.
Work to normalize speech should be carried out not just by a speech therapist, but by a speech pathologist with sufficient qualifications and experience. When correcting dysarthria, special speech therapy techniques are used, without knowledge of which it is impossible to help a dysarthric child. And, of course, a speech pathologist must have great patience and endurance, because correction of dysarthria is usually difficult and takes a lot of time. The child may not make contact, refuse to complete the proposed tasks, or perform them incorrectly.
Despite all the efforts of specialists, in some cases the correction does not bring the desired results. The reason for this may be problems in the family. For a child to speak, he must be surrounded with love and care. Parental support is of great importance.
Soft palate massage
The massage is aimed at activating the tone of the soft palate and increasing the palatopharyngeal reflex. The main indication for massaging the muscles of the soft palate is the nasal tone of the voice. These movements are used only when the muscle tone of the soft palate is reduced. General recommendations for massage are as follows: the massage effect is usually directed not only to the muscles of the soft palate, but also to the lingual-palatine and pharyngeal-palatal arches; massage must be combined with passive and active gymnastics aimed at stimulating the palatine and pharyngeal muscles; massage movements are performed with the thumb or index finger of the right hand. Massage of the soft palate may include the following movements.
- Perform stroking, rubbing, kneading and screwing movements in the direction from the hard palate over the entire surface of the soft palate.
- Stroking, kneading and rubbing movements from right to left, grasping the lingual-palatal arches.
- Pressing movements made by the thumb or index finger over the entire surface of the soft palate in the longitudinal and transverse directions.
- The child pronounces the sound a or e for a long time. At this time, use your thumb or index finger to make rubbing and kneading spiral movements in the transverse and longitudinal directions.
- The child pronounces the sounds a or e briefly, abruptly, using a firm sound attack. At this time, perform jerking movements with the thumb in the area of the soft palate and palato-lingual arches. IN
postoperative period for rhinolalia, massaging movements should be carried out extremely carefully (only after the doctor’s permission) in two directions: longitudinally, along the line of the surgical suture, and transversely, along the border of the hard and soft palate. The movements at the beginning of the course of postoperative massage should be very light, stroking, and only gradually should one move on to kneading and pressing movements. It is very important to combine an activating massage of the soft palate with active and passive-active exercises aimed at reflex contraction of the muscles of the soft palate, muscles of the pharynx and muscles of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Passive and passive-active exercises that stimulate the work of the velopharyngeal muscles.
Using a spatula, which touches the root of the tongue, induce a reflex contraction of the muscles of the back wall of the pharynx and soft palate. Imitate chewing. Drink water in small sips or imitate swallowing movements (successive repeated swallowing movements lead to an increase in the time during which the soft palate is in a raised position). Coughing - this movement is performed repeatedly on one exhalation (leads to complete closure of the velopharyngeal ring). Yawning is a movement imitated by the child following the speech therapist. Repeatedly pronounce the vowels a, e with a firm voice attack. Gargle with small portions of warm water.
Tongue frenulum massage
If the frenulum of the tongue is shortened, massage movements are used to help stretch it. Using the thumb and index finger of your left hand, grasp the tip of your tongue and lift it up. The mouth is open. Using the index finger and thumb of your right hand, use a stretching motion to slide along the frenulum of the tongue from bottom to top.
Massage of the mucous membrane of the gums and hard palate In some cases, in addition to muscle tone disorders, a child may experience weakness of kinesthetic sensations. In such cases, in order to overcome articulatory praxis disorders, the complex of massage movements includes massage of the mucous membrane of the hard palate and gums.
- The child's mouth is open. The thumb is located on the outer side of the upper gum, and the index finger is on the inner side. Pressing vigorously on the gums, make movements from right to left, and then from left to right, first along the upper, and then in the same way along the lower gum (Fig. 102).
- Using your thumb or index finger, vigorously move along the hard palate, starting from the upper front teeth, towards the soft palate to the border with the soft palate and back.
Setting the sound R
There are many reasons for the incorrect pronunciation of the sound R. And it is advisable to exclude them before the age of readiness to pronounce the sound P, that is, up to 5 years. It is best to consult a speech therapist when the child turns 5 years old. Sometimes a pediatric dentist may refer you to a speech therapist if he notices any abnormalities during the examination. The best time to start visiting the dentist is 3-4 years, before obvious dental problems appear. But let's return to the consultation with a speech therapist.
During the consultation, the speech therapist examines the general mobility of the tongue, the structural features of the articulatory apparatus (lips, cheeks, palate, frenulum of the tongue), notes the type of swallowing, since it affects the formation of the bite, studies the features of sound pronunciation and the state of speech, records the type of breathing (nasal, oral, oronasal ), marks the position of the tongue. The classes that the speech therapist develops individually for each child, taking into account the cause of the pronunciation disorder, are aimed at establishing and automating the sound R.
The Dial-Dent clinic uses an integrated approach. If a speech therapist (or pediatric dentist, or orthodontist) identifies any of the reasons listed below, then you can undergo the necessary treatment in our clinic.
LITERATURE.
- Dyakova E.A. Speech therapy technologies Speech therapy massage: textbook. aid for students Ed. Center "Academy" issue-6
- Ogloblina I.Yu., Tantsyura S.Yu. Speech therapy massage: games and exercises.
- Prikhodko O. G. Features of speech therapy work for dysarthria with children suffering from cerebral palsy and other types of neurological pathology // Development and correction. - 1999. - Issue. 5.
- Serbina A.F., Voloskova N.N. A set of techniques for massaging speech and facial muscles for dysarthria. Dysarthria, clinical, neurolinguistic, psychological and pedagogical aspects of the problem: Educational and methodological manual. — Stavropol, 1996
Contraindications
Speech therapy massage for children with dysarthria cannot be performed when the child has:
- rash, swelling of various types on the skin;
- exacerbation of herpes infection;
- colds, viral diseases;
- inflammatory processes of the oral cavity and lips - stomatitis, gingivitis, caries, fungal infection;
- inflammatory processes of nearby organs - conjunctivitis, rhinitis, lymphadenitis, furunculosis;
- cuts, abrasions, hematomas;
- severe chronic diseases - oncological, cardiovascular, hematological, neurological, psychiatric.