The development of speech in a young child (1-3 years) is a very important stage in mastering their native language. The baby’s speech not only develops rapidly, it is formed. Therefore, helping a child develop speech during this period is especially important. Properly organized speech communication and speech classes not only stimulate the child’s speech development, but also help compensate for possible disorders, for example, a lag in speech development.
How to develop a child's speech
We continue the conversation about the development of a child’s speech , which began in the first part of the article devoted to this problem.
The movements of the body and organs involved in speech production have common mechanisms, therefore the development of fine motor skills of the hands directly affects the development of speech. It is for this reason that finger exercises for the development of speech in children should take a strong place in your activities with your child.
Training finger movements will, as it were, prepare a platform for further speech development. You can start training your baby’s fingers within the first 5 months.
Now let's see how you can help your child master their native speech, teach him correct pronunciation, constructing phrases and forming thoughts.
Remember: classes should be held in the most easy, fun and playful way possible. Then they will bring real benefits and bring real pleasure to both of you.
A set of measures for speech development (to be carried out at home):
- Development of fine motor skills
- Speech gymnastics
- Logorhythmics
We do not mention here such areas of work on speech development as speech therapy massage, special exercises for practicing various sounds, developing phonemic hearing, and some others. They are the area of application of exclusively professional knowledge and skills. Here it is better to trust a specialist rather than try to cope with this task yourself.
Benefits for developing fine motor skills:
- Matryoshka dolls
- Velvet paper
- Plasticine
- Mosaic
- Laces
- Beans, peas
- Semolina
- Salty dough
- Counting sticks
- Multi-colored clothespins
- Beads
- Cloths with sewn buttons
- Stencils
- Massage ball
- Wooden construction sets
Fine motor skills:
- Passive gymnastics - massage for the development of fine motor skills.
- Active gymnastics - games for the development of fine motor skills: poems and nursery rhymes, finger games, finger theater.
Creating a developmental environment
In order for a child’s speech to develop, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for this. The most important thing is to talk to the child as much as possible, because speech is based on imitation - repeating words and phrases after an adult. Speech should constantly surround the baby; he should “bathe” in speech. To do this, the adult comments on all everyday situations, routine moments and other events in the baby’s life.
For example, washing: “Let’s go wash. Let's open the tap. No, not this way, the other way. Like this. Where's the soap? Here's the soap. Take soap and wash your hands. Put the soap in the soap dish. Let me help you. Three hands good. Now let's wash off the soap. Place your hands under the water - like this. Now let's wash our face. Take water into your palms and rub your face. Close the tap. Now let's shake the water off our hands - like this. Where's the towel? Take a towel and dry your face and hands. Well done! Look how clean it has become.”
Perhaps such a constant conversation with the baby will initially cause some difficulties for adults and will require a change in communication style and behavior. But as experience shows, this is a matter of training: if there is a desire and enough persistence, then an adult can, over time, learn to communicate with the baby more constructively from the point of view of the child’s speech development. At the same time, with experience comes a “sense of balance”: you need to speak constantly, but at the same time not overdo it and not be too verbose, speak with normal volume, simple phrases and only to the point.
Passive gymnastics (massage)
It is better if an experienced professional shows you the massage technique, but you can master the simplest techniques yourself.
The massage is performed with one hand, the other holds the massaged hand. Session duration: 3 – 5 minutes; carried out several times a day.
Massage includes the following types of movements:
- Stroking - performed in different directions;
- Rubbing - differs from stroking with a greater force of pressure (the hand does not slide over the skin, but moves it);
- Vibration - applying frequent blows with the tips of half-bent fingers;
- Massage using a special ball - with the ball you need to make movements in a spiral from the center of the palm to the tips of the fingers; practical advice: you need to use a hard ball, that is, it should not be easily deformed (then the impact will be maximum);
- Flexion-extension of the fingers - the fingers are initially clenched into a fist, each in turn is extended and massaged from the side of the palm in a circular motion from the base to the tip.
What to do if the child has not started speaking?
At the age of 2, my daughter stubbornly refused to speak, despite all my attempts to use a comprehensive and varied approach to the development of the speech apparatus. This was felt especially acutely when I saw the disapproving glances of my relatives, who believed that I was simply not working with my daughter.
Any parent will be concerned about the silence of a child at two years old. How can we determine whether this is a consequence of an illness, some kind of developmental disorder, or is it an individual characteristic of the child? There are several reasons for “silence” and ways to resolve them.
| Cause | Solution | |
| 1. | Heredity | If one of the child’s parents began to speak late, then this feature can be inherited. In this situation, you just need to bide your time. |
| 2. | Features of character and temperament | Some children can be shy and timid even at 2 years old. If the baby is not very willing to play with other children, prefers loneliness and is generally quite calm emotionally, then perhaps his speech development will not be as rapid as that of other peers. |
| 3. | No need for speech | If, at each child’s request, the mother immediately gives him the right thing or performs a certain action, then the baby does not need to develop speech. The child should be given the opportunity to show his need in every possible way, playing at the “stupid adult.” |
| 4. | ENT diseases and neurological defects | It happens that the cause of speech delay is disorders of the ENT organs (defects, diseases) or various neurological abnormalities. In this case, consultation with an otolaryngologist and neurologist is necessary. It would also be a good idea to show the baby to a psychologist and speech therapist. It is recommended to contact several specialists to get different opinions. The doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment and give recommendations. |
| 5. | Excessive parental pressure | Parents who want their children to start speaking as early as possible sometimes go too far and literally force the child to speak. At such a tender age, the baby’s psyche is very vulnerable and under the pressure of his parents he can become completely silent. You should reconsider your methods of speech development and, perhaps, give your child a break. |
| 6. | Lack of interest | The baby may simply not like the developmental games that his mother plays with him, considering this or that game the most effective. You need to take a close look at the child’s interests and offer him activities that will bring him pleasure. |
| 7. | Lack of society | If all the child’s communication occurs only with mom or dad, then speech development can proceed quite slowly. Communication with peers will give him a lot of pleasure and arouse interest in communicating with them. If your child does not go to kindergarten, you can attend educational clubs, where age-appropriate group classes are held, or simply communicate with other children on the playground. |
Active gymnastics: games for developing speech using fine motor skills
Game aids:
- Butterflies made of colored paper
- Leaves of colored paper
- Pinwheel
- Cotton balls
- Paper boat
Games for children from 2 months:
- That's how different they are. Objects of various textures and shapes are placed in the child’s hand. The baby must grab the object and hold it for a while. This exercise develops not only motor skills, but also tactile sensations. It’s good if you comment on what is happening: “This ball is smooth,” “This hedgehog is prickly,” etc.
Games for children from 9 months
- Prefabricated nesting dolls. First you need to collect one doll, then gradually complicate the game; after 2 years it should be a triple matryoshka.
- Pyramids. First you need to use a classic pyramid, the size of the rings of which decreases towards the top.
- Trace along the outline. You need to make cards with images of objects known to the baby, for example, a house, a tree, a car, and paste over their outlines with velvet paper. The essence of the game: an adult guides the baby’s finger along the contour and names the object. Then the outline is covered with beads or peas and the game is repeated.
- Cups and spoons. The child uses a spoon to pour sugar or semolina from one cup to another. You can also transfer beans, peas or nuts by hand.
- Modeling from plasticine. You need to start with a cylinder, and over time complicate the tasks: a ball, a carrot, a snake.
During the games, do not forget to comment on your actions and explain to your child everything that you do.
Games for children from 1 year:
- Strong palms. The child squeezes rubber toys. The best thing is the rubber hedgehog: the needles act like a massager.
- Mosaic. First you need to lay out simple shapes: paths, flowers, squares, and then move on to more complex ones: houses, cars, Christmas trees.
- Constructor. The size of the parts and the complexity of the design depend on the age of the baby: you need to start with the largest parts and the simplest structures, for example, building a turret.
- Beads. The size of the beads also depends on the age of the child. First, instead of beads, you can use balls from pyramids with round parts and string them on a thick cord; then the size of the parts must be gradually reduced, moving on to real beads. For the exercise, medium-sized beads already strung are used. The goal is to teach the child to lay out the outlines of objects from beads. For example, you can lay out a circle, square, heart, spiral, etc.
- Laces. Since lacing has different contents, it makes sense to play with the lacing process - for example, ask the child to sew a dress for his mother (lace-button) or lace shoes (lace-boot).
- Magic tray. Sprinkle a thin layer of semolina onto a tray and run the child’s finger over the cereal. The child is then shown how to draw various shapes. At the age of 2 - 3 years, you can draw numbers and letters.
- Multi-colored clothespins. The essence of the game is to teach the child to independently attach clothespins, and to make the game interesting, you can do this according to a thematic principle: rays to the sun, needles to the hedgehog, rain to the cloud, grass to the ground. Of course, for this you first have to make preparations. This is a rather difficult task for a child. Don't try to achieve results right away. To begin, take the baby’s hands in yours and do the exercise with him.
- Cinderella. You need to mix white and red beans and ask your child to sort them by color.
- Funny pictures. Spread the plasticine evenly over a sheet of cardboard and show your child how to lay out drawings using peas.
- Counting sticks. Show your child how to use counting sticks to lay out different shapes. It is advisable that the counting sticks are not smooth, but ribbed: this serves as an additional massage for the fingers.
- Little sculptor. Dough modeling (dough recipe: 1 cup flour, 1/2 cup salt, a little water). The advantage of dough over plasticine in this case is that the crafts can subsequently be used as toys.
- Fasten the button. You will need two pieces of thick fabric. On one of them, sew three buttons of different diameters, in the second, cut loops of appropriate size. First, show your child how to fasten the buttons, commenting on your actions: “We insert the large button into the large buttonhole, the medium button into the middle one, and the small button into the small one.” Then take the child's hands in yours and repeat the exercise. After this, you can invite the baby to try to fasten the buttons on his own. Don’t insist if the baby doesn’t want to or if he can’t do it. This is a very difficult exercise and requires practice to perform successfully.
- Stencils. It is recommended to start with stencils for internal tracing (it is easier for a child to trace inside than outside) and with the simplest shapes (circle or square). Practical advice: you can buy ready-made stencils, but it is better to make them yourself. The fact is that most standard stencils are small in thickness, and it is inconvenient for a child to trace them, since the pencil keeps slipping off. Therefore, the stencils must be quite voluminous. A good solution is to cut them out of a piece of linoleum or a shoebox.
How does speech develop in children under 2 years of age?
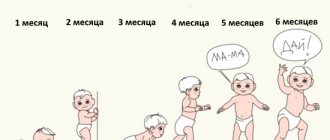
Speech development occurs in stages, and each stage is present in any case , regardless of the nationality and language spoken by others. My child was no exception and went through all stages of speech development. Some stages lasted longer, some shorter, but in the end the child spoke fully.
- Scream. With my first child, I had a hard time understanding why my daughter was screaming, but with my second baby, I unmistakably learned to recognize when he was screaming from hunger or when he was just bored. From the moment of birth, the only way for a child to communicate with mom and dad is to cry. With it, he expresses feelings of hunger and thirst, physical discomfort, draws attention to himself if he is hot or cold, clothes are tight or uncomfortable, and also if the baby is in pain. Attentive parents can also quickly learn to distinguish between different types of crying.
- Booming. From about 3 months, newborns begin to hum: most often this happens when the baby is happy and thus expresses a feeling of satisfaction. However, this period does not have to coincide with the beginning of the party. My first daughter began to walk only at 4.5 months, being completely healthy and without any deviations, but my son was already walking and singing in every way at 2 months. The child learns to move his tongue to pronounce sounds and trains the speech apparatus in every possible way. The buzz is usually reproduced in the form of the words “Agu”, “Ua”, “Gaaa”, “Guuu”.
INTERESTING! All nations of the world have children who walk in exactly the same way.
- Pronunciation of syllables and babbling. By about 7-8 months, children can pronounce different syllables, and they are not yet associated with certain images and words. The baby may say “Ma-ma-ma-ma-ma” without meaning his mother at all. However, this is an important stage in which the child masters the main part of sounds.
- First words. At the age of one, my first child could only say so much: “baba”, “dad”, “yum-yum” and a couple more phrases from his personal repertoire that cannot be translated into human language. By the age of one year, a baby can know and pronounce up to 10 words. Moreover, these may not always be full words. For example, instead of the word “dog,” a child may still say “Woof-woof,” which in his mind is associated with a specific image. It is also acceptable to pronounce truncated words, for example, “kava” instead of “cow”.
- Conscious speech. By the age of two, a child usually has a certain set of words that, at the very least, he can communicate with adults. Usually this vocabulary is enough to call mom and ask for a toy. It is considered normal if a child speaks about himself in the third person: “Masha is playing” instead of “I am playing.” It is from this stage that speech will rapidly develop every day, and the vocabulary will fill up.
Finger Theater
Finger theater is an exciting game that:
- Stimulates the development of fine motor skills;
- Introduces the child to the following concepts of shape, color, size;
- Helps develop spatial perception (the concepts of “right”, “left”, “next to each other”, etc.);
- Develops imagination, memory, thinking and attention;
- Helps develop vocabulary and activates speech functions;
- Forms creative abilities and artistic skills;
- Introduces basic mathematical concepts.
For children aged 1 – 2 years (using the example of the fairy tale “Kolobok”):
- First, introduce your child to the characters in the fairy tale. Invite your child to look at and touch the figures. Then put each character on your finger in turn and describe it.
- Introduce your child to the name of each finger on his hand. For example, you can say this: “I have a Kolobok sitting on my index finger.”
- Then act out a fairy tale for your child. Place the characters on your fingers and cross your arms. Start telling the story, raising your fingers with the characters as the action progresses. For example, the fairy tale “Kolobok” can be told as follows. Thumbs up with Grandma character. Tell your child that today this hero will bake Kolobok. Rhythmically tap the heels of your palms against each other without releasing your fingers. At the same time, say: “Grandma is kneading the dough.” Using the same principle, play up the appearance of each character.
For children aged 2 – 4 years (using the example of the fairy tale “Kolobok”):
- Ask your child if he remembers the fairy tale “Kolobok”. Remind him if necessary.
- Then ask your child to place the characters on the table in the order they appear in the story. At the same time, ask to characterize each of them according to the principle: “Grandma is old, kind, caring; Kolobok is round, ruddy, mischievous,” etc.
- Ask your child questions about the fairy tale. For example: “Why did grandma decide to bake Kolobok? Why did he leave his grandmother and grandfather? Who did he meet on the way?
- Then act out a fairy tale in front of the little spectator using a finger theater.
- At the end, ask your child to act out a fairy tale in front of you using a finger theater. If necessary, prompt him.
Fun ABC lesson
This group of games helps children learn a lot of new things from the life of words, expand their vocabulary, and knowledge about language.
Ball game "Say the opposite."
Winter summer. Heat - cold. True False. Rich man - poor man. Bitter - sweet. Useful - harmful...
"The Magic Wand of the Fairy Slovarina"
To play you need a “magic” wand. One end of the stick decreases, and the other increases.
An adult player names a word, then touches one of the children with a stick. The child calls this word either diminutive or increasing, depending on the end of the stick with which the child was touched.
House - house - house. Bridge - bridge - bridge. Rain - rain - rain. Cat - cat - cat...
Author: Krugovykh Margarita Aleksandrovna
Senior teacher of MADOU d/s No. 7 in Ishim
Everyone knows what an important function breathing performs in the life of the human body. In addition to its main physiological function - gas exchange - breathing also provides such a function as speech breathing. Speech breathing (diaphragmatic) is the basis of sounding speech, the source of the formation of sounds and voices.
The mechanism of this type of breathing is inherent in us from the very beginning. This is the oldest type of breathing, inherent in all warm-blooded animals and 90% of the total need for breathing is carried out due to it.
The main muscle that powers this type of breathing is the diaphragm . It separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities. When you inhale, the diaphragm relaxes and, falling, presses on the abdominal organs, which in turn are pressed against the abdominal wall, causing it to protrude and round. As you exhale, the diaphragm contracts, compresses the lungs, and the abdominal wall retracts. In this case, the upper part of the chest remains motionless. Outwardly, it looks like belly breathing.
When correcting speech disorders, there is a need to specially organize and develop speech breathing; breathing exercises become of particular importance. The corresponding gymnastics is aimed at developing in children the skills of correct rational breathing and voluntary control of the process of air flow movement.
Finger games for speech development
The essence of the finger motor skills lesson is to teach the child to use his fingers to depict some objects or living beings. In this case, all finger movements must be explained to the baby. This will help the child understand concepts such as “top”, “bottom”, “right”, “left”, etc. After the child learns how to do the exercises himself, you can try to act out scenes or short fairy tales, distributing the roles among yourself and your little actor (for example, a meeting between a hedgehog and a bunny in the forest). Here are some examples of such exercises.
- Finger game “Bunny”. The index and middle fingers are straightened, the rest are clenched into a fist. Little man. “Run” with your index and middle fingers on the table. Finger game “Hedgehog”. Clasp your hands, straighten the fingers of one hand and the thumb of the other. Cat. Connect the middle and ring fingers with the thumb, raise the index and little fingers up. Horned goat. The index and little fingers are straight, the thumb is on the bent ring and middle fingers. Butterfly. Cross your hands at the wrists and press your palms with the backs of your hands facing each other, fingers straight; palms with straight fingers make slight movements in the wrists - “butterfly flies.” Glasses. Fold the fingers of your right and left hands into rings and bring them to your eyes.
In addition to these examples, you yourself can come up with many interesting and entertaining exercises for your child to develop speech.
Types of speech
Speech can be active or passive:
- Active - the one that the baby uses. The child knows the words he has learned, can confidently pronounce them, and construct sentences with their help.
- Passive is the one that the child understands, but for certain reasons does not pronounce. For example, he may know the word “TV”, but not say it because it is difficult for him.
It is very important to develop both active and passive speech of a child.