A child does not speak at 2 years old: causes, symptoms, is it worth contacting a neurologist? The child does not speak at the age of 2 years. Normally, upon reaching this age, the baby should actively communicate with parents and loved ones, otherwise this may be a sign of SPD
From the first days of a child’s life, the most important component of human life begins to form – SPEECH. The ability to speak and understand the speech of other people is inextricably linked with processes such as memory, attention, and thinking. Only with the help of speech can a person fully exist and harmoniously join the society of other people. Therefore, it is extremely important for parents to know the basic norms of speech development in children and the symptoms that may signal certain deviations in order to begin treatment on time and prevent serious problems in the child’s health in the future.
What is ZPRR
Delayed mental speech development of a child is a disease in which he lags behind age norms in his psycho-emotional development. Characterized by speech dysfunction, behavioral disorders, emotional disorders - rigidity or lability. Some children also experience motor dysfunction.
Develops against the background of diseases of the brain or central nervous system. On the one hand, a special neurological status can cause a delay in the development of the psyche and speech, on the other hand, the pathology itself negatively affects mental development.
About the benefits of articulation gymnastics and breathing exercises
To teach a child to speak and clearly pronounce sounds, talking and communicating with him alone will not be enough. It is important to do articulation gymnastics at the same time. Training the articulatory apparatus contributes to the correct pronunciation of words in the future.
Below are several articulation gymnastics exercises. Demonstrate and explain to your child how to perform them. He will love this fun idea.
"Pendulum". Open your mouth and move your tongue like a pendulum from side to side, touching the corners of your mouth.
Using your tongue, try to reach the tip of your nose, chin, and cheeks.
"Fence". You need to close your teeth tightly so that your tongue remains behind the fence, and smile widely.
“Open and close your mouth.” Having opened your mouth, you need to stay in this position for a few seconds and then close it.
"Baby Elephant's Trunk" Pull your lips forward like a tube and breathe.
"Piglet." Move your elongated lips in a circle, left and right, up and down.
"Hamster". Take a breath into your mouth, pretending to be a hamster. Alternately deflate the left and right cheek. Then, on the contrary, pull in your cheeks strongly. Inflate and use your palms to deflate them.
Causes of delayed mental speech development of a child
There are many factors that can trigger the disease. They can be divided into groups:
- Intrauterine development. Hypoxia, fetal infections. Its development after birth is influenced by illnesses and injuries that the mother suffered during pregnancy.
- Complicated childbirth. Traumatic, premature or rapid birth, entanglement.
- Diseases in the first year of life. Neuroinfections, brain injuries.
- Genetic factors. Chromosomal abnormalities and heredity - the disease tends to worsen in the next generation.
Delayed mental speech development of a child may occur against the background of diseases that disrupt the functioning of the brain. These include: congenital diseases of the central nervous system, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy, brain tumors, disorders of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
As a rule, parents learn about the situations listed above - congenital disorders, primary diseases and injuries - immediately and provide assistance to their child - they undergo treatment and rehabilitation courses.
But there are situations when a child is born physically and mentally healthy, grows and develops in accordance with age norms. And then suddenly he is diagnosed with SPD. Social factors can contribute to this : overprotection or, conversely, cruelty, violence or indifference towards the child, severe psychological trauma, unfavorable psychological climate in the family.
Who to contact for help
The reasons leading to speech delay are different. To solve a problem, parents sometimes have to contact several specialists. Among them, five main ones can be distinguished - speech therapist, defectologist, ENT (to exclude hearing impairment), neurologist or neuropsychiatrist.
There are various methods for correcting general speech underdevelopment (GSD) and tempo delay (RTD), which are used by speech therapists and speech pathologists. In combination with the necessary medication correction prescribed by doctors, they give excellent results.
How to test your child's hearing at home
Drug treatment is used only in severe cases; it is often possible to do without it. Sometimes it is not needed at all, but doctors prescribe medications. A good speech therapist can compensate for some of them by simply working with the baby; there will be no need to take them.
Remember that only doctors have the right to prescribe medications. Speech therapists do not have this right.
For their part, parents must create a rich speech environment during the correction to stimulate the child’s speech. You need to force the baby to talk, pretend that you don’t understand him if he is trying to explain with gestures what he wants.
When visiting a specialist, parents of a child with delayed speech development need to openly talk about possible problems with the child’s health in order to receive effective help from him.
In case of speech delay, parents can work with their children independently. Many do just that: for the first time they turn to a speech therapist for advice, and based on the knowledge and materials acquired, they begin independent work.
The task of the speech therapist in this case is to diagnose speech development and identify the child’s problems. After this, parents understand the current situation and begin to work with the baby independently.
Reviews about a specialist are important, but there is a nuance. Just because a speech therapist helped the son or daughter of your friend/neighbor, this does not mean that he will be able to help your child. All children are different, with their own characteristics and skills, and it is not always possible for a specialist to find an approach to a child and solve his problems.
Pay attention to the recommendations and experience of the speech therapist. You can decide whether you will go to him after you see him at work and make sure that the child is interested in the process. The best way to evaluate a speech therapist is to come for a diagnosis and see how the speech therapist works, how the baby reacts, and how interested he is.
The state is trying to the best of its ability to help children with speech delays. For this purpose, state centers for psychological, pedagogical and medical and social assistance have been created. They are located in every district of large cities and provide services free of charge. But getting there is not easy, since there are many children with problems, and the number of places is limited.
Symptoms of mental retardation of speech
A young patient will not be officially diagnosed until 4 or even 5 years old. But the first prerequisites can be noticed even in the first months of a newborn’s life. If a violation is suspected, the pediatrician will definitely ask the parents leading questions - and based on the information received, he can already assume a delay in the mental development of speech.
Here are the signs by which you can suspect him.
- At 4 months, the baby does not smile, ignores the parents’ verbal address to him, their gestures and facial expressions;
- At 8 months the baby does not try to repeat words using sounds, and at 12 months he is verbally passive;
- At 1.5 years old, he does not understand the meaning of simple words, does not respond to his name, does not formulate requests at a primitive level (“give”), does not chew;
- At 2 years old he knows very few words and does not learn new ones, and later his vocabulary contains no more than 20 words, there is no simple phrasal speech;
- A three-year-old child does not speak in sentences, “swallows” endings, speaks slowly, draws out sounds, does not conduct a dialogue - instead of answering, he repeats the question asked.
Parents should pay attention to other signs that accompany the disorder. So, if a child is hyperactive, aggressive, inattentive, has difficulty remembering new things, has a poor imagination and emotions, is uncommunicative, and physically weak - all this should alert parents and become a reason to contact a pediatrician.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Dr. Komarovsky is a famous pediatrician who became widely known thanks to television programs. In them, he gives expert advice to mothers of children regarding various parenting problems.
In his programs, he repeatedly discussed the topic of children's speech development.
Main points:
- According to Dr. Komarovsky, mothers begin to sound the alarm too early about what the child is saying. Laughing, he says that mothers come to him with this problem when the baby is not yet a year old.
- Also, in his speeches, Komarovskikh repeatedly speaks about the harm of modern gadgets on the development of children. According to the doctor, modern children “communicate much more with phones and tablets than with their mother and father.” Komarovsky emphasizes the importance of communication between parents and children. Modern parents are very busy and themselves experience constant stress, however, despite the high pace of life, it is extremely important to find time every day to communicate with the child, says Evgeniy Olegovich. According to the doctor, there is no point in taking the baby to the doctors and “looking for a magic pill” if he experiences a lack of communication in his family. Emotional communication with mom and dad sometimes gives a much greater result in the development of a child’s speech than drug treatment.
- In his program “What to do if a child of 2 years old does not speak,” Komarovsky explains in detail the difference in the development of children who play with gadgets and toys. Evgeniy Olegovich explains that when a child plays with a simple rubber ball or doll, he always needs a connecting object between the toy and himself - an adult. The adult explains to the child exactly how to play with this object, talks about its properties, and reacts emotionally to the child’s play with the object. Emotional communication between an adult and a baby stimulates his verbal communication.
First, the child develops a need to understand what adults tell him. Thus, so-called passive speech is formed - the baby’s ability to understand speech addressed to him.
At 2 years old, a child should be able to follow double instructions. For example: Take the Masha doll and give it to me.” If a child at 2 years old does not speak, but understands the speech of adults, we can say that he has passed stage 1 of speech development - the formation of passive speech. The next stage is the development of active speech, when the child begins to speak individual words and then build sentences from them.
What to do if the child does not speak
For parents who are worried that their child is still not talking at 2 years old, Komarovsky recommends that they consult a doctor.
Surveys
- Examination by an ENT specialist It is necessary to conduct a hardware hearing examination and make an audiogram that will show the baby’s hearing level, as well as the range of sounds that he hears.
- Consultation with a neurologist Neurological pathologies are a common cause of deviations in speech development, from mild to severe. An examination by a neurologist will allow you to diagnose existing diseases and begin to treat them in a timely manner. Before going to a neurologist, try to remember all the important milestones of development: When the child began to roll over, sit, walk • When the baby began to walk, understand the speech of adults addressed to him • What skills and abilities he has now. Your doctor will definitely ask you about this, so be prepared to answer these questions.
- Consultation with a speech therapist A speech therapist will help identify developmental disorders of the speech apparatus. The most common pathologies are: • frenulum • hypotonicity of the facial muscles and tongue.
- Consultation with a child psychologist
The psychologist will examine the baby’s speech and identify his deviations from the norm. It will also help you figure out whether there are psychological reasons for the lack of speech.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
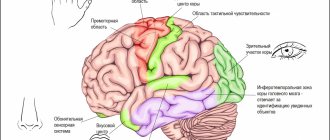
Diagnosis is approached in a comprehensive manner. This means that a small patient is examined by different specialists - a pediatrician, an otolaryngologist, a neurologist, a speech therapist. In addition to collecting an anamnesis, examining and assessing the child’s health, he is sent for hardware diagnostics. This is necessary because, against the background of ZPRD, organic matter changes, in particular, the work of the left hemisphere of the brain, which is responsible for the development of speech, is disrupted. Therefore, the final diagnosis is made based on the results of examinations - EEG, computed tomography, evoked potentials technique.
After diagnosis, comprehensive treatment begins. A neurologist, psychologist, speech therapist, and reflexologist take part in it. Parents play a huge role - without them it is impossible to achieve success.
Diagnosis or how to identify the disorder
Diagnosing patients is a rather difficult task. Survey methods include the following:
Questioning a child. If he doesn't speak well, he needs help from a group of doctors. The first task is to exclude organic pathologies. To do this, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. An ENT doctor identifies pathologies of the ears (otitis), nasopharynx and oropharynx (adenoids, tonsillitis). Eliminates hearing loss. If it is impossible to determine the intensity of hearing on site, the child is referred to an audiologist.
The audiologist checks the patency of the auditory tract, uses a special apparatus, and draws a chart. It is easier to work with this data.
The child is then examined by a neurologist. Conducts basic examination, checks reflexes. Prescribes instrumental diagnostic methods. For example:
- duplex scanning of cerebral vessels to assess the intensity of blood flow in cerebral structures;
- if necessary, prescribes ECHO KG, ECG, and also electroencephalography to monitor the work of the heart (it is responsible for feeding the brain), brain activity.
If no organic pathologies are found, they look for mental disorders and problems. Clinical psychologists come into play. A series of tests are carried out, adapted to the child’s age. For perception, representation, speech. Everything that is involved in the speaking process and can be disrupted. In addition to the tests, the specialist talks with the child, finds out how poorly he speaks and what is the reason, and makes recommendations.
As a rule, in the matter of diagnosis one cannot do without a speech therapist-defectologist. His task is to study the speech apparatus. And then correct the violations and teach the patient to speak correctly.
The help of a psychiatrist is also necessary. Its task is to identify possible disorders of higher nervous activity: autism, mental retardation, and other types of dementia. All this is part of the psychiatrist.
If a child speaks poorly at the age of 5, consultation with all specialists will be required. Because complex violations are possible. In system.
Which doctor should I see next? Speech and intellectual impairments occur with endocrine disorders. Therefore, it would not be amiss to consult with an endocrinologist.
Comprehensive treatment of the disease
The longer the baby does not speak, the longer his mental development “slows down.” Therefore, it is necessary to begin treatment for delayed mental development of speech as early as possible. Various methods are used.
Microcurrent treatment
The reflexologist applies an ultra-low current to the bioactive points of the brain that are associated with speech. This helps restore damaged areas of the central nervous system. You can start reflexology as early as six months old babies. As a rule, a course of 10–12 sessions is prescribed, and after 2.5 months it is repeated.
Transcranial micropolarization
The physiotherapy procedure consists of a targeted effect on certain areas of the brain. As a result, new neural connections are formed in it. The area of the cerebral cortex that needs to be stimulated depends on the problem. The procedure is safe, does not cause adverse reactions and is effective.
Bioacoustic correction for ZPRD
The essence of the method is for the little patient to listen to the electrical signals of his own brain. They are converted through equipment into music - acoustic waves. As a result of such listening, impaired brain functions are restored. The BAC technique combines the latest technologies of music therapy, biofeedback and neurotherapy.
Speech therapy correction of mental retardation
Classes of a speech therapist-defectologist are aimed at developing not only speech, but also thinking, motor skills, and memory. Little patients learn to pronounce sounds correctly, form words, sentences, and speak in phrases. You can study from the age of 2, although in practice speech therapists take children from at least 4 years old. But in the case of delayed mental development of speech, correction should begin as early as possible. At 4 years old, quite a lot of time will have been lost and not all functions will be restored. Therefore, you need to either make an appointment with a speech pathologist-speech pathologist earlier, or begin correctional work with other specialists in their profile.
Speech therapy massage is also useful - it strengthens and stimulates the chewing and facial muscles. As a result, it becomes easier for the baby to pronounce sounds and syllables.
Drug therapy for PVRD
Medicines are prescribed by a pediatric neurologist after hardware diagnostics. Therapy is selected depending on the pathology. As a rule, these are nootropic drugs - Cortexin, Actovegin, Encephabol and their analogues.
Alternative correction methods
Additional methods can be connected:
- Consultations with a child psychologist. They are effective if a delay in the child’s mental speech development occurs against the background of an unfavorable climate in the family, psychological trauma, or errors in upbringing. Play, music, and art therapy work well with young patients;
- Osteopathy. By manually influencing certain areas, the doctor balances the functioning of the nervous system and psyche, and activates the speech centers of the brain. This is an effective direction; experienced osteopaths literally work wonders;
- Dolphin therapy. The method is more common in Europe and the USA. It relaxes the nervous system, but has proven itself, for example, as part of the treatment of autism (and they also lag behind in mental and speech development).
As part of the main treatment, the listed auxiliary techniques give very good results. Discuss with your doctor (pediatrician or neurologist) whether it is worth connecting them in your case.
Why do children speak poorly?
There may be several reasons. Conventionally, they can be divided into organic and social.
Organic
Among these, lesions of the brain and hearing organs predominate. Less commonly, developmental disorders of the speech apparatus.
- Encephalopathy
A characteristic pathological process for children under 3-5 years of age. Accompanied by general disorders of higher nervous activity. Intelligence and memory decrease. In addition to speech dysfunction, behavioral problems or hyperactivity and attention deficit disorder (ADHD) are observed. Or lethargy, drowsiness, weakness. Both options are dangerous. Without special treatment, it is impossible to achieve functional restoration. They will continue to fade, development will slow down significantly. It is necessary to contact a neurologist.
- Birth injuries
Head injuries (TBI) and other options. Also asphyxia, for example, when the neck is compressed by the umbilical cord. Variations are possible. Birth injuries cause persistent disturbances in the functioning of cerebral structures. At best, only speech will be impaired. More severe problems, including secondary dementia, are also possible. Although there will be no organic underdevelopment in the clinic.
- Prematurity
Babies born prematurely are at greater risk. Because the brain continues to develop and form, without the help of the mother's body. Without excess nutrients and oxygen. The body has to produce everything on its own. Consequently, the resource that children born at the right time have is spent. Such children become sickly, they are weaker than their peers and often begin to speak later. You can cope with this situation, especially if you adhere to a normal regime, create the right diet and regularly exercise your brain. According to the age.
- Intrauterine hypoxia
Happens more often than you might think. If the baby inside the womb does not receive enough oxygen, the brain suffers. The process is possible both during pregnancy and in the last trimester. Right before labor is resolved. Both options are equally dangerous. In the first case, the fetus is guaranteed to get problems. At the very least, it will be bad to speak. Disorders such as encephalopathy and hypothalamic syndrome are also possible. In the second case, death from hypoxia is possible. Childbirth in cases of acute oxygen deficiency is resolved by cesarean section.
- TBI
Acquired, for example, in the early years: concussion, hematoma and other forms. Accompanied by severe damage to cerebral structures.
- Autism
Mental illness. Severe forms of autism are characterized by a complete absence of speech. The child speaks poorly or does not speak at all. 3 years - no question. The child is 7 years old - the function still does not develop. In milder forms, individual phrases are possible, but only in certain situations when biological needs are affected. High-functioning autistic people, such as those with Asperger's syndrome, do not suffer from such disabilities. However, they have problems understanding emotions and expressing them. Therefore, speech may be poor in modulation and intonation, which is quite normal for such patients.
- Down syndrome, separately there is oligophrenia in varying degrees
Recovery is impossible, but some measures are being taken to adapt. People with mild mental retardation develop most easily in this group. There is sufficient vocabulary and opportunities to use it.
- Hearing loss
A condition in which the patient hears in only one ear. In this case, the child speaks very poorly, although the intellectual component is normal. The reason is that the young patient simply does not hear correctly what others are saying. The more pronounced the disorder, the worse the speech. You need to work with a speech pathologist and audiologist.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain
Meningitis or encephalitis. It is quite difficult to meet the second one in a city. Rural residents risk several times more, since natural areas are infested with ticks. Possible tick-borne encephalitis. Meningitis can become a complication of inflammatory and infectious diseases. In any case, urgent treatment is needed with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Under the supervision of infectious disease specialists and neurologists.
- Congenital anomalies of the speech apparatus
For example, a short frenulum of the tongue. Require surgical treatment. At least if the child cannot adapt to the deviation.
Social
Reasons that are due to parental influence and environmental influence.
- Overprotection
If in this case the question arises, why does a 4-year-old child speak poorly, the answer is because there is no need for it. Plus, there is no normal example. Therefore, a young patient needs to be looked after moderately, speak correctly, and not babysit. Because when he hears incorrect examples, he adopts them.
- Insufficient guardianship
Back side. Again, there is no normal speech example, there is not enough verbal practice.
- Lack of social connections
It is found in the so-called Mowgli children. Speech is a socially determined mechanism and method of communication. Without other people it does not develop. Formation of skills after 7 years is very difficult. Pedagogical neglect also occurs in urban environments. Suffice it to recall high-profile cases when parents locked their children in basements for years.
Doctors are studying all the reasons. Based on the provoking factor, treatment is selected.
The role of parents in the treatment of SPD
Without the participation of mom and dad, even the best specialist will not be able to cure their child. Their task is to follow all doctors’ recommendations. For example, doing exercises at home to develop fine and gross motor skills, playing outdoor games, listening to and guessing musical instruments, putting together puzzles, constantly talking to the child - only with such comprehensive work of doctors and parents can he be helped.
Another important point. Do not replace verbal communication with TV and smartphone. The speech your child hears on TV or from cartoons interferes with the formation of his own speech. His passive vocabulary will be good, but his active vocabulary will not. “Mechanical” voices activate the right hemisphere when the left hemisphere is responsible for speech formation. Thus, gadgets inhibit speech development and provoke mental retardation, which, in turn, can lead to a delay in the mental development of speech. Therefore, it is better not to turn on the TV, radio, tablets and other devices at all in front of your child.
Spend more time with your son or daughter, go out into nature - this helps improve your psycho-emotional state.
When is a child ready to speak?
For the first year, mother and child are in symbiosis. The baby cannot speak; his only language is crying. The mother develops an amazing ability to understand his “language” and translate it into universal human language: now the baby wants to drink, then he wants to eat, and in the evening he wants to sleep. Mom can satisfy his needs. Thanks to this, the child survives the first year.
Gradually, the baby stops latching, begins to crawl, and takes his first steps. This is a very significant event for him. Now he feels separate from his mother. He can move closer or further from her as much as he wants, he can run, he can reach the treasured shelf with a bright toy. It is at this age that the first words appear. As soon as the child begins to feel separate from the mother, the need to talk appears.
On the other hand, by the end of the first year, the mother gradually comes out of fusion with the child and loses her superpower to read minds. Now the child, in order to express himself and his needs, needs to learn to speak his mother’s language.
Forecasts and consequences: what to expect?
The effectiveness of treatment depends on many factors. The main ones are the age of the small patient, the severity of the delay in the child’s mental speech development and primary diseases.
Unfortunately, with deep-seated disorders or therapy started in 5-6 year old children, one cannot expect great results. Only in 0.2% of cases out of 100% is it possible that he will start talking. If a child has not mastered speech at the age of 7, he will never speak again.
If the parents turned for help when the baby was 2–3 years old, then there is every chance of a full recovery. In this case, everything depends on the degree of underdevelopment, the participation of parents and the methods used for treatment.
If parents expect that the child will speak on his own sooner or later, they are only wasting time. If this is not the individual pace of development of a particular baby, but really a problem, it will not go away on its own. Against the background of mental and speech underdevelopment, children suffer from poor memory and thinking, perceive and process information distortedly, and cannot concentrate attention. In the future, this leads to changes in personality - the child becomes irritable, closed, uncommunicative, and develops a feeling of inferiority.
What to do if your child speaks poorly
Treatment required. The intensity and nature of therapy depend on the specific clinical case and the cause of the disorder. Here are some options:
- removal of adenoids, if a person cannot speak due to their growth;
- complex therapy of sore throat, inflammatory lesions of the pharynx;
- plastic surgery of the speech organs, for example, the frenulum of the tongue;
- correction of hearing loss, as an option - with the help of a hearing aid or internal cochlear apparatus;
- prescribing nootropic drugs and drugs for correcting cerebral blood flow and metabolism in cerebral structures;
- specific therapy for mental disorders, communication with the child, work with a speech therapist - the child should speak as much as possible, it is important to create the right verbal environment for him (adults should pronounce words correctly and interact with the patient as much as possible, placing all responsibility on the doctor is not a good idea, the effect will be much less).
As needed, exercises for the speech apparatus and physiotherapy are prescribed.
My child does not speak, is silent, speaks little, speaks poorly!
At a Sarclinic consultation, parents ask: “ Why doesn’t a 3-year-old child speak, doesn’t speak , what should I do?” “ A 4-year-old child speaks poorly and is silent !” “Why doesn’t a boy speak for 5 years, where should I go?” “A 6-year-old girl does not speak, speaks poorly, how to treat?” “ Why does a child speak poorly or say few words? “ How to teach a child to speak and talk?” “What to do if a preschooler, schoolchild, boy, girl does not speak in sentences, as if he has porridge in his mouth?” “How to help a child if speech development suffers, there is no active speech, speech centers suffer, and there is no vocabulary?” “Children younger than us form sentences, and we moo, where should we turn if just mooing is all?” “When will the baby start talking?” Let's look at the main reasons why babies don't speak.
The earlier treatment for speech disorders is started, the higher its effectiveness.
When speech development is delayed, an important point is the time of initiation of treatment. If a child does not speak 10 words per year, then there is no need to wait until he is 7 years old when he “starts speaking on his own.” After all, precious time is wasted. The later treatment is started, the more difficult it will be to catch up with healthy children of the same age, since with increasing age the lag will become noticeably larger and larger. Some children, when their parents address them, understand the speech addressed to them, but do not respond, there are only gestures. Some children do not understand the spoken language and do not speak. Which is very bad. And if children speak little, indistinctly, then speech correction is needed.