Article:
A speech therapy examination should be based on general principles and methods of pedagogical examination: it should be complex, holistic and dynamic, but at the same time it should have its own specific content aimed at analyzing speech disorders.
Each speech disorder is characterized by its own set of symptoms, and some of them turn out to be the main primary symptoms for each disorder, the core ones, while others are only additional and only stemming from the main defect, i.e., secondary.
The methodology and techniques for conducting the survey must be subject to the specifics of its content.
The complexity, integrity and dynamism of the examination are ensured by the fact that all aspects of speech and all its components are examined, moreover, against the background of the entire personality of the subject, taking into account the data of his development - both general and speech - starting from an early age.
Speech therapy examination includes the following points:
1. First name, last name, age, nationality.
2. Complaints from parents, educators, teachers.
3. Early development data: a) general (briefly); b) speech (in detail, by period).
4. Brief description of the child at present.
5. Hearing.
6. Vision.
7. The child’s reaction to his speech difficulties.
8. Intelligence.
9. The structure of the organs of articulation, their mobility.
10. Speech: a) impressive; b) expressive - from the point of view of phonetics, vocabulary, grammatical structure; whether he speaks at length; c) written language - reading and writing.
11. Conclusion.
The first three points are filled out from the words of the mother, teacher, teacher accompanying the child, and based on the documentation provided. In cases where an adult applies, these sections are filled out according to the applicant’s words.
A brief description can be formulated from the words of the parents (educator, teacher), or can be presented by the child care institution sending the child. It is desirable that it contain information about what the child is interested in and how he reacts to his speech difficulties.
It is advisable to fill out the hearing and vision examination data on the basis of the submitted certificates from the otolaryngologist and ophthalmologist. If there are no specialists, then the speech therapist must check the hearing and vision himself and establish (by questioning) at what age the deviation from the norm was noted.
The state of intelligence is the main factor in the analysis of speech impairment. It is important to find out what comes first: a severe speech disorder that delays the overall development of the child, or mental retardation that delays and distorts speech development.
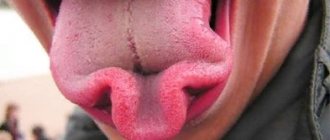
The speech therapist obtains data on the structure of the articulation organs based on an examination of the oral cavity. He establishes the mobility of the articulatory apparatus, inviting the child to make the basic movements of each of the organs (lips, tongue, soft palate), while noting the freedom and speed of movement, its smoothness and uniformity of movement of the right and left sides (tongue, lips, soft palate), and also the ease of transition from one movement to another.
First of all, the speech therapist must identify the level of development of the child’s intelligence and analyze his speech in detail. There are special techniques to clarify these issues.
The examination begins with a conversation. The topic for the conversation and the manuals that the speech therapist will use are considered and selected in advance, taking into account the age of the child.
During the conversation, the speech therapist tries to establish contact with the subject, and also reveals how the child understands his speech, whether he uses a phrase, and whether he pronounces sounds correctly. Establishing contact and the conversation itself help the speech therapist get an idea of the general mental and speech development of the child, and some of the characteristics of his personality.
Another methodological method of the examination will be the active observation of the speech therapist over the child in the process of his activities, which is organized by the speech therapist, offering him various materials (toys, pictures) and setting him various tasks of the game and educational plan. Tasks related to the processes of abstraction and generalization are of great importance.
A full understanding of speech is a necessary prerequisite for the correct use of speech and for further successful learning. Therefore, when starting to examine a child, the speech therapist studies all aspects of speech: its impressive and expressive sides.
When examining the impressive side of speech (speech understanding), the speech therapist focuses on how the child understands:
a) names of various everyday objects; b) generalizing words (clothing, dishes, furniture, fruits, vegetables, transport, etc.; c) a phrase of an everyday nature; d) a short text told or read to him. When examining speech understanding, you should not require a verbal response from the child. It is enough to receive it with the help of a gesture, selection of the necessary pictures, facial expressions, and individual exclamations.
When examining the expressive side of speech, the speech therapist studies: a) vocabulary; b) grammatical structure; c) sound pronunciation; d) voice, its tempo and smoothness.
Analyzing the children's answers, the speech therapist pays attention to the pace of speech (too fast or too slow, monotony or expressiveness of speech), smoothness or its disruption by more or less frequent and severe hesitations - stuttering. When stuttering, auxiliary movements of the arms, legs, and head may be noted.
To examine sound pronunciation, the speech therapist selects subject pictures so that their names include the sounds being tested at the beginning, middle and end of words. If the child incorrectly pronounces a sound in a word, the speech therapist suggests pronouncing this word with this sound by imitation, and then forward and backward syllables with this sound. The nature of the incorrect pronunciation of the sound is noted: the sound is omitted, replaced by another constantly or only in some words, distorted. If a child can pronounce both sounds in isolation, but still confuses them, you should check whether he distinguishes them by ear.
To do this, you can do the following types of work: a) repeat after the speech therapist combinations of sounds like ta-da and da-ta; b) correctly name the pictures (house, volume); c) correctly indicate one of the pictures named by the speech therapist, the names of which differ only in the sounds they mix (for example, bear - bowl or rat - roof, etc.) It is completely possible to check the discrimination of similar sounds if the child knows the letters and can write under dictation of syllables, words, phrases with the indicated sounds, since oral speech disorders (sometimes even already overcome) are reflected in one way or another when teaching literacy. Thanks to this, the analysis of violations of written speech allows us to more deeply identify the entire violation as a whole.
If there are difficulties in mastering literacy, it is necessary to check how the child is acquiring reading and writing skills in accordance with the program.
In order to identify the most characteristic difficulties for each subject in mastering written language, it is necessary to test not only writing skills, but also reading. So, with regard to reading, determine how the child reads by letters, syllables or whole words, and whether he correctly understands the text being read. When carrying out written work, the speech therapist takes into account the correctness of copying, writing under dictation and independent writing, analysis of errors in writing (errors on spelling rules, errors that distort the structure of the word, and errors of a phonetic nature).
Material for examination of written speech should be taken in accordance with the child’s stage of learning.
The speech therapist conducts a speech examination in various types of activities of the child - play, study, and observes him in communication with others. In this regard, it is possible to identify the characteristics of the child’s personality and his behavior: active or passive, collected, organized, obedient or disorganized, spoiled, stable in play, in work or easily distracted, brave, easily makes contact or timid, shy, aware of his speech difficulties, is embarrassed by them or treats them indifferently.
As a result, the examination becomes comprehensive, comprehensive and dynamic and makes it possible not only to analyze speech disorders, but also to outline a plan for the most effective help.
Guidelines for speech therapy diagnostics
From the experience of primary speech therapy examination.
So, the first question that is asked to the child is: “Who did you come with?” Here we look at both the contactability and the grammatical correctness of the answer.
Then: “How old are you? When's your birthday? Winter or summer? (knowledge of the names of seasons and months is immediately determined).
Next, if the child is silent, they try to make him talk with the help of toys. For examination, jars of different sizes and colors should be ready so that they can be used to build a pyramid to determine the level of visual and effective thinking (for children 3-4 years old). Inserts such as Seguin boards to determine whether the child knows geometric shapes (also for 3-4 and 5-6 years old).
Then counting skills are tested.
They place mushrooms in front of the child and ask him to give his aunt 2 mushrooms and take 3 or 4 for himself (depending on the age of the child). Who had more mushrooms? For 5-6 year olds, you can ask how much more.
Then you can play with the same mushrooms, determining the degree of proficiency in prepositions. The speech therapist aunt hides them under the table, then behind the back, then in a jar, and the child answers where the mushroom hid or where it is now (at the same time we look at the grammar: under the table, but under the table; behind the back, but behind the back) .
Complex prepositions are also tested, but as a rule, children 5 years old still speak them poorly and answer the question: “Where did I get the fungus from? (if it was behind your back or under the table). - “From the back. From the table” But 6-year-olds should already know these prepositions.
Next comes the time, if it’s not entirely clear yet, to go over the sounds. They are asked to repeat phrases rich in problematic sounds like:
For 4-5 years old, words and phrases can be based on pictures: a ripe orange, a boat has oars, a car has four tires, an owl sleeps on a branch, a cow has horns.
For 6-year-olds to hear: An old grandmother was drying clothes on a line. Lena ate and ate porridge and didn’t finish it. Funny Smeshariki walked and carried green balls. The scythe hare runs barefoot. The girl has a clean collar. etc.
To clarify the correct reproduction of the syllable structure, ask to repeat the words:
For 4-5 year olds: window sill, count candies to five: one candy, two candies...
For 6-year-olds: aquarium, electricity, juicer, lawn mower, window sill, etc.
To clarify phonemic perception, they are asked to repeat pairs and triplets of syllables:
For 4-5 year olds: pa-ba, da-ta, ka-ka-ga, la-la-ya
For 6-year-olds: yes-ta-da, sa-za-sa, sa-sa-za, la-la-la, pa-pa-pi….
Be sure to look at the structure of the articulatory apparatus to find out what the mobility of the tongue is (left-right, up-down), whether the hyoid frenulum is normal, whether it can click the tongue, suck on a “mushroom”, look at salivation (is there or is normal), whether the tongue deviates when performing an eye test (the child is asked to look at the tip of a pen, which is moved left and right, up and down, with his tongue hanging out).
If the tongue is tense, there is a tremor, it moves to one side or the other, then these may be signs of erased dysarthria, which requires longer correctional work, with enhanced art gymnastics and additional massage.
The purpose and objectives of speech therapy examination
Daria Kolesnik
The purpose and objectives of speech therapy examination
Introduction
A speech therapy examination of a child is extremely necessary to determine the level of his speech development.
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of children with minimal brain dysfunctions, which lead to impaired development of higher mental functions, including speech. The diagnostic study of such children presents certain difficulties, since this group of children has not only speech, but also communicative and emotional-volitional disorders of varying degrees of severity.
Thus, a diagnostic study, on the one hand, makes it possible to determine the violation or immaturity of functional systems, including speech, and thereby approach the cause of the difficulties experienced by the child, and on the other hand, a comprehensive diagnosis helps to determine special correctional teaching methods that can provide assistance in overcoming these difficulties.
Purpose of speech therapy examination
The speech therapy examination based on general principles and methods of pedagogical examination : it must be complex, holistic and dynamic, but at the same time it must have its own specific content aimed at analyzing speech disorders. The complexity, integrity and dynamism of the examination are ensured by the fact that all aspects of speech and all its components are examined, moreover, against the background of the entire personality of the subject , taking into account the data of his development - both general and speech.
The subject of speech therapy examination is to identify the characteristics of speech formation and speech disorders in children with various developmental disorders. The object of speech therapy examination is speech and closely related non-speech processes. The subject of the examination is a person (a child suffering from a speech disorder. At the present stage of development of pedagogy, the subject-subject basis of the relationship between a teacher and a student has been proven. Therefore, it is advisable to talk about a child with a speech disorder not as an object, but as a subject of the pedagogical process.
So what is a speech therapy examination ?
A speech therapy examination is a set of measures aimed at identifying speech disorders in the subject through a comprehensive and complete study of speech, its individual components, taking into account personal development data from an early age.
Speech therapy examination includes 2 independent sections:
— “General diagnostics”
(memory, attention, counting, thinking, emotions)
.
— “Speech diagnostics”
(oral speech, reading, writing, auditory-verbal memory)
.
The main purpose of the examination is to assess the development of speech, that is, the degree of compliance of the level of speech development, especially the coherence of speech and its communicative function, with age standards, to determine the ways and means of correctional and developmental work.
Objectives of speech therapy examination
tasks follow from the goal :
1) identification of features of speech development for subsequent consideration when planning and conducting the educational process;
2) identifying negative trends in development to determine the need for further in-depth study;
3) identifying changes in speech activity to determine the effectiveness of teaching activities.
The following tasks are also highlighted :
1) identifying the volume of speech skills;
2) comparing it with age norms, with the level of mental development;
3) determination of the relationship between the defect and the compensatory background of speech activity and other types of mental activity;
4) analysis of the interaction between the process of mastering the sound side of speech, the development of vocabulary and grammatical structure;
5) determining the ratio of impressive and expressive speech.
The speech therapy literature presents a large number of methods for examining speech (Filicheva T. E., Chirkina G. V., 1985; Zhukova N. S., Mastyukova E. M., Filicheva T. B., 1990; Usanova O. N., 1990; Volkova L.S., 1995, etc.). What they have in common is that they analyze the phonetic-phonemic, lexical, and grammatical levels of speech development with varying degrees of detail and make judgments about the child’s coherent speech.
Each child should be examined individually , depending on the nature and severity of the speech disorder, with selective use of standard speech therapy tasks .
During a speech therapy examination of a child, a systematic approach to the analysis of speech disorders should be fully used: not only the impaired component of speech activity is identified, but also its relationship with other disorders or intact components of speech. It must be remembered that speech disorders can appear selectively against the background of normal intelligence and intact sensory functions (auditory and visual)
. If a violation of any component of speech is detected, it is necessary to check the degree of possible violation of other speech processes dependent on it. The manifestation of speech disorders can be both a cause and a consequence of any other disorders.
When choosing tasks, it is necessary to take into account the normal state of speech development for the child’s age.
When conducting a speech therapy examination, the following methods are used:
• Study of documentation;
• Conversation method;
• Speech therapy testing;
• Observational method.
Before the examination begins, the speech therapist must study all documents (characteristics, expert opinions)
.
A preliminary analysis of documents allows the speech therapist to build a hypothesis for his examination in order to identify speech problems.
It is advisable to begin the speech therapy examination procedure with a conversation . During the conversation, it becomes clear what the child’s speech environment is like, whether he is aware of his speech deficiency (if any)
and how he reacts to it.
Have parents contacted a speech therapist before , what correctional work was carried out and what was its result. Before conducting an examination of the child , it is necessary to find out what speech deficiencies, in the opinion of the parents (legal representatives), the child has, what difficulties he is experiencing in learning. It is also necessary to clarify information about early speech development (if it has not been obtained earlier or is insufficient)
.
Before starting the actual speech therapy examination , it is necessary to check the child’s physical hearing, since speech disorders are often caused by hearing loss. With normal hearing, a child should hear and repeat words and phrases spoken in a whisper at a distance of 6-7 meters from the auricle. When testing hearing, visual perception of speech should be excluded. The boundaries of perception of whispered speech are determined: the perception of a whisper at a distance of less than 3 meters indicates the need for a special consultation with an audiologist to clarify the state of hearing.
Only after all these procedures can you begin to directly examine the state of the child’s speech.
After the examination , a conclusion is made about the state of the child’s speech, and the necessary development program is recommended, which takes into account his speech, age and individual psychophysiological characteristics.
Conclusion
The system of speech therapy examination is described in the literature on speech therapy and developed in various instructive, directive and methodological documents. But, when examining a child , one should not forget that no scheme can provide for all cases of speech impairment in children. Therefore, a speech therapist can fully use the entire arsenal of techniques and tools available to him.
conclusions
Analyzing the data from a speech therapy examination , the speech therapist determines which group the disorders identified in the child should be classified into.
The examination is carried out comprehensively, dynamically, comprehensively and makes it possible to outline an individual plan for the most effective assistance to the child, to see the general speech situation and trends in its development, to conduct high-quality functional diagnostics of speech disorders in the initial stages of education, to make a speech diagnosis: the degree and nature of the impairment of oral and written speech . This is necessary for the correct organization of an individual approach in frontal, subgroup and individual classes.