The relationship of speech pathologies with dentofacial anomalies and their myofunctional correction
Yu. N. Belousov Candidate of Medical Sciences, orthodontist, assistant at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry of Tyumen State Medical Academy (Tyumen), doctoral student at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry of NSMU (Novosibirsk)
I. L. Marakulina orthodontist, assistant at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry of Tyumen State Medical Academy (Tyumen)
Yu. R. Bikshanova 5th year student of the Faculty of Dentistry of Tyumen State Medical Academy (Tyumen)
P. A. Zhelezny , MD, Professor, Head of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, NSMU (Novosibirsk), President of the Regional StAR (Novosibirsk)
Speech is the main means of communication, the basis of thinking. The correct functioning of speech abilities is determined by the correct functions of the speech organs, normal hearing, sufficient communication with adults, and a full-fledged speech environment. The maxillofacial region, like all other systems of the human body, is a functional self-regulating system capable of adapting to changing external conditions. But improper distribution of muscle pressure during chewing, as well as in violation of the functions of breathing, swallowing and speech formation, is the main cause of most anomalies and deformations of the maxillofacial area. Recently, myofunctional disorders of the maxillofacial region have become a serious problem and are increasingly occurring in both children and adults.
Often, a speech therapist is the first person parents of children with myofunctional problems turn to for help because speech impairment bothers them. With such disorders, it is very important to promptly diagnose the child correctly and explain to parents the root cause of the disorders as a complex problem, and not just as a speech problem. This may require consultation and assistance from other specialists - an orthodontist, a dental surgeon, an otolaryngologist.
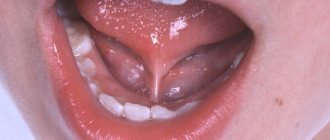
Among the most common anomalies of the structure of the oral cavity that require correction in preschool age are: abnormal attachments of the frenulum of the tongue, upper and lower lips, small vestibule of the oral cavity, supernumerary teeth. A shortened frenulum of the tongue is sometimes detected in parents or close relatives of children, which can be considered a family trait. At the same time, malocclusions can be similar, and then the sounds “r”, “l”, “s”, as well as hissing sounds with a shortened frenulum of the tongue are usually pronounced incorrectly.
It is important to take into account the degree of dependence of the correct articulation of sound on a specific anomaly in the structure of the articulatory apparatus. Thus, with mechanical dyslalia, it is often necessary to first correct anomalies in the structure of the child’s dental system for subsequent correct production of sounds.
Speech pathologies are a widespread problem today. The joint work of doctors and teachers in children's preventive institutions makes it possible to early identify such conditions as deviations from the norm in children's health, congenital and acquired diseases that affect the development of speech and contribute to speech pathology. However, despite the fact that today everything is available to carry out preventive medical work: orthodontists who are proficient in new myofunctional treatment methods, the enthusiasm of doctors who want to carry out this work, the problem remains relevant due to low educational work: parents do not know how to deal with dental anomalies necessary from a very early age for children. Often, it is the speech therapist who is the first point of contact for parents of children with myofunctional abnormalities, since speech dysfunction for parents is the most obvious aspect of the child’s developmental delay. In most cases, speech pathologies are in one way or another associated with congenital and acquired pathologies of the speech organs, therefore, one cannot limit oneself to examining a child starting classes with a speech therapist only with a psychiatrist, otolaryngologist and ophthalmologist; a thorough examination by an orthodontist is necessary in order to timely identify disorders in the development of the dental system.
Speech impairment in children is diagnosed after the age of 3; deviations appear precisely during the period of formed occlusion, when children develop bad habits. Speech development is a complex process, the correct implementation of which requires normal function of the brain, nerve pathways and the correct development of the organs that form the speech apparatus. These include: respiratory organs, chewing organs, vibrators (vocal cords), resonators (larynx, oral cavity and nose) and articulators (tongue, lips, teeth, lower jaw, soft palate).
Mechanical dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus, associated with deviations in the structure of the peripheral speech apparatus. The following types of mechanical dyslalia are distinguished: palatal, lingual, dental and labial. Palatolalia is associated with pathology of the palate, glossolalia - with an anomaly of the tongue or a violation of its functions, dentolia - with a violation of the shape or position of the teeth.
Impaired pronunciation of the sound [p] is observed with a shortened frenulum of the tongue, narrowing of the jaws, deep bite, and impaired mobility of the tip of the tongue. For children aged 3 to 5 years, training using a plate with a bead is effective; breathing exercises are used to normalize nasal breathing. If necessary, plastic surgery of the lingual frenulum is prescribed at the age of 2-2.5 years. For children over 5 years old, the use of a T4K trainer is recommended.
Among the most common anomalies of the structure of the oral cavity that require correction in preschool age are the following: abnormal attachments of the frenulum of the tongue, upper and lower lips, small vestibule of the oral cavity, supernumerary teeth.
The pronunciation of the sound [t] is characterized by the withdrawal of the lower jaw simultaneously with the explosion of the lingual-palatal seal, producing the sound [t]. The distance between the upper and lower incisors is up to 5 mm. The tip of the tongue is raised to the necks of the upper incisors and forms a strong closure when pronouncing the sound [t] and less strong when pronouncing the sound [d]. Impaired pronunciation of these sounds occurs with an open bite, inserting the tongue between the dentition and improper swallowing. For children under 5 years of age, it is recommended to use a tongue plate with a flap; during the day, for 30 minutes, warm up the muscles that lift the tongue; for this purpose, a vestibular plate with a bead is used, as well as an Infant children's trainer. For children over 5 years old, the T4K myofunctional trainer is recommended for effective speech correction.
When pronouncing the hissing sounds [ш] and [ж], the lips are slightly protruded forward; there should be a minimum distance between them, as well as between the upper and lower teeth. A gap is formed between the hard palate and the tongue, the lateral edges of the tongue close with the upper chewing teeth, and the extended tip of the tongue is raised, but does not come into contact with the hard palate. Distortion of hissing sounds [w] and [zh] is facilitated by deep bite, prognathism, and lingual tilt of the teeth. We recommend comprehensive training using a vestibular plate with a bead and a T4K myofunctional trainer.
The articulation of the sounds [s] and [z] is carried out as follows: the upper and lower incisors are brought closer together by approximately 1-1.5 mm and are located either in the same frontal plane, or the lower incisors are slightly more lingual. The tongue in the middle part is raised and expanded. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower incisors, and its lateral edges adjoin the palatal surfaces of the upper lateral teeth. A longitudinal V-shaped groove is formed in the middle of the back of the tongue. Passing through it, a stream of air creates a pronounced whistling sound. Impaired clarity of sounds [s] and [z] is caused by labiodental stigmatism - a violation of the correct pronunciation of whistling sounds. When pronouncing the sound [s], the lower lip is pulled towards the upper incisors, “deforming” the speech gap. With interdental sigmatism, the tongue is placed between the upper and lower incisors and instead of a whistling tone, a lisp is acoustically formed. Dental sigmatism is characterized by a movement of the tip of the tongue in which it, resting against the upper incisors, closes the exit of the air stream.
Impaired pronunciation of sounds is observed with open bite, crossbite, mouth breathing, and infantile type of swallowing. For children under 5 years of age, the use of a plate with a flap or a prophylactic model of the Infant trainer, model T4K, is recommended for tongue piercing. Thus, it is important to take into account the degree of dependence of the correct articulation of sound on a specific anomaly in the structure of the articulatory apparatus. Thus, with mechanical dyslalia, it is often necessary to first correct anomalies in the structure of the child’s dental system for subsequent correct production of sounds. That is why, in order to develop a correct and consistent treatment plan for such combined pathologies, it is very important to ensure interaction and effective cooperation between the speech therapist and the orthodontist, which allows for the timely elimination of anatomical disorders in the structure of the organs involved in articulation and the correction of the maxillofacial development of the child as a whole.
Literature
1. Kalashnikova I. L. Vestibular plates in the work of a speech therapist // Speech therapist. - 2004, No. 3. - P. 121. 2. Kostina Ya. V., Chapala V. M. Speech correction in children // An orthodontist’s view. — 2008.