Clinic La Salute Neuropsychology What to do if a child does not understand spoken speech
Receptive language disorder involves a complete or partial absence of auditory perception of spoken words. Deafness has nothing to do with this; the main problem lies in the baby’s brain and his mental state.
If your child does not understand spoken speech at 3 years old, this is a reason to think about his condition. Some parents consider the baby’s delayed development to be normal, but sometimes this factor is a symptom of a serious illness. Let's consider in what cases minor delays in speech development are natural, and when they talk about violations, what should parents do when pathologies are identified.
Pediatric neuropsychology
How to understand that a child does not understand speech
Adults may mistakenly think that the baby does not perceive their speech well. Therefore, it is important to distinguish the norm from deviation. There are main signs of the disorder:
- Impaired understanding. In this case, the child:
- does not respond to calls to him, as if he were deaf;
responds to whispers, but not to loud speech;
- does not respond;
- does not understand the same request formulated differently;
- confuses the meaning of questions and gives answers at random;
- when responding to a phrase, pays special attention to the adult’s facial expression;
- requests made in an unusual environment are met with confusion and misunderstanding;
- constantly repeats the question asked.
- Reflection of adult behavior. The child often repeats the gestures of the person talking to him or phrases heard from cartoons and television shows. He does this unconsciously, considering this to be his own initiative. The stronger the disorder, the more repeated phrases are found in his speech.
- Possibility of initiation. Despite poor understanding, the child can still start a conversation first with the correct phrases and engage in dialogue.
- Reduced communication. The child remembers how his previous attempts to maintain a conversation ended, when phrases inserted incorrectly in meaning led to aggression or ridicule. Such negative experiences cause him to avoid all social interactions. Among his peers, he prefers to communicate with quiet guys and not get involved with active “ringleaders”.
- Increased productivity on visual tasks explained in nonverbal ways.
- Striving for consistency. A child with this disorder will always want to keep his social circle unchanged due to the lack of understanding of other adults.
- Increased anxiety. This is not a symptom of the receptive disorder itself, but is caused by an adaptation disorder. The environment and family directly influence the degree of anxiety of the child.
- Obsessive actions. Lip biting, finger wringing, and many other habits are signs of tension caused by maladjustment.
- Inability to control your behavior. Children with receptive disorder are often hyperactive and impulsive. In the absence of an adult who regulates his actions, this manifests itself especially strongly.
If several of the listed symptoms coincide with the child's behavior, but you are not sure that he has a receptive disorder, the following tests can be performed.
For a child from 1.5 to 3 years old
Ask your child to bring any item: toys, fruits, vegetables. If he fulfills the request or simply looks at the named thing, then he has no violation.
For a child 3 years or more
A baby can be considered healthy if he is able to:
- Fulfill any complex request. For example, take a toy and put it in a box.
- Point to pictures with a specific action. For example, find a person who is eating or sleeping.
When testing, it is worth considering that the child may know exactly the set of words that are required of him. Therefore, this method cannot be considered completely reliable.
Possible reasons why a child does not understand speech
This symptom accompanies many disorders and diseases. To determine the cause of the disorder, you need to visit a specialist for further diagnosis. Let's consider the factors that cause misunderstanding of addressed speech.
Hearing loss
Children who become deaf at an early age or are born deaf do not even perceive non-speech sounds. Due to such limitations in knowledge of the surrounding world, intellectual deficits develop and learning difficulties arise.
Mowgli syndrome
“Children-Mowgli” have no experience of communicating with people, since from childhood they were isolated or among animals. Because of this, they lack understanding of speech. The development of social skills occurs through imitation of others. They repeat the sounds and gestures they hear, but cannot give an adequate response to calls.
Autism
Children with low-functioning autism have poor auditory perception. However, they understand speech selectively, reacting only to topics of great interest to them, while not responding to their own name or responding to requests.
Alalia
Children with sensory alalia do not divide sounds into speech and non-speech, and also do not speak themselves. They perceive people's speech as meaningless noise. They cannot connect the object and its name. In mild cases of the disease, understanding some words is possible.
Landau-Kleffner syndrome
Unlike previous disorders, with this disease, receptive impairment manifests itself between the ages of 3 and 7 years within six months. First, the child loses the ability to understand speech, and then to speak independently. Symptoms also include epileptic seizures.
Aphasia
Different forms of aphasic syndrome exhibit different symptoms. There may be a complete misunderstanding of phrases or only a partial one. Brief description of the types of pathology:
- Semantic. The main defect of this type of disease is impressive agrammatism, that is, the child does not understand complex speech patterns that reflect cause-and-effect and spatial relationships.
- Dynamic. Implies partial understanding of speech due to lack of concentration.
- Total. With this form, only situational perception is preserved; abstract topics are inaccessible to the child’s understanding. He cannot both perceive and communicate.
- Acoustic-mnestic. Short phrases are understood by the child without problems, but, having heard a detailed speech series, he is lost because he cannot retain a large amount of information in memory.
- Acoustic-gnostic. The child reacts only to the adult’s gestures and facial expressions, without listening to requests.
Mental retardation
Congenital oligophrenia implies a poor vocabulary, problems with sound pronunciation and problems with analyzing information. The degree of change in speech perception depends on the level of the disease:
- Idiocy - understanding is practically zero, with the exception of a partial reaction to facial expressions and gestures.
- Imbecility - perceives only a narrow range of situational, everyday topics. The child accepts new information with great difficulty.
- Moronism - the patient can carry on a light conversation, but does not have developed abstract and logical thinking.
Dementia
In addition to weakening intelligence, children with this disease are plagued by reduced speech activity. Symptoms are comparable to a total form of aphasia.
Why can a child of 2 years be silent or speak poorly?
Of course, the reasons why a baby may not talk or do it with great difficulty at this age can be caused by injuries, illnesses or developmental delays. However, experts identify 2 more reasons, not related to the above problems, why a baby may experience difficulties with speech formation:
- Lack of sufficient spoken communication. Speech therapists say that it is necessary to talk with the baby from the first days of his life. This should be done not only so that he hears words and sentences, but also to awaken his interest in speech. Subsequently, this will help to captivate the child, and he himself will strive to quickly master conversational skills.
- Slurred, fluent, or rapid speech in adults. If the child’s environment communicates too incomprehensibly for the baby, he simply will not be able to understand and repeat the words of adults. Parents should speak more slowly, more clearly and expressively, and not only in direct communication with the baby, but also when they are simply nearby.
Speech norms for children
Knowing what children should be able to do at different ages helps judge the presence or absence of pathology.
| Age | Norm for development of auditory skills |
| From 0 to 1.5 years | The child listens to the parent’s voice and reacts to intonation. Distinguishes the voices of loved ones, knows his own name. Accepts simple requests, for example, to stop doing something or to give a hand. By the age of 1.5 years, he begins to understand the names of some objects and recognizes them in pictures. |
| From 1.5 to 2 years | The child can point to a specific action in a plot drawing, for example, show who is sleeping or eating |
| From 2 to 3 years | Able to carry out requests with multiple actions, such as walking into another room and taking an apple from a cup. Understands fairy tales and stories heard |
| From 4 to 5 years | The child perceives complex sentences, as well as the meaning of various prepositions |
Standards for developing speaking skills
It is important to note that normative indicators are fairly generalized and dry data. They do not take into account the individual physiological and psychological characteristics of the child, which in most cases play a decisive role. In many cases, only specialists can determine whether the baby has any difficulties or abnormalities.
Be that as it may, the official norms for the development of the speech apparatus in children are considered to be:
- up to 5-6 months – the period of humming, when the baby makes sounds that are intonationally similar to familiar words;
- 7-8 months – 1 year 2 months – imitation of animals, repetition of monosyllabic words (“give”, “ma”, “ba”, “meow”, “woof”);
- 1 year 2 months – 2 years 6 months – expansion of vocabulary, compilation of the first phrases, phrases and sentences;
- 2 years 7 months – 3 years 5 months – consolidation and clear formulation of sentences, word games, composing stories out loud.
It should also be taken into account that girls begin to speak much earlier than boys. They actively imitate adults, quickly copying their words, intonation and pronunciation. In turn, boys find it easier to form grammatically correct sentences.
How to help your child
It is important to provide the baby with the conditions for development. Relatives and specialists should participate in this.
Rules for interaction between parents and children
A child with this disorder needs not only psychological and medical help, but also understanding from mom and dad. To facilitate learning, adults need to:
- Take your child for a walk regularly.
- Read light stories with pictures together.
- Conduct training sessions.
- Compose phrases from words that the child can understand. For example, replace the sentence “let’s go open the door” with the simple word “door”.
- Limit TV viewing. The baby will remember random words and phrases from advertisements and cartoons, which will complicate his learning.
- Provide the child with a sense of security and mutual understanding. Eliminate punishments for misconduct.
- Observe how the baby reacts to your speech. For example, he can: ignore a request or do something different from what was asked, better perceive information from one of the parents, carefully monitor gestures.
- Each action is accompanied by the same comment. For example, if you call your baby for a walk, repeat “let’s go for a walk” every time.
When addressing a child, you should follow these rules:
- look the baby in the face when talking;
- voice actions recently performed together, for example: “we ate” or “we went to the park”;
- speak in as short sentences as possible;
- pronounce words loudly, clearly and clearly, without distorting intonation;
- point to the named object.
Health care
If you notice symptoms of a receptive disorder, the first thing you should do is make an appointment with several specialists:
- Neurologist.
- Otolaryngologist. The doctor will confirm or rule out the presence of ear diseases.
- Speech therapist. Assess the degree of speech development and help you master the language.
- A psychiatrist who will work to prevent the development of mental disorders in a child.
During the examination, you may be redirected to other doctors, and may also be prescribed vitamins or nootropics to facilitate learning. Massages, physiotherapy, and psychological correction are also used for treatment.
Neuropsychological support
Neuropsychology helps evaluate disorders in detail. During the examination, the doctor examines systemic dynamic changes in the child’s brain. This allows for the development of an individualized treatment plan that addresses all aspects of the receptive disorder.
To be examined by an experienced specialist, visit the La Salute clinic. A neuropsychologist with 14 years of experience works here. Danilina Kamilla Kasimovna will understand your problem, draw up an individual plan for correcting the child’s condition, and help the child establish communication with peers and adults.
Speech therapy correction
The help of a speech therapist is necessary throughout the correction of the disorder. It can be carried out either individually or in a group of several children. Possible training methods:
- Tomatis - most effective when a disorder occurs in the first two stages of development of speech perception;
- ABA program – intensive study of the diagnosis, based on individual characteristics;
- Logorhythmics is a system of motor exercises in which movements are combined with the utterance of special phrases or musical accompaniment.
Classes with a speech therapist are aimed at the comprehensive development of the child, knowledge of the environment and adaptation. As a result of the correction, the following are processed:
- perception;
- memory;
- attention;
- communication skills;
- speech disorders.
Delayed speech development is one of the most pressing problems in pediatric neurology today, which, unfortunately, also affects absolutely healthy children. What to do if your child does not speak? Often the parents themselves are the cause of a child’s speech difficulties. What to do and what not to do so that your child speaks correctly and on time.
The main stages of child speech development
You can start developing your baby’s speech from the first day of his birth. The first thing you need to pay attention to is how the baby cries. A baby’s cry from birth is very different, it becomes especially expressive in the first month of life, from it you can understand what the baby needs: he is cold, he is in pain, he wants to eat or go to the toilet, or maybe he just wants his mother to hold him in his arms. . If the child does everything correctly intonationally, then an attentive mother quickly learns to understand the difference and respond to these “requests.” In this case, mental and then speech development occurs harmoniously. If your child cries monotonously, at the same level, and does not respond well to the voice, consult a doctor.
If the child is healthy and has no hearing problems, then in response to positive emotions in the second month of life he begins to “walk.”
Along with the “humming”, the first laughter appears - squealing in response to emotional communication with an adult. The sounds of “humming” are already distinguished by a certain variety with a predominance of combinations of guttural and vowel sounds (“gu”, “ge”, “ha”, etc.) With these sounds he tries to communicate, reacts to what is happening around him. If the baby does not start to “walk”, consult a doctor; perhaps he has a problem with his ears. At two months, the period of onomatopoeia begins: the baby carefully follows his mother’s lips when she talks to him, and seems to be trying to repeat these movements, but so far silently.
So, by 3.5-4 months, a true “humbling” is formed, where the child focuses on the pronounced sound, syllable, as if listening to himself. During the period of true “humming,” the sounds become longer, melodious, and more varied. Along with laryngeal and vowel sounds, labial sounds and combinations of vowels and labials are increasingly appearing. By six months, the child develops babbling speech - he begins to pronounce some individual letters and syllables. During this period, it is important to monitor intonations - how he speaks, how he cries. At six months, a healthy child should already be chatting, pronouncing certain syllables, and repeating specific sounds after his mother. During the period of babbling, imitation of the sounds of an adult becomes more distinct.
By the end of the pre-speech period, the child’s nonverbal forms of communication with others become more complex. Communication is carried out using both hands, more differentiated facial expressions and sounds. The child reaches out his hands to his mother, utters separate sounds, as if asking “take me.” Then facial expressions become more complex. She becomes more expressive, symbolic gestures appear. The child can communicate using one hand. Babbling words of various intonations appear.
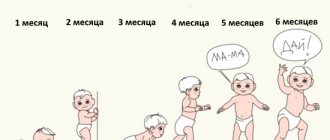
By the age of one year, a child should speak from 8 to 10 simple words: “mom”, “dad”, “baba”, “give”, “na”, that is, short simple words of several syllables. It is during this period that early speech development ends and motor speech begins to form as a way of communication between people.
After one and a half years, a child easily pronounces familiar and unfamiliar words by imitation, both addressed to him and accidentally heard from others. Intensive development of motor speech usually begins in the second half of the 2nd year of life. Until one year and six months, a child pronounces about 30 words with simple sound composition. At two years old, a child already speaks more than 200 words, he has almost phrasal speech, he should already be able to formulate a simple thought or request: “Mom, let’s go to the store, you promised to buy me a toy.” However, he may still pronounce some sounds unclearly. By the age of three, a child’s speech contains up to 1200-1500 words, including almost all parts of speech.
This development is considered normal. But this happens only when the parents constantly talk to the child, tell him fairy tales, and sing lullabies. A very big problem today is that live speech is increasingly being replaced by gadgets. Because of this, many children who were initially born healthy from a neurological point of view do not begin to speak in time.
If a healthy child at 2.5-3 years old does not speak phrasal speech at all and, at best, only speaks a few simple words, he has a delay in speech development, and this, unfortunately, must be treated.
Speech develops gradually
It takes time for a child to learn to speak correctly and construct logical, figurative phrases. When a child is just learning to walk, he takes his first hesitant steps with his mother’s help, and after six months to a year he is already running, jumping and dancing on his own. The same thing happens with speech: it develops gradually. The child not only remembers new words, but also at the same time trains articulatory muscles and learns to control intonation. This takes more than one year. Therefore, if at 3-3.5 years old your child is just beginning to pronounce the first words and construct the simplest phrases like “Mom, give me”, then by the age of six, when it’s time to go to school, he will not have developed full-fledged phrasal speech. It is important to develop speech gradually, but from a very early age.
Causes of delayed speech development
The first and most basic reason is brain damage due to ischemia, hemorrhage, and infection. But such deviations are immediately diagnosed, doctors monitor the child and take all necessary measures. These are the patients with whom a neurologist, psychologist and speech therapist are already working.
But there is a category of patients who are born absolutely healthy. But due to errors in learning, they also begin to experience delays in speech development. Most often, the reason is parents’ excessive fascination with mechanical sound, that is, sound from a TV, computer, tablet, phone. Children who watch a lot of cartoons or constantly play with singing-talking toys develop passive speech well, but their own active speech is not formed. This occurs due to the difference in wavelength between live speech and mechanical speech. In order for a child to start talking, you need to talk to him as much as possible, read fairy tales yourself, and sing lullabies.
Under no circumstances should a TV or radio be allowed to work in the background in the room where the baby spends time. Of course, if you want to show your child some cartoon or program on the computer, this can and should be done, but after watching the device you need to turn it off and put it away.
Of course, all these devices and toys allow mom to relax a little or do some of her own business. But when they replace live communication, this leads to serious problems with the child’s psyche. It’s better to prevent such things from happening than to have to spend years catching up. To restore the correct speech pattern in a three-year-old child, to change his perception, a lot of effort and time is required: the child cannot quickly catch up with such gaps, he has to resort to intensive drug treatment, and additional classes with speech therapists. This is a long and difficult path. Why bring it to this point if you can do everything right from the very beginning?
Why you need to sing lullabies
Singing lullabies is an important part of raising a child. The most famous lullabies, for example, “bayu-bayushki-bayu,” were invented back in the 5th-6th centuries, and it is no coincidence that we still sing them to children. They are built specifically in the timbre and wavelength fluctuations that are understandable to the child, calm him, and develop the brain. Each age has its own songs that need to be sung. Humming such lullabies to a small child and simultaneously rocking him in your arms creates the basis for proper mental development.
Nowadays, many couples approach pregnancy planning with full responsibility: they lead a healthy lifestyle, undergo all tests, read books about the health and raising of the unborn child. Include in this preparation and learning at least a few lullabies to sing to your baby. No matter how simple they may seem to you, they contain folk wisdom that has been proven over centuries for the correct development of personality, this is very important. Sing these lullabies for at least a year.
By the age of two, when the child already understands phrasal speech well, songs can be selected that are more plot-based, so that while the mother sings, he can imagine this picture in his head.
Talk to your child as much as possible
Don’t rush into conversations with your baby, calmly and measuredly tell him what’s happening around him, voice your actions. Then he will begin to perceive by ear the name of this or that object, and this is how passive speech is formed. From six months onwards, add details about the color and volume of objects: “small toy”, “red ball”. When you do this constantly, the child learns to hear and understand you.
This helps to explain to the baby after a year that panties should be dry, that is, it is quite early to potty train the child, and not use diapers all the time. At one and a half years old, the child is able to hold the bladder and control his pelvic functions. This is one of the important links in mental development. Of course, he will eventually learn to ask to go to the toilet himself, but these skills will come much later and not in the form in which he would like.
Therefore, it is very important to accustom yourself to talk to your baby as much as possible and limit mechanical sounds around him as much as possible - these are the most important parts of preventing speech development delays. If we build this correctly, then at the age of 2.5 years the child begins to speak in phrasal speech, and parents have no problems with his behavior or learning. If your child at 2.5 years old does not speak, especially if there is no so-called gibberish speech, he is silent and does not voice the game, a request addressed to you for something, then this is not a variant of the norm, this is a problem that needs to be dealt with.
How to talk to a child
- You need to talk to your child in a normal timbre; it is your tone and timbre that the child knows from his prenatal state.
- Try to speak in simple phrases, but do not lisp or distort words.
- If a child has a problem with vision or hearing, then the mother needs to start brightly painting her lips as early as possible so that he can watch her lips and understand exactly how she pronounces sounds.
- If a child had problems with swallowing in the first year of life, then, unfortunately, problems with sound pronunciation cannot be avoided. You can start working with a special speech therapist already in the first months of the baby’s life, even in the pre-speech period.
- Solve all problems as soon as they appear, do not put it off and do not wait for it to go away on its own. It won't work.
Is it a speech therapy garden or a regular one?
So, the child has grown up, and it’s time to decide which preschool institution to take him to. At this moment, it is important to figure out whether your baby has mental and speech problems, and what they are.
When the baby does not have any serious medical problems, start with a regular kindergarten. If in the first year your speech does not level out and develop to the required level, then you should apply for a medical-pedagogical commission. It runs from February to June. You can get a referral from a preschool or call them and make an appointment. To pass the medical-pedagogical commission, you must have a conclusion from a neurologist, speech therapist, or psychiatrist about the state of your child’s health.
If a child begins to speak in phrases, but does not pronounce certain sounds, then you can take him to a regular kindergarten that has speech therapy groups. There they work with children with normal psycho-speech development, but with incorrect settings for the sounds themselves. Typically, a speech therapist begins working with such children at the age of five in order to improve their speech and correct all weak sounds before school. On average, it takes three months to set and consolidate one sound.
One of the common disorders in children 3-3.5 years old is the so-called porridge in the mouth, when, due to a violation of the innervation of the speech muscles, the child cannot pronounce some sounds clearly and clearly. In this case, you cannot do without the help of a specialist; it is better to contact a neurologist to determine the exact cause of dysarthria and carry out the necessary treatment, if necessary; you also need to visit a special speech therapy garden. This requires an integrated approach: simultaneous coordinated work of a speech therapist, neurologist and psychologist.
The distribution of children into specialized groups or kindergartens is carried out by a medical-pedagogical commission.
And again, I repeat, it is much easier to prevent speech development delays, so that those children who could speak, but did not start due to lack of parental attention, do not end up in special groups. To do this, it is important not just to talk with the child, but to hear what he is talking about, try to understand him and respond to his words. I assure you, if you establish this contact from childhood, it will last a lifetime and will help your child become a good member of the family, society, reliable support and support for you.
How to prevent stuttering
There are times when a child does not begin to speak for a long time, but at the same time they work with him, he accumulates a large passive vocabulary, and can compose phrases in his head. If you start his speech process too actively, he will not be able to cope with the flow of speech and will begin to stutter. Most often this happens at 2.5-3 years. Children with tics (obsessive blinking, blinking, sniffing, etc.) are especially susceptible to stuttering. If you notice that the child begins to stammer at the beginning of speech, this is a signal that you need to contact a neurologist to solve the problem. Of all obsessive disorders, stuttering is the most difficult problem, which can take years to treat.
The pacifier and the child's speech development
Another important aspect of preventing speech delay is prolonged use of pacifiers and prolonged breastfeeding. I mean the situation when a pacifier or mother’s breast is in the child’s mouth not for soothing or feeding, but just like that, in a state of wakefulness. In this case, the problem arises purely mechanical: in order to speak, the mouth must be free, but if the mouth is busy, then it is impossible to speak - the nipple or breast is in the way.
The pacifier can be used when the child falls asleep, when he is sick, or when he hits himself, but it must be removed while he is awake. After two years, the pacifier should be completely abandoned. This will help avoid speech problems and maintain proper bite, which will significantly reduce your financial costs in the future when an orthodontist treats your beloved child’s unsightly teeth.
The same applies to the mother's breast. It should be a source of food or a means of calm, nothing more. Of course, breast milk contains a lot of good substances, but it is needed only until the child begins to eat normal human food. Breast sucking is very important for the formation of psychological communication between mother and child. But by the age of two, the child already understands spoken speech well and can speak himself, so this connection only strengthens and will not be interrupted in any way after the child is weaned.
It is important to wean your baby from thumb sucking from the very beginning. By the age of 2.5-3 years, the child should be comfortable without a pacifier, mother's breast, or thumb sucking. Why? During sucking, rocking-forward movements give a feeling of calm and sedation. With age, the child’s need for such movements weakens; now he needs to explore the world around him and be active. And if a child continues to suck a finger or a pacifier, then he automatically transfers himself to the infant period, behaves like a baby and does not give himself the opportunity to fully develop.
Gadgets: harm or benefit
Modern devices, on the one hand, are very useful, but when it comes to children, you need to be extremely attentive and careful. Nobody says that you shouldn’t use TV and gadgets at all. This is an important part of modern life, children should be able to master them. But a small child does not yet have the skills of speech, movements, motor skills, proper mental development, criticism, self-criticism, and the ability to control oneself are incorrectly formed. Therefore, it is very dangerous to uncontrollably give him something that can provoke abnormal development.
In Russia, little is said about this, and today in most families gadgets are used beyond the permissible limit; for each family member, including an infant, there are from two to three gadgets. At the same time, in the same high-tech Japan, children are allowed to use a telephone or computer only from the age of five, when the nervous system has matured. And I agree with their approach. Yes, you can turn on some educational games or cartoons for your child, but no more than 30-40 minutes a day on a good screen with good sound. It is better to avoid tablets and smartphones, because young children quickly develop color and tactile addiction.
Into the wilderness, into the village
Finally, I would like to advise all parents to spend more time with their children outdoors. This will be especially useful for children who have problems with psycho-speech development. The best thing is to go to the countryside for several weeks or even months, where there are only living sounds of nature from a running stream, the rustling of leaves on trees, the buzzing of a bee and other sounds, where there is no urban, mechanical sound from the hum of wires. This will not only help normalize sleep and give peace of mind, but will also give the child’s brain overloaded with information the opportunity to rest and gain strength to overcome all difficulties in speech development.
Chief pediatric neurologist of the Ministry of Health of the Tver Region Galina Anatolyevna Zueva
VIEW SCHEDULE √ CHECK OUT PRICES
You can make an appointment or get a consultation by calling: +7;; +7 914-704-32-22.
Or, fill out the form online:
If you have any questions, ask them in the comment form below↓↓↓
How should parents behave if their child does not understand spoken language?
It can be very difficult for mom and dad to raise a child with a receptive disorder because the child does not pay attention to the adult's speech. Due to his unstable behavior, increased anxiety and whims for no apparent reason, it seems impossible to train him in any way to perceive the information he hears.
However, do not despair and be left alone with the problem. It is necessary to contact specialists so that they can comprehensively understand the violation and develop an effective correction method. The neuropsychologist at the La Salute clinic not only conducts diagnostics to identify the source of abnormalities, but also helps stimulate the development of children with various forms of disorders.