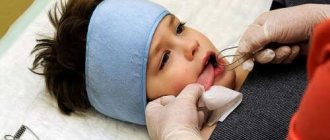
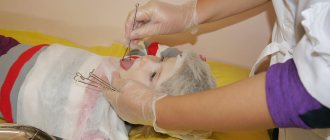
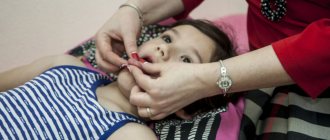
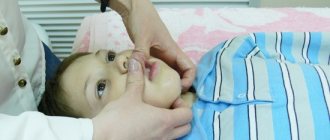
Speech therapy massage is one of the main elements of the rehabilitation program for patients suffering from dysarthria. Rehabilitologists at the Yusupov Hospital use various types of massage for dysarthria: probe, acupressure, facial muscles, tongue. Depending on the type and degree of dysfunction of the articulatory and facial muscles, specialists select one or another type of influence.
The program of speech therapy massage for dysarthria in patients in the acute phase of stroke, traumatic brain injury, and demyelinating diseases of the nervous system is discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council, in which doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category take part. The medical staff is attentive to the problems of patients with speech impairment.
Probe speech therapy massage for dysarthria
Speech therapy massage of the tongue for dysarthria, performed with the help of probes, is a unique method of correcting speech disorders, which promotes:
- Normalization of muscle tone;
- Improving voice condition;
- Establishing the correct pronunciation of sounds;
- Improving emotional and psychological state;
- Normalization of speech breathing.
Probe massage for tongue dysarthria is carried out according to the method of E. Novikova. Before starting the massage, perform gymnastic exercises for the tongue:
- "Swing". The protruding tongue moves from one corner of the mouth to the other. The mouth is open;
- "Blowout." The patient folds his lips into a smile, places his tongue on the lower lips and blows forcefully;
- "Horse". It is necessary to “click” your tongue, making sure that the lower jaw does not move.
Tongue massage is carried out in a lying position, with the patient maximally relaxed. The massage therapist uses a napkin with one hand to hold the tongue in an extended position. Performs massaging exercises from the tip of the tongue to the root. First, massage the side parts, then the middle, and as close to the root as possible, as far as the gag reflex allows. Each technique (piercing, rolling, pressing) is performed using special probes. They can be replaced with a small spoon or toothbrush.
Probe massage of the tongue is not performed if the gag reflex is increased. Sometimes muscle spasms occur during a massage. It causes pain. To relieve pain, you should brew black tea with nettle in a 1:2 ratio. Brew one teaspoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water and infuse. The patient is allowed to hold the warm infusion in his mouth until the spasms are relieved, then he is asked to spit it out.
The duration of the course of probe massage of the tongue varies from 10 to 320 days. After 1.5-2 months it needs to be repeated. If desired, relatives can learn how to massage the tongue at home on their own. The patient can perform self-massage of the tongue for dysarthria. The first sessions should be supervised by a speech therapist.
IV. How to massage?
Next, we’ll talk about how to massage a child’s face, use spoons, and perform articulation and finger massage to develop speech.
Logomassage of the face
Follow these instructions, unless otherwise directed by your doctor: when performing a massage, move from top to bottom, try not to strain. Don't forget that your hands are real medicine!
Logomassage with spoons
Spoons allow you to have a good effect on speech areas. Be sure to make sure the spoons have a smooth surface! Any small hangnails can injure a child’s skin! It is enough to repeat all movements 7-8 times.
Articulation massage for speech development
This type of massage requires the use of a spatula or toothbrush. In principle, it can be done by hand. Don't forget to wear medical gloves! Place a sterile cloth nearby to remove saliva. If the child feels pain, stop the session.
Before starting the procedure, it will be useful to relax the child: to do this, massage the collar area, neck muscles and jaws.
Finger logomassage for speech development
Massaging your fingers is the easiest way. There is no need for any serious knowledge or precautions here. All caring mothers and fathers do this. This massage is most useful for children who have not yet turned one year old.
The fact is that the nerve endings of the hands are considered to be connected to the speech areas in our brain. Therefore, finger massage can improve the baby’s speech. To enhance the effect, you can use a rubber ball.
All the procedures described really make it possible to correct sound pronunciation, form correct speech breathing, strengthen the voice and stabilize the emotional state. Therefore, we recommend that you perform different types of procedures to speed up speech correction.
Read our article for more details on how to learn to speak beautifully and competently as an adult >>>
Sets of tools for logomassage
Logomassage probes are special instruments made of wire. They are used to mechanically influence the tongue and other organs of the child’s articulatory apparatus. Their use allows you to introduce sounds to your baby and correct speech pronunciation. Probes are an exclusively domestic invention. In the EU and USA, speech therapists do not use probes - they do not even know the technology for handling them!
For the first time, the use of special tools for speech correction was invented by the Russian speech therapist, professor and teacher of the deaf, Fedor Andreevich Rau. He also developed the first forms of probes that are used by speech therapists to this day.
It is customary to divide instruments for logomassage into staged and massage. Staged ones are used for Rau and Volkova therapy, as well as for intermediate techniques.
Massage probes are used in the Novikova technique.
Probes are most often made of steel and wire. In stores you can buy sets of probes for performing different logomassage techniques. Typically, such kits contain from seven to 12 instruments. The sets cost between 2-3 thousand rubles. The following tools may also be useful to perform the procedure:
- massage stick;
- tongue raising device;
- mirror (for examining the mouth);
- wine cork (for articulation gymnastics);
- mouth dilators.
Facial massage for dysarthria
To simulate muscles in patients suffering from dysarthria, the following techniques are used:
- Stroking and kneading the forehead. The speech therapist stands to the right of the person being massaged and moves his kneading right hand in a zigzag manner across the forehead from the nose to the beginning of the hair. With a light stroking motion, moves the left hand along the forehead from the frontal tuberosity to the temple;
- Kneading the nose. The speech therapist uses the palmar surface of the terminal phalanges of the thumb and index fingers of the right hand to make a slightly vibrating zigzag movement from the end of the nose to its base and to the sides along the wings of the nose, and at this time supports the back of the head with his left hand;
- Kneading the zygomatic area. The speech therapist moves a weakly clenched hand across the face of the person being massaged from the midline outward and at the same time upward from the lower jaw to the cheekbones to the lower eyelid. If the technique is performed on the right side of the face, the speech therapist is located to the right of the patient. The massage is performed with the thumb and forefinger bent at a right angle. The movement is directed from the lower jaw and ear through the cheek bones to the lower eyelid.
To smooth the frontal muscles, the speech therapist stands behind and strokes the index and middle fingers of both hands across the forehead from its midline to the temporal region. Facial vibration is performed according to the following algorithm:
- The speech therapist stands behind;
- Four fingers of both hands, except the thumbs, are located between the cheek bones and the lower jaw;
- Makes frequent oscillating movements back and forth;
- After several such movements on one part of the face, he moves his hands to another part.
To smooth out the muscles between the lip and chin, the speech therapist stands on the right. With two thumbs, he strokes under the lower lip, continuing the movement to the ascending branch of the lower jaw.
Correction of pronounced sounds by probe massage of the tongue
The most common speech disorder is dysarthria. The baby has problems with articulation and pronunciation of many sounds. With this diagnosis, speech therapists prescribe probe massage.
This method accelerates the correct formation of sounds and improves the functioning of the articulatory muscles of the face, improving the child’s fine motor skills. Without this procedure, correction of dysarthria may take 5-10 years. The method does not require special conditions. It can be done by a speech therapist who has special knowledge and skills.
However, this is an adjunct to therapy and not a panacea for all speech problems. It prepares the ground for the development of speech skills in the baby. Other stages of therapy should be carried out in parallel.
If the massage is performed incorrectly, the child may develop fear and fear of instruments. Some speech therapists act very rudely. After this, the baby may refuse the procedures.
Acupressure for dysarthria
To restore speech function in patients with dysarthria, reflexologists use acupressure massage. It is combined with motor exercises and self-massage for dysarthria, since active motor exercises increase the patient’s chances of recovery. The main principle of treatment using acupressure is to restore patency and activate the activity of meridians, normalize the circulation of energy and blood.
To treat dysarthria and contracture of the tongue muscles, reflexologists use a tonic acupressure technique. Affects the following points:
- The junction of the posteromedial and external calcaneal meridian is located on the border of hair growth in the soft part of the occipital recess;
- Conjugation of the anteromedian meridian and the internal supporting meridian" - located under the chin, at the elevation of the protrusion of the larynx, under the base of the tongue (on the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage;
- Located in the recess between the tendons of the flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum (to determine the location of this point, the patient is asked to clench the hand into a fist and bend it to the forearm).
The patient can also perform acupressure massage independently. The first sessions should be carried out under the supervision of a reflexologist.
Who is tongue massage recommended for?
Tongue massage can be both stimulating and relaxing. And also combined, when one area of the tongue needs to be relaxed and the other stimulated! This is where the indications for tongue massage come from. Speech therapy massage is indicated for patients:
- with speech impairments;
- disorders of chewing and swallowing function;
- with malocclusion;
- undergoing orthodontic treatment (bite correction and teeth straightening);
- undergoing orthopedic treatment (dental prosthetics);
- with a short frenulum of the tongue for the purpose of non-surgical stretching;
- with hypertonicity of the tongue and masticatory muscles (bruxists and claunchers - people who clench and grind their teeth);
- with increased stress on the speech apparatus (teachers, lecturers, etc.).
Massage techniques to stimulate paretic muscles
Speech therapy massage for paretic syndrome is carried out to strengthen the muscles. Movements should be carried out intensively, with pressure. Rubbing, kneading, pinching are used. Forehead massage is performed to strengthen and stimulate the frontal muscles. Using the index, middle and ring fingers of both hands, stroke the forehead from the middle to the temples. Massage movements are done 6–8 times, 2–3 times a day. The following exercise is performed with the second phalanges of the index, middle and ring fingers clenched into a fist. Kneading movements are performed 6-8 times twice a day.
Rubbing the forehead from the middle to the temples is carried out with the first phalanges of the index, middle and ring fingers. When rubbed, the skin of the forehead is pulled tight. Rubbing movements are performed 4–6 times, twice a day. Strengthening and stimulating the frontal muscles can be done using spiral movements from the middle of the forehead to the temples. They are performed with the pads of the index, middle and ring fingers of both hands 4–6 times, 1 time per day.
Cheek massage is carried out by stroking, rubbing, kneading the cheek muscles. Kneading and rubbing the cheeks is carried out with both hands in the direction from the nose to the cheeks twice a day for 6-8 seconds. To stimulate the muscles that lift the angle of the mouth, the index, middle and ring fingers of both hands perform counterclockwise rotational stroking movements on the surface of the cheeks twice a day 8-10 times.
Activation of the muscles that lift the mandible is carried out using spiral rubbing of the masticatory muscle from the temples to the corners of the jaw. The movements are performed with the pads of the index, middle and ring fingers of both hands in a spiral 8–10 times, 2–3 times a day.
To strengthen and activate the muscles that lift the corner of the mouth and upper lip, pinching the cheeks is performed. Pinching movements are made with the index, middle and thumbs of both hands in a circle counterclockwise. Acupressure massage stimulates paretic muscles in dysarthria.
Contraindicated for whom
Massage is contraindicated for the following diseases:
- acute inflammatory processes in the oral cavity: viral diseases (herpes), rash caused by bacterial infection, gingivitis, etc.;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- acute infectious disease;
- high body temperature;
- symptomatic epilepsy;
- intracranial hypertension.
Also, speech therapy massage is impossible in cases where the child, due to age or mental state, is unable to listen to the doctor, has a negative attitude towards his actions, and cannot sit still.
Massage for erased dysarthria
Latent dysarthria refers to mild disorders of speech function in children. Speech therapy massage for dysarthria in pictures allows parents to master exercises aimed at strengthening or relaxing articulatory muscles, stimulating proprioceptive sensations. Speech kinesthesia is important in the formation of impressive and expressive speech. Massage for erased dysarthria enhances cerebral circulation and metabolic processes in the neurons of the brain, which improves the flow and formation of many mental processes (attention, memory), harmonizes all processes that occur in the whole organism.
When working with children suffering from latent dysarthria and speech pathology, speech therapists and rehabilitation therapists use various types of massage of reflexogenic zones (feet, hands, scalp), segmental reflex, linear, acupressure massage. Speech therapy massage is a method of active mechanical influence. It changes the condition of muscles, blood vessels, nerves and tissues of the peripheral speech apparatus.
Under the influence of massage, the elasticity of muscle fibers, strength, volume and contractile function, and muscle performance increase. Massage for latent dysarthria is one of the methods of energetic and physical influence on the human body. It soothes, relieves pain, helps overcome illness, and promotes the physical, mental and physical development of children.
The use of speech therapy massage for erased dysarthria can significantly reduce the time of correctional work, especially on the formation of the pronunciation aspect of speech. Thanks to the use of massage, the formation of normative pronunciation of sounds in some cases occurs spontaneously. In order to undergo a course of acupressure, relaxing or stimulating, probe speech therapy massage for dysarthria, to find out the price, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.
Contraindications and conditions
Despite its high effectiveness with the comparative simplicity of the exercises, massage from a speech therapist has a number of contraindications. In particular, it is not used in the presence of infectious diseases, including influenza. Obviously, massage should not be performed if you have herpes and other skin diseases. Other contraindications include conjunctivitis and stomatitis.
Speech therapy massage is performed in a well-ventilated area at room temperature. It is advisable to carry it out every day or at least every other day in cycles of 10-20 sessions. Then you need to take a break for a couple of months to let your muscles get used to the new possibilities. After this, if there is such a need, the course should be repeated.
Delayed speech development: how to help your child speak
№8 (185) September, 2018
Continuation.
Starts at No. 6(183). “Dysarthria”: diagnosis and speech therapy correction techniques
The fourth lesson is taught by clinical speech therapist-speech pathologist of the highest category, rehabilitation specialist at the Center for Child Neurology and Medical Rehabilitation, Tatyana Kalabukhova.
Good speech is the most important condition for the comprehensive development of children. The richer and more correct a child’s speech, the easier it is for him to express his thoughts, the wider his opportunities for understanding the surrounding reality. A child with well-developed speech easily enters into communication with others, he can clearly express his thoughts, desires, ask questions, and agree with peers about playing together. Conversely, a child’s slurred speech complicates his relationships with people and often leaves an imprint on his character.
Dysarthria is a speech disorder in which the movements of the articulatory apparatus are disrupted, that is, the mobility of the speech organs (lips, soft palate, tongue) is limited, and as a result, sound pronunciation is disrupted, speech becomes less intelligible, blurred and unclear. Children with dysarthria find it difficult not only to pronounce sounds, but also to chew and swallow. The voice of dysarthric children is quiet, weak, and sometimes harsh, hoarse. The rhythm of breathing is disrupted, speech loses its smoothness.
Depending on the area of brain damage, various manifestations of dysarthria are possible: from severe forms with swallowing problems. salivation, paresis of the muscles of the larynx, to mild “erased” forms, in which slurred speech with a nasal tinge is noted. There is even a “cold” form of dysarthria, which occurs only in a cold room or in winter.
There is a speech therapy classification based on the intelligibility of a child’s speech for others. There are 4 degrees of severity of speech impairment. From mild (I), which can only be detected with a special examination, to others this disorder may look like unclear diction.
To a severe (IV) degree, when the child’s speech is incomprehensible even to parents or is completely absent.
Since dysarthria is a neurological diagnosis, a speech therapist deals with the correction of impaired speech functions, and drug treatment is prescribed by a neurologist. Speech therapy work with dysarthric children should begin at an early age, since timely speech therapy help in 75% of cases helps to avoid many problems in the further development of the child. Dysarthria in infancy can manifest itself as:
- - difficulties in sucking breasts, bottles, pacifiers;
- - impaired swallowing during drinking, eating, swallowing saliva, the child chokes, often burps;
- - disorders of chewing and biting in older age.
At the Center for Pediatric Neurology and Medical Rehabilitation, I, as a clinical speech therapist, conduct speech therapy massage courses to stimulate sucking, swallowing, and subsequently chewing in children from 1 month, including children on tube feeding. Under the supervision of a specialist, the mother is taught the elements of a special massage to stimulate sucking and practice swallowing (massage should be carried out before each feeding). The need for the mother to keep a “Feeding Diary” of the baby is explained (taking into account regurgitation and supplementary feeding through a tube). Our main task is to remove the child from tube feeding and normalize his nutrition.
Recovery of the sucking reflex is slow; it can be stimulated by special speech therapy massage and acupressure stimulation at home:
*Massage of facial muscles
On a child's face, stroking and kneading are carried out with both hands evenly on both sides.
1. From the middle of the forehead to the temples.
2. From the middle of the forehead to the ears.
3.From the middle of the forehead to the ears and then through the cheeks to the chin.
4.From eyebrows to scalp.
5.From the back of the nose to the ears.
6.From the earlobes along the cheeks to the wings of the nose.
*Tongue massage
It is convenient to massage the tongue with a pacifier placed on a spatula, or with a finger in a fingertip.
1. Stroking the tongue from its middle to the tip. Gradually move closer to the root of the tongue.
2. Stroking from the midline of the tongue to the sides.
3. Patting over the entire surface of the tongue and along the edge of the tongue from top to bottom.
*Massage of lips and orbicularis oris muscle
Massage the child's lips is performed with the index or middle fingers of both hands.
1. Stroking above the upper lip and under the lower lip from the middle to the edges.
2. Kneading the lip between the thumb and index finger, “rubbing” the lip. The massage is performed on the upper and lower lips.
3. Fingers are placed in the corners of the mouth, lips are stretched into a smile, and then gathered into a “tube”.
At about 5 months, babies begin to put everything in their mouth, which is how they learn the movements of their jaws, tongue, and lips. If for some reason this does not happen, you can teach your child to bite and chew yourself, or seek help from a specialist.
Since biting and chewing are important parts of a child's learning to feed themselves, I recommend starting with special aids designed to provide stimulation and exercise to the lips, cheeks, tongue and gums. These can be teethers, vibrating sticks, syringes and other instruments. They can be found on speech therapy websites and in pharmacies.
The process of learning to bite and chew is long, so it is necessary to follow the sequence of work:
Stage 1 – Show your child how to bite so that the baby understands what this word means. This stage can be turned into a fun game if you take turns feeding the doll. Let the child feed you too. Use a sound or word (“bite”, “am-am”).
Stage 2 – Aimed at developing correct mouth opening when chewing. Place the teether between the chewing surfaces of the teeth and help the gums close and open. When doing this, use the word “bite”. Do this in front of a mirror so your baby can see him biting (if it doesn't distract him too much).
Stage 3 – After the child understands the word “bite” and learns how to do it, start chewing. Make up to 20-25 chewing movements on each side (in difficult cases, help with your hand, holding your chin and repeating the lowering and raising of the lower jaw in time with chewing).
Stage 4 – Use long teethers to develop bilateral chewing and increase jaw strength. Change sides to stimulate movement of chewing activity: 3-5 on one side, then on the other. Start with the side teeth, gradually moving to the back teeth.
Stage 5 - When the child has learned to bite and chew, dip the teether in puree while working - this will allow you to transfer the new skill to real food.
And praise, praise, praise the baby!
To overcome hypersalivation (excessive drooling) in children with dysarthria, it is necessary to teach the child to suck with closed lips, swallow saliva with his head thrown back and in his normal position. Drooling can be constant or worsen under certain conditions. Even mild drooling, such as wetness of the corners of the mouth during speech, or a slight leakage of saliva may indicate dysarthria. Before performing any articulation exercise, the speech therapist reminds the child to swallow saliva and blot the inside of the mouth with a napkin.
The main stages of speech therapy correction for hypersalivation:
1.Cryotherapy of active points in the lip area.
2.Rinse the mouth using medicinal herbs, mineral water, jelly and kefir.
3. Speech therapy massage and point massage.
4. Chewing solid food.
5.Static and dynamic facial and articulation exercises.
6. Breathing exercises and pronouncing vowels on a firm attack.
Recommendations from a speech therapist for parents with hypersalivation in children:
- — People around you should constantly monitor the position of the child’s mouth and remind him of the need to keep his mouth closed when he is not eating or talking.
- — It is important that the child develops a differentiated sensation of dry and wet chin.
- — During classes, it is necessary to pause at certain intervals and invite the child to swallow saliva.
Based on my practical experience, with systematic work, drooling decreases and the child has better control over swallowing.
In most cases, dysarthric children have some behavioral characteristics. For example, kids don’t like to lace their shoes or button their own buttons. This is due to poorly developed fine motor skills. Such children cannot hold a pen or pencil correctly, control the pressure, or use scissors. This is why most dysarthric people have poor handwriting. Children find it difficult to exercise and dance. Musical hearing is impaired. Children cannot accurately perform various motor exercises; they are clumsy.
Treatment of dysarthria in children requires an integrated approach, combining drug therapy, speech therapy correction and rehabilitation.
Drug treatment of dysarthria in children
Treatment is based on therapy of the underlying neurological disease, as well as the use of nootropic drugs. They help improve mental activity, memory, and stimulate cognitive functions.
Speech therapy work and rehabilitation
Speech therapy correction consists of special classes for children. The speech therapist draws up an individual speech card, which contains diagnostic results and a detailed plan for correcting the defect with a description of the exercises:
- - for the development of fine motor skills - finger games, gymnastics;
- - for the development of articulatory motor skills - articulatory gymnastics, speech therapy massage;
- - for speech and physiological breathing - breathing exercises;
- - to correct impaired pronunciation and consolidate correct pronunciation;
- - for the formation of expressiveness of speech and verbal communication.