Acoustics
When considering the acoustic properties of sounds, the following vibration characteristics are analyzed:
- frequency, which determines the pitch of sound;
- amplitude, responsible for its strength;
- a combination of different vibrations that affects timbre.
Acoustic classification is dichotomous, that is, it identifies pairs that are opposite to each other. From this point of view, vowels:
- all are vocal, as they are formed by tone;
- all are non-consonant, that is, they are characterized by greater strength than consonants;
- all are continuous;
- the front vowels ([e], [i]) are high, and the middle and back vowels ([a], [o], [u] [s]) are low;
- vowels of the lower and middle rise ([a], [e], [o]) are compact, that is, their vibrations are relatively close to each other, the vowels of the upper ([i], [ы], [у]) are diffuse;
- rounded vowels [o], [u] are flat, unrounded vowels [a], [e], [i], [s] are non-flat.
Diphthongs and Triphthongs
Depending on whether the acoustics of a sound changes during its articulation, there are:
- monophthongs,
- diphthongs,
- triphthongs.
Monophthongs are integral and do not break down into elements. Diphthongs and triphthongs, on the contrary, contain transitions from one sound type to another (and a third).
REFERENCE! In turn, they can be descending (the top of the syllable is the first vowel), ascending (the top of the syllable is the last vowel), and ascending-descending triphthongs occupy an intermediate position.
Russian vowels are predominantly monophthongs. Exceptions are iotated sounds corresponding to the letters i, ё, yu, e. However, if they are paired with consonants, they denote a monophthong and only soften the preceding sound.
For example: “I sing” [poy'u] or “yula” [y'ula], where [y'y] is an ascending diphthong; but in the word “love” [l'ubof'] there is no diphthong.
Thus, vowel sounds are represented in the world's languages in all their diversity. Some of their characteristics are inherent in Russian-language speech, others are expressed only as articulatory defects.
Related posts:
- Rhoticism in speech - complete information Rhotacism (problem with the sound [P]) is the most common disorder in children...
- A child does not know how to say R - we’ll show you how to teach it. To teach a child to pronounce the letter R, you need to regularly perform special...
- What do we know about Morse code? Morse code was created to transmit short information. But use...
- Teaching a child to read Teaching reading in preparation for school. When can you teach a child...
What does phonetics study?
This is the science of the main side of human speech - sound. She studies a very important component of language, since without sounds, which represent the sound shell of words, people would not be able to communicate orally at all. But in order for verbal communication to be of high quality, a person must clearly distinguish a word from others that sound similar to it. This is precisely why understanding and studying the phonetic laws of language is necessary.
To distinguish between words, the forms of these words, as well as phrases and sentences, the phonetics of the Russian language has a rich arsenal of tools.
How to make money if you know Russian
If you are ok with spelling and punctuation (or generally ok, despite minor shortcomings), you can make money on the Internet from texts.
At first, the income will be small - 40-60 rubles. per page, but gradually you will find your niche and earn at least 200-400 rubles. per page. This is really true, because I myself have walked this path, from text exchanges where they pay pennies to individual cooperation with webmasters.
If you don’t know where to start, come to the “Copywriting from Scratch” course, which we created with Vasily Blinov. We will tell you in simple words what copywriting is in principle, how to correctly write articles on the Internet, how to do optimization, and carry out semantic analysis of texts.
The course includes five practices - you will write articles for the websites vsvoemdome.ru and iklife.ru. We pay for each practice. Students who complete the course pay back half of its cost and have 5 texts in their portfolio published on thousands of blogs.
Sign up for the course “Copywriting from scratch”
What are vowel sounds?
Our speech consists of words. Each word in turn is made up of sounds. In order for sound to appear, we use various organs: lungs, windpipe, larynx, mouth, tongue, nose and lips. With the help of the speech organs, a person can pronounce sounds that merge into a word.
The sounds in the word are not the same. Some sounds are made by voice, while others consist of noise and voice. When we begin to speak, we exhale air from the lungs, which rushes down the windpipe into the larynx. The larynx contains the vocal cords. If a stream of air passes freely through them and then does not encounter any obstacles on its path, then the result is a vocal sound consisting of a tone. If, when exhaling, the air makes its way through various obstacles, then a characteristic noise is obtained, typical of consonant sounds.
It is enough to change the position of your lips and you will get different vowel sounds with your voice.
To form the vowel sound [o], it is enough to round the lips, and by stretching them out with a tube, we get the sound [u]. The vowel sound [a] is pronounced with the mouth wide open. The sound [and] requires you to stretch your lips in a smile.
So, in the Russian language there are six vowel sounds. These sounds in writing are indicated by the corresponding letters: Vowel letters: o, a, u, i, s, e
Vowels differ from consonant sounds in that they can be pronounced for a long time or sung:
REFERENCE! Vowels are sometimes called “mouth openers” because they require you to open your mouth wide to pronounce them louder. This distinguishes them from consonants - “mouth-closers”, because in order to make them louder, you need to bring the organs of the mouth as close as possible.
PLAN – SOUND CHARACTERISTICS DIAGRAM
| (GL.) | VOWEL | CONSONANT | (CONS.) |
| SHOCKED (UD.) UNSTOCKED (UNHAUDED) | |||
| ZVONKY (ZV.) | DEAF (DEAF) | ||
| SOLID (TV) | SOFT (SOFT) | ||
| PAIR (PARN.) | UNPAIRED (UNPAIRED) | ||
Literature
- Misarenko G. G. Methods of teaching the Russian language to junior schoolchildren with correctional and developmental technologies: a textbook for students of secondary pedagogical educational institutions. – M.: Academy, 2004.
- Elkonin D.B. Selected psychological works. M., 1989.
Phonology
Phonology (from the Greek “sound” and “teaching”) is a branch of linguistics devoted to the study of the structure of the sound structure of a language and the functioning of sounds in the language system.
If we take a vowel sound as a phoneme - a unit of language that does not have independent lexical and grammatical meaning - then its functions are obvious:
- act as the core of a syllable, that is, its obligatory element. In some languages, sonants or obstruents take on this role.
- bear emphasis, that is, highlight words within a word;
- determine tone, that is, use pitch to differentiate meaning within words or morphemes.
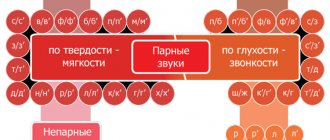
Classification of consonant sounds of the Russian language
Consonant sounds can be hard and soft, dull and voiced. If sounds that according to these characteristics are divided into pairs, there are also unpaired ones. The table will help you understand the overall picture:
| Sound | Voiceless/voiced | Hard/soft | Paired/unpaired |
| b | voiced | solid | doubles |
| V | voiced | solid | doubles |
| G | voiced | solid | doubles |
| d | voiced | solid | doubles |
| and | voiced | solid | doubles |
| h | voiced | solid | doubles |
| To | voiced | solid | doubles |
| l | voiced | solid | doubles |
| m | voiced | solid | doubles |
| n | voiced | solid | doubles |
| P | deaf | solid | doubles |
| R | voiced | solid | doubles |
| With | deaf | solid | doubles |
| T | deaf | solid | doubles |
| f | deaf | solid | doubles |
| X | deaf | solid | doubles |
| ts | voiced | solid | unpaired |
| h | deaf | soft | unpaired |
| w | deaf | solid | doubles |
| sch | deaf | soft | unpaired |
| th | voiced | soft | unpaired |
| b' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| V' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| G' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| d' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| z' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| To' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| l' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| m' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| n' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| P' | deaf | soft | doubles |
| R' | voiced | soft | doubles |
| With' | deaf | soft | doubles |
| T' | deaf | soft | doubles |
| f' | deaf | soft | doubles |
| X' | deaf | soft | doubles |
It is worth understanding in more detail the characteristics that it describes.
So what are voiced and voiceless consonants? This is a characteristic of tonality that indicates whether the vocal cords are used when pronouncing a sound or not. If not, the sound is dull. If yes - sonorous.
Hardness and softness are also pronunciation characteristics. Soft sounds are produced when the middle back of the tongue rises towards the soft palate.
When pronouncing a consonant sound, the vocal tract always narrows, that is, the sound seems to overcome an obstacle.
Accordingly, consonants can be paired in terms of hardness/softness and dullness/voice, and then they will be called paired. Those who do not have such a pair are unpaired.
Word and phrase stress, intonation
It is necessary in order to divide the speech stream into separate parts, which ultimately helps the listener to understand what the speaker is saying.
Word stress helps to separate different forms of a word and identical words that differ only with its help.
Functional words and interjections do not have their own stress and, in a phonetic sense, are part of the independent word to which they refer.
Phrase stress allows you to highlight the most important word within one statement. With its help, you can interpret exactly the same phrases in different ways.
As for intonation, it allows you to make sentences declarative, interrogative or exclamatory.